[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
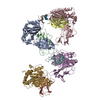
Yorodumi- EMDB-12048: Focused map- CyclinA-CDK2-class. Ubiquitin ligation to F-box prot... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-12048 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Focused map- CyclinA-CDK2-class. Ubiquitin ligation to F-box protein substrates by SCF-RBR E3-E3 super-assembly: CUL1-RBX1-SKP1-SKP2-CKSHS1-Cyclin A-CDK2-p27. Transition State 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ubiquitin / ubiquitin ligase / E3 ligase / F-box protein / RBR ligase / Cullin-RING-Ligase / CRL / SCF / NEDD8 / Post-translational modification / ubiquitylation / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcyclin-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation / negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / negative regulation of cardiac muscle tissue regeneration / negative regulation of kinase activity / positive regulation of protein polyubiquitination / autophagic cell death / FOXO-mediated transcription of cell cycle genes / Parkin-FBXW7-Cul1 ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development ...cyclin-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation / negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / negative regulation of cardiac muscle tissue regeneration / negative regulation of kinase activity / positive regulation of protein polyubiquitination / autophagic cell death / FOXO-mediated transcription of cell cycle genes / Parkin-FBXW7-Cul1 ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / cellular response to cell-matrix adhesion / F-box domain binding / cyclin A2-CDK1 complex / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition / cell cycle G1/S phase transition / cellular response to luteinizing hormone stimulus / PcG protein complex / G2/M DNA replication checkpoint / regulation of exit from mitosis / negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process / epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by p107 (RBL1) and p130 (RBL2) in complex with HDAC1 / cellular response to leptin stimulus / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / maintenance of protein location in nucleus / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / RHO GTPases activate CIT / male pronucleus / female pronucleus / nuclear export / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle / cellular response to cocaine / AKT phosphorylates targets in the cytosol / epithelial cell apoptotic process / response to glucagon / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process / molecular function inhibitor activity / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to lithium ion / positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / regulation of heterochromatin organization / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex / cyclin A2-CDK2 complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / G2 Phase / Y chromosome / cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of heterochromatin formation / p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response / X chromosome / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / Prolactin receptor signaling / Constitutive Signaling by AKT1 E17K in Cancer / cellular response to antibiotic / regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / centriole replication / protein kinase inhibitor activity / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / inner ear development / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / regulation of DNA replication / centrosome duplication / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / microtubule organizing center / : / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / G0 and Early G1 / cochlea development / animal organ regeneration / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / cullin family protein binding / Estrogen-dependent nuclear events downstream of ESR-membrane signaling / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / protein monoubiquitination / cyclin-dependent kinase / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / Cajal body / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
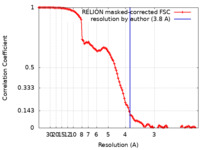
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Horn-Ghetko D / Prabu JR / Schulman BA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Ubiquitin ligation to F-box protein targets by SCF-RBR E3-E3 super-assembly. Authors: Daniel Horn-Ghetko / David T Krist / J Rajan Prabu / Kheewoong Baek / Monique P C Mulder / Maren Klügel / Daniel C Scott / Huib Ovaa / Gary Kleiger / Brenda A Schulman /    Abstract: E3 ligases are typically classified by hallmark domains such as RING and RBR, which are thought to specify unique catalytic mechanisms of ubiquitin transfer to recruited substrates. However, rather ...E3 ligases are typically classified by hallmark domains such as RING and RBR, which are thought to specify unique catalytic mechanisms of ubiquitin transfer to recruited substrates. However, rather than functioning individually, many neddylated cullin-RING E3 ligases (CRLs) and RBR-type E3 ligases in the ARIH family-which together account for nearly half of all ubiquitin ligases in humans-form E3-E3 super-assemblies. Here, by studying CRLs in the SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) family, we show how neddylated SCF ligases and ARIH1 (an RBR-type E3 ligase) co-evolved to ubiquitylate diverse substrates presented on various F-box proteins. We developed activity-based chemical probes that enabled cryo-electron microscopy visualization of steps in E3-E3 ubiquitylation, initiating with ubiquitin linked to the E2 enzyme UBE2L3, then transferred to the catalytic cysteine of ARIH1, and culminating in ubiquitin linkage to a substrate bound to the SCF E3 ligase. The E3-E3 mechanism places the ubiquitin-linked active site of ARIH1 adjacent to substrates bound to F-box proteins (for example, substrates with folded structures or limited length) that are incompatible with previously described conventional RING E3-only mechanisms. The versatile E3-E3 super-assembly may therefore underlie widespread ubiquitylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_12048.map.gz emd_12048.map.gz | 8.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-12048-v30.xml emd-12048-v30.xml emd-12048.xml emd-12048.xml | 28.3 KB 28.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_12048_fsc.xml emd_12048_fsc.xml | 11.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_12048.png emd_12048.png | 54.3 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_12048_msk_1.map emd_12048_msk_1.map | 125 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-12048.cif.gz emd-12048.cif.gz | 8.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_12048_half_map_1.map.gz emd_12048_half_map_1.map.gz emd_12048_half_map_2.map.gz emd_12048_half_map_2.map.gz | 98.4 MB 98.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12048 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12048 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12048 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12048 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7b5rMC  7b5lC  7b5mC  7b5nC  7b5sC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_12048.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_12048.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
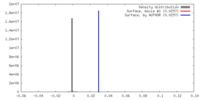
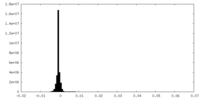
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
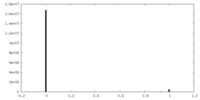
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_12048_msk_1.map emd_12048_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
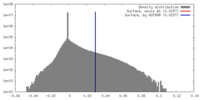
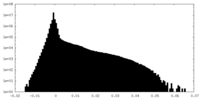
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_12048_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
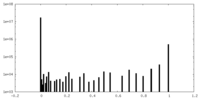
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_12048_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : NEDD8-CUL1-RBX1-SKP1-SKP2-CKSHS1-Cyclin A-CDK2-p27-UBE2L3~Ub~ARIH...
| Entire | Name: NEDD8-CUL1-RBX1-SKP1-SKP2-CKSHS1-Cyclin A-CDK2-p27-UBE2L3~Ub~ARIH1. Transition State 1 composite map. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: NEDD8-CUL1-RBX1-SKP1-SKP2-CKSHS1-Cyclin A-CDK2-p27-UBE2L3~Ub~ARIH...
| Supramolecule | Name: NEDD8-CUL1-RBX1-SKP1-SKP2-CKSHS1-Cyclin A-CDK2-p27-UBE2L3~Ub~ARIH1. Transition State 1 composite map. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 300 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Cullin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cullin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 89.800367 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSSTRSQNPH GLKQIGLDQI WDDLRAGIQQ VYTRQSMAKS RYMELYTHVY NYCTSVHQSN QARGAGVPPS KSKKGQTPGG AQFVGLELY KRLKEFLKNY LTNLLKDGED LMDESVLKFY TQQWEDYRFS SKVLNGICAY LNRHWVRREC DEGRKGIYEI Y SLALVTWR ...String: MSSTRSQNPH GLKQIGLDQI WDDLRAGIQQ VYTRQSMAKS RYMELYTHVY NYCTSVHQSN QARGAGVPPS KSKKGQTPGG AQFVGLELY KRLKEFLKNY LTNLLKDGED LMDESVLKFY TQQWEDYRFS SKVLNGICAY LNRHWVRREC DEGRKGIYEI Y SLALVTWR DCLFRPLNKQ VTNAVLKLIE KERNGETINT RLISGVVQSY VELGLNEDDA FAKGPTLTVY KESFESQFLA DT ERFYTRE STEFLQQNPV TEYMKKAEAR LLEEQRRVQV YLHESTQDEL ARKCEQVLIE KHLEIFHTEF QNLLDADKNE DLG RMYNLV SRIQDGLGEL KKLLETHIHN QGLAAIEKCG EAALNDPKMY VQTVLDVHKK YNALVMSAFN NDAGFVAALD KACG RFINN NAVTKMAQSS SKSPELLARY CDSLLKKSSK NPEEAELEDT LNQVMVVFKY IEDKDVFQKF YAKMLAKRLV HQNSA SDDA EASMISKLKQ ACGFEYTSKL QRMFQDIGVS KDLNEQFKKH LTNSEPLDLD FSIQVLSSGS WPFQQSCTFA LPSELE RSY QRFTAFYASR HSGRKLTWLY QLSKGELVTN CFKNRYTLQA STFQMAILLQ YNTEDAYTVQ QLTDSTQIKM DILAQVL QI LLKSKLLVLE DENANVDEVE LKPDTLIKLY LGYKNKKLRV NINVPMKTEQ KQEQETTHKN IEEDRKLLIQ AAIVRIMK M RKVLKHQQLL GEVLTQLSSR FKPRVPVIKK CIDILIEKEY LERVDGEKDT YSYLA UniProtKB: Cullin-1 |
-Macromolecule #2: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2
| Macromolecule | Name: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.817785 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHRKHLQEIP DLSSNVATSF TWGWDSSKTS ELLSGMGVSA LEKEEPDSEN IPQELLSNLG HPESPPRKRL KSKGSDKDFV IVRRPKLNR ENFPGVSWDS LPDELLLGIF SCLCLPELLK VSGVCKRWYR LASDESLWQT LDLTGKNLHP DVTGRLLSQG V IAFRCPRS ...String: MHRKHLQEIP DLSSNVATSF TWGWDSSKTS ELLSGMGVSA LEKEEPDSEN IPQELLSNLG HPESPPRKRL KSKGSDKDFV IVRRPKLNR ENFPGVSWDS LPDELLLGIF SCLCLPELLK VSGVCKRWYR LASDESLWQT LDLTGKNLHP DVTGRLLSQG V IAFRCPRS FMDQPLAEHF SPFRVQHMDL SNSVIEVSTL HGILSQCSKL QNLSLEGLRL SDPIVNTLAK NSNLVRLNLS GC SGFSEFA LQTLLSSCSR LDELNLSWCF DFTEKHVQVA VAHVSETITQ LNLSGYRKNL QKSDLSTLVR RCPNLVHLDL SDS VMLKND CFQEFFQLNY LQHLSLSRCY DIIPETLLEL GEIPTLKTLQ VFGIVPDGTL QLLKEALPHL QINCSHFTTI ARPT IGNKK NQEIWGIKCR LTLQKPSCL UniProtKB: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 |
-Macromolecule #3: Cyclin-dependent kinases regulatory subunit 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-dependent kinases regulatory subunit 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.679211 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSHKQIYYSD KYDDEEFEYR HVMLPKDIAK LVPKTHLMSE SEWRNLGVQQ SQGWVHYMIH EPEPHILLFR RPLPKKPKK UniProtKB: Cyclin-dependent kinases regulatory subunit 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: S-phase kinase-associated protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.679965 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPSIKLQSSD GEIFEVDVEI AKQSVTIKTM LEDLGMDDEG DDDPVPLPNV NAAILKKVIQ WCTHHKDDPP PPEDDENKEK RTDDIPVWD QEFLKVDQGT LFELILAANY LDIKGLLDVT CKTVANMIKG KTPEEIRKTF NIKNDFTEEE EAQVRKENQW C EEK UniProtKB: S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: cyclin-dependent kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 34.056469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MENFQKVEKI GEGTYGVVYK ARNKLTGEVV ALKKIRLDTE TEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELNH PNIVKLLDVI HTENKLYLVF EFLHQDLKK FMDASALTGI PLPLIKSYLF QLLQGLAFCH SHRVLHRDLK PQNLLINTEG AIKLADFGLA RAFGVPVRTY (TPO)HEVVTLWY ...String: MENFQKVEKI GEGTYGVVYK ARNKLTGEVV ALKKIRLDTE TEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELNH PNIVKLLDVI HTENKLYLVF EFLHQDLKK FMDASALTGI PLPLIKSYLF QLLQGLAFCH SHRVLHRDLK PQNLLINTEG AIKLADFGLA RAFGVPVRTY (TPO)HEVVTLWY RAPEILLGCK YYSTAVDIWS LGCIFAEMVT RRALFPGDSE IDQLFRIFRT LGTPDEVVWP GVTSMPD YK PSFPKWARQD FSKVVPPLDE DGRSLLSQML HYDPNKRISA KAALAHPFFQ DVTKPVPHLR L UniProtKB: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
-Macromolecule #6: Cyclin-A2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-A2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.609574 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLGNSAPGPA TREAGSALLA LQQTALQEDQ ENINPEKAAP VQQPRTRAAL AVLKSGNPRG LAQQQRPKTR RVAPLKDLPV NDEHVTVPP WKANSKQPAF TIHVDEAEKE AQKKPAESQK IEREDALAFN SAISLPGPRK PLVPLDYPMD GSFESPHTMD M SIILEDEK ...String: MLGNSAPGPA TREAGSALLA LQQTALQEDQ ENINPEKAAP VQQPRTRAAL AVLKSGNPRG LAQQQRPKTR RVAPLKDLPV NDEHVTVPP WKANSKQPAF TIHVDEAEKE AQKKPAESQK IEREDALAFN SAISLPGPRK PLVPLDYPMD GSFESPHTMD M SIILEDEK PVSVNEVPDY HEDIHTYLRE MEVKCKPKVG YMKKQPDITN SMRAILVDWL VEVGEEYKLQ NETLHLAVNY ID RFLSSMS VLRGKLQLVG TAAMLLASKF EEIYPPEVAE FVYITDDTYT KKQVLRMEHL VLKVLTFDLA APTVNQFLTQ YFL HQQPAN CKVESLAMFL GELSLIDADP YLKYLPSVIA GAAFHLALYT VTGQSWPESL IRKTGYTLES LKPCLMDLHQ TYLK APQHA QQSIREKYKN SKYHGVSLLN PPETLNL UniProtKB: Cyclin-A2 |
-Macromolecule #7: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.188303 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSNVRVSNGS PSLERMDARQ AEHPKPSACR NLFGPVDHEE LTRDLEKHCR DMEEASQRKW NFDFQNHKPL EGKYEWQEVE KGSLPEFYY RPPRPPKGAC KVPAQESQDV SGSRPAAPLI GAPANSEDTH LVDPKTDPSD SQTGLAEQCA GIRKRPATDD S STQNKRAN ...String: MSNVRVSNGS PSLERMDARQ AEHPKPSACR NLFGPVDHEE LTRDLEKHCR DMEEASQRKW NFDFQNHKPL EGKYEWQEVE KGSLPEFYY RPPRPPKGAC KVPAQESQDV SGSRPAAPLI GAPANSEDTH LVDPKTDPSD SQTGLAEQCA GIRKRPATDD S STQNKRAN RTEENVSDGS PNAGSVEQ(TPO)P KKPGLRRRQT UniProtKB: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














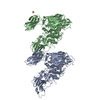


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)