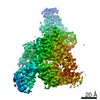
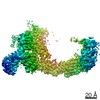
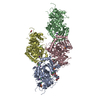
登録情報 データベース : PDB / ID : 7b5nタイトル Ubiquitin ligation to F-box protein substrates by SCF-RBR E3-E3 super-assembly: NEDD8-CUL1-RBX1-UBE2L3~Ub~ARIH1. (E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ...) x 2 Cullin-1 NEDD8 Polyubiquitin-C Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 L3 キーワード / / / / / / / / / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / / 解像度 : 3.6 Å データ登録者 Horn-Ghetko, D. / Prabu, J.R. / Schulman, B.A. 資金援助 組織 認可番号 国 European Research Council (ERC) H2020 789016-NEDD8Activate German Research Foundation (DFG) SCHU 3196/1-1
ジャーナル : Nature / 年 : 2021タイトル : Ubiquitin ligation to F-box protein targets by SCF-RBR E3-E3 super-assembly.著者 : Daniel Horn-Ghetko / David T Krist / J Rajan Prabu / Kheewoong Baek / Monique P C Mulder / Maren Klügel / Daniel C Scott / Huib Ovaa / Gary Kleiger / Brenda A Schulman / 要旨 : E3 ligases are typically classified by hallmark domains such as RING and RBR, which are thought to specify unique catalytic mechanisms of ubiquitin transfer to recruited substrates. However, rather ... E3 ligases are typically classified by hallmark domains such as RING and RBR, which are thought to specify unique catalytic mechanisms of ubiquitin transfer to recruited substrates. However, rather than functioning individually, many neddylated cullin-RING E3 ligases (CRLs) and RBR-type E3 ligases in the ARIH family-which together account for nearly half of all ubiquitin ligases in humans-form E3-E3 super-assemblies. Here, by studying CRLs in the SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) family, we show how neddylated SCF ligases and ARIH1 (an RBR-type E3 ligase) co-evolved to ubiquitylate diverse substrates presented on various F-box proteins. We developed activity-based chemical probes that enabled cryo-electron microscopy visualization of steps in E3-E3 ubiquitylation, initiating with ubiquitin linked to the E2 enzyme UBE2L3, then transferred to the catalytic cysteine of ARIH1, and culminating in ubiquitin linkage to a substrate bound to the SCF E3 ligase. The E3-E3 mechanism places the ubiquitin-linked active site of ARIH1 adjacent to substrates bound to F-box proteins (for example, substrates with folded structures or limited length) that are incompatible with previously described conventional RING E3-only mechanisms. The versatile E3-E3 super-assembly may therefore underlie widespread ubiquitylation. 履歴 登録 2020年12月5日 登録サイト / 処理サイト 改定 1.0 2021年2月10日 Provider / タイプ 改定 1.1 2021年2月17日 Group / カテゴリ / citation_authorItem / _citation.title / _citation_author.name改定 1.2 2021年3月10日 Group / カテゴリ Item / _citation.page_first / _citation.page_last改定 1.3 2024年10月23日 Group / Database references / Structure summaryカテゴリ chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond ... chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / em_admin / pdbx_entry_details / pdbx_modification_feature Item _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession ... _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession / _em_admin.last_update / _pdbx_entry_details.has_protein_modification
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 要素
要素 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 ドイツ, 2件
ドイツ, 2件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2021
ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2021


 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク ダウンロード
ダウンロード 7b5n.cif.gz
7b5n.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF形式
PDBx/mmCIF形式 pdb7b5n.ent.gz
pdb7b5n.ent.gz PDB形式
PDB形式 7b5n.json.gz
7b5n.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON形式
PDBx/mmJSON形式 その他のダウンロード
その他のダウンロード 7b5n_validation.pdf.gz
7b5n_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB検証レポート
wwPDB検証レポート 7b5n_full_validation.pdf.gz
7b5n_full_validation.pdf.gz 7b5n_validation.xml.gz
7b5n_validation.xml.gz 7b5n_validation.cif.gz
7b5n_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/7b5n
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/7b5n ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/7b5n
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/7b5n リンク
リンク 集合体
集合体
 要素
要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CUL1 / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CUL1 / 発現宿主:  Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) / 参照: UniProt: Q13616
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) / 参照: UniProt: Q13616 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: UBC / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: UBC / 発現宿主: 
 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NEDD8 / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NEDD8 / 発現宿主: 
 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: UBE2L3, UBCE7, UBCH7 / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: UBE2L3, UBCE7, UBCH7 / 発現宿主: 
 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ARIH1, ARI, MOP6, UBCH7BP, HUSSY-27 / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ARIH1, ARI, MOP6, UBCH7BP, HUSSY-27 / 発現宿主: 
 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: RBX1, RNF75, ROC1 / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: RBX1, RNF75, ROC1 / 発現宿主:  Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)


 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
 FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM
FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM 解析
解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー






















 PDBj
PDBj



















