[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10421: Human kinesin-5 motor domain in the GSK-1 state bound to microtubules -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10421 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
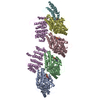
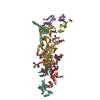
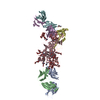
| Title | Human kinesin-5 motor domain in the GSK-1 state bound to microtubules | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Human kinesin-5 motor domain bound to microtubules and the drug GSK-1 | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | kinesin / microtubule / mitosis / inhibition / motor / CELL CYCLE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationspindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / mitotic centrosome separation / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport ...spindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / mitotic centrosome separation / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Mitotic Prometaphase / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / kinesin complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / microtubule motor activity / MHC class II antigen presentation / spindle organization / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / microtubule-based movement / mitotic spindle assembly / MHC class II antigen presentation / mitotic spindle organization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / neuron migration / spindle pole / mitotic spindle / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / ciliary basal body / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / cell division / GTPase activity / protein kinase binding / GTP binding / protein-containing complex / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
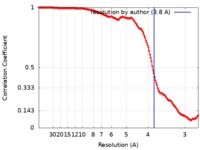
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pena A / Sweeney A | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3 items United Kingdom, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2020 Journal: Structure / Year: 2020Title: Structure of Microtubule-Trapped Human Kinesin-5 and Its Mechanism of Inhibition Revealed Using Cryoelectron Microscopy. Authors: Alejandro Peña / Aaron Sweeney / Alexander D Cook / Julia Locke / Maya Topf / Carolyn A Moores /  Abstract: Kinesin-5 motors are vital mitotic spindle components, and disruption of their function perturbs cell division. We investigated the molecular mechanism of the human kinesin-5 inhibitor GSK-1, which ...Kinesin-5 motors are vital mitotic spindle components, and disruption of their function perturbs cell division. We investigated the molecular mechanism of the human kinesin-5 inhibitor GSK-1, which allosterically promotes tight microtubule binding. GSK-1 inhibits monomeric human kinesin-5 ATPase and microtubule gliding activities, and promotes the motor's microtubule stabilization activity. Using cryoelectron microscopy, we determined the 3D structure of the microtubule-bound motor-GSK-1 at 3.8 Å overall resolution. The structure reveals that GSK-1 stabilizes the microtubule binding surface of the motor in an ATP-like conformation, while destabilizing regions of the motor around the empty nucleotide binding pocket. Density corresponding to GSK-1 is located between helix-α4 and helix-α6 in the motor domain at its interface with the microtubule. Using a combination of difference mapping and protein-ligand docking, we characterized the kinesin-5-GSK-1 interaction and further validated this binding site using mutagenesis. This work opens up new avenues of investigation of kinesin inhibition and spindle perturbation. #1:  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Mechanism of microtubule-trapped human kinesin-5 inhibition revealed using cryo-EM Authors: Pena AP / Sweeney A | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10421.map.gz emd_10421.map.gz | 1.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10421-v30.xml emd-10421-v30.xml emd-10421.xml emd-10421.xml | 21.1 KB 21.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10421_fsc.xml emd_10421_fsc.xml | 15.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10421.png emd_10421.png | 203 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10421.cif.gz emd-10421.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10421 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10421 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10421 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10421 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ta3MC  6tiwMC  6ta4C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10421.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 506 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10421.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 506 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human kinesin-5 motor domain bound to microtubules and the drug GSK-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of Human Kinesin 5 and microtubules
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of Human Kinesin 5 and microtubules |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of Human Kinesin 5 and microtubules
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of Human Kinesin 5 and microtubules / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1B chain and Tubulin beta chain
| Supramolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1B chain and Tubulin beta chain / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Kinesin-like protein KIF11
| Supramolecule | Name: Kinesin-like protein KIF11 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.113129 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGSYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEAAGNKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKESESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGSYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEAAGNKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKESESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQMFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNVQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMSAT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY QDAT UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1B chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1B chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.780117 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLISQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRIHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRSIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YQPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GVD UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1B chain |
-Macromolecule #3: Kinesin-like protein KIF11
| Macromolecule | Name: Kinesin-like protein KIF11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.727461 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHSSG VDLGTENLYF QSMASQPNSS AKKKEEKGKN IQVVVRCRPF NLAERKASAH SIVECDPVRK EVSVRTGGLA DKSSRKTYT FDMVFGASTK QIDVYRSVVC PILDEVIMGY NCTIFAYGQT GTGKTFTMEG ERSPNEEYTW EEDPLAGIIP R TLHQIFEK ...String: MHHHHHHSSG VDLGTENLYF QSMASQPNSS AKKKEEKGKN IQVVVRCRPF NLAERKASAH SIVECDPVRK EVSVRTGGLA DKSSRKTYT FDMVFGASTK QIDVYRSVVC PILDEVIMGY NCTIFAYGQT GTGKTFTMEG ERSPNEEYTW EEDPLAGIIP R TLHQIFEK LTDNGTEFSV KVSLLEIYNE ELFDLLNPSS DVSERLQMFD DPRNKRGVII KGLEEITVHN KDEVYQILEK GA AKRTTAA TLMNAYSSRS HSVFSVTIHM KETTIDGEEL VKIGKLNLVD LAGSENIGRS GAVDKRAREA GNINQSLLTL GRV ITALVE RTPHVPYRES KLTRILQDSL GGRTRTSIIA TISPASLNLE ETLSTLEYAH RAKNILNKPE VNQKL UniProtKB: Kinesin-like protein KIF11 |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: G2P |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 521.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 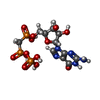 ChemComp-G2P: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: 6-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3,4-dihydro-1~{H}-quinolin-2-one
| Macromolecule | Name: 6-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3,4-dihydro-1~{H}-quinolin-2-one type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MZK |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 291.268 Da |
| Chemical component information | 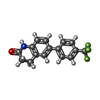 ChemComp-MZK: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)