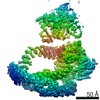
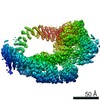
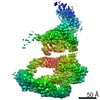
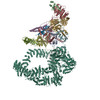
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-10446タイトル SAGA-TBP filtered to show the position of the DUB domain 複合体 : SAGA bound to TBP複合体 : TATA-box binding protein (TBP)複合体 : SAGA component複合体 : Polyubiquitin-B複合体 : SAGA complexリガンド : x 1種 / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Komagataella phaffii GS115 (菌類) / Homo sapiens (ヒト) / Komagataella phaffii (strain GS115 / ATCC 20864) (菌類)手法 / / 解像度 : 20.0 Å Papai G / Frechard A 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 French National Research Agency ANR-15-CE11-0022-01 French National Research Agency ANR-10-LABX-0030-INRT French National Research Agency ANR-10-IDEX-0002-02
ジャーナル : Nature / 年 : 2020タイトル : Structure of SAGA and mechanism of TBP deposition on gene promoters.著者 : Gabor Papai / Alexandre Frechard / Olga Kolesnikova / Corinne Crucifix / Patrick Schultz / Adam Ben-Shem / 要旨 : SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase) is a 19-subunit complex that stimulates transcription via two chromatin-modifying enzymatic modules and by delivering the TATA box binding protein (TBP) to ... SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase) is a 19-subunit complex that stimulates transcription via two chromatin-modifying enzymatic modules and by delivering the TATA box binding protein (TBP) to nucleate the pre-initiation complex on DNA, a pivotal event in the expression of protein-encoding genes. Here we present the structure of yeast SAGA with bound TBP. The core of the complex is resolved at 3.5 Å resolution (0.143 Fourier shell correlation). The structure reveals the intricate network of interactions that coordinate the different functional domains of SAGA and resolves an octamer of histone-fold domains at the core of SAGA. This deformed octamer deviates considerably from the symmetrical analogue in the nucleosome and is precisely tuned to establish a peripheral site for TBP, where steric hindrance represses binding of spurious DNA. Complementary biochemical analysis points to a mechanism for TBP delivery and release from SAGA that requires transcription factor IIA and whose efficiency correlates with the affinity of DNA to TBP. We provide the foundations for understanding the specific delivery of TBP to gene promoters and the multiple roles of SAGA in regulating gene expression. 履歴 登録 2019年11月1日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2020年2月12日 - マップ公開 2020年2月12日 - 更新 2024年9月25日 - 現状 2024年9月25日 処理サイト : PDBe / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Komagataella phaffii GS115 (菌類) /
Komagataella phaffii GS115 (菌類) /  Homo sapiens (ヒト) /
Homo sapiens (ヒト) /  Komagataella phaffii (strain GS115 / ATCC 20864) (菌類)
Komagataella phaffii (strain GS115 / ATCC 20864) (菌類) データ登録者
データ登録者 フランス, 3件
フランス, 3件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2020
ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2020
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_10446.map.gz
emd_10446.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-10446-v30.xml
emd-10446-v30.xml emd-10446.xml
emd-10446.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_10446.png
emd_10446.png emd-10446.cif.gz
emd-10446.cif.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10446
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10446 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10446
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10446 emd_10446_validation.pdf.gz
emd_10446_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_10446_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_10446_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_10446_validation.xml.gz
emd_10446_validation.xml.gz emd_10446_validation.cif.gz
emd_10446_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10446
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10446 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10446
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10446 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_10446.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_10446.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)























