+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9567 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
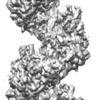
| Title | Human RAD51 post-synaptic complexes | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA repair / ATPase / homologous recombination / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpresynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin ...presynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin / DNA strand invasion / cellular response to hydroxyurea / mitotic recombination / DNA strand exchange activity / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / lateral element / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / telomere maintenance via recombination / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / reciprocal meiotic recombination / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / nuclear chromosome / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / replication fork processing / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / response to X-ray / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / interstrand cross-link repair / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / condensed nuclear chromosome / cellular response to ionizing radiation / meiotic cell cycle / male germ cell nucleus / cellular response to gamma radiation / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / PML body / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Meiotic recombination / response to toxic substance / single-stranded DNA binding / site of double-strand break / double-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / chromosome, telomeric region / mitochondrial matrix / response to xenobiotic stimulus / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / enzyme binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu J / Zhao L | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, China,  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2017Title: Cryo-EM structures of human RAD51 recombinase filaments during catalysis of DNA-strand exchange. Authors: Jingfei Xu / Lingyun Zhao / Yuanyuan Xu / Weixing Zhao / Patrick Sung / Hong-Wei Wang /   Abstract: The central step in eukaryotic homologous recombination (HR) is ATP-dependent DNA-strand exchange mediated by the Rad51 recombinase. In this process, Rad51 assembles on single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) ...The central step in eukaryotic homologous recombination (HR) is ATP-dependent DNA-strand exchange mediated by the Rad51 recombinase. In this process, Rad51 assembles on single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and generates a helical filament that is able to search for and invade homologous double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), thus leading to strand separation and formation of new base pairs between the initiating ssDNA and the complementary strand within the duplex. Here, we used cryo-EM to solve the structures of human RAD51 in complex with DNA molecules, in presynaptic and postsynaptic states, at near-atomic resolution. Our structures reveal both conserved and distinct structural features of the human RAD51-DNA complexes compared with their prokaryotic counterpart. Notably, we also captured the structure of an arrested synaptic complex. Our results provide new insight into the molecular mechanisms of the DNA homology search and strand-exchange processes. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9567.map.gz emd_9567.map.gz | 56.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9567-v30.xml emd-9567-v30.xml emd-9567.xml emd-9567.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_9567.png emd_9567.png | 96.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-9567.cif.gz emd-9567.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9567 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9567 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9567 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9567 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_9567_validation.pdf.gz emd_9567_validation.pdf.gz | 458.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_9567_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_9567_full_validation.pdf.gz | 458 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_9567_validation.xml.gz emd_9567_validation.xml.gz | 6.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_9567_validation.cif.gz emd_9567_validation.cif.gz | 7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9567 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9567 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9567 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9567 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5h1cMC  9566C  9568C  5h1bC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9567.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9567.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.306 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human RAD51 post-synaptic complex
| Entire | Name: Human RAD51 post-synaptic complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human RAD51 post-synaptic complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Human RAD51 post-synaptic complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.18 kDa/nm |
-Supramolecule #2: Human RAD51
| Supramolecule | Name: Human RAD51 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #3: DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: DNA / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #4: DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: DNA / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.008074 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAMQMQLEAN ADTSVEEESF GPQPISRLEQ CGINANDVKK LEEAGFHTVE AVAYAPKKEL INIKGISEAK ADKILAEAAK LVPMGFTTA TEFHQRRSEI IQITTGSKEL DKLLQGGIET GSITEMFGEF RTGKTQICHT LAVTCQLPID RGGGEGKAMY I DTEGTFRP ...String: MAMQMQLEAN ADTSVEEESF GPQPISRLEQ CGINANDVKK LEEAGFHTVE AVAYAPKKEL INIKGISEAK ADKILAEAAK LVPMGFTTA TEFHQRRSEI IQITTGSKEL DKLLQGGIET GSITEMFGEF RTGKTQICHT LAVTCQLPID RGGGEGKAMY I DTEGTFRP ERLLAVAERY GLSGSDVLDN VAYARAFNTD HQTQLLYQAS AMMVESRYAL LIVDSATALY RTDYSGRGEL SA RQMHLAR FLRMLLRLAD EFGVAVVITN QVVAQVDGAA MFAADPKKPI GGNIIAHAST TRLYLRKGRG ETRICQIYDS PCL PEAEAM FAINADGVGD AKD UniProtKB: DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3')
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3') / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.692778 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA (5'-D(P*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*A)-3')
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(P*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*A)-3') / type: dna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.773904 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA) |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ANP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 506.196 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ANP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.075 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 25mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 50mM KCl, 1mM dithiothreitol, 1mM AMP-PNP and 2mM MgCl2 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 20 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 101.325 kPa |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 289 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 7676 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 7420 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 3-14 / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 528 / Average exposure time: 8.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: 2.5 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.5 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Number classes used: 78 Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 15.8 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 56.18 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF Software:
Number images used: 30194 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment selection | Number selected: 41146 | ||||||
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER Details: Randomly assigned euler angle for each segment and using back projection to generate initial model. | ||||||
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE Software:
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















