[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7781: Cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of cardiac myo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7781 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
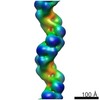
| Title | Cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of cardiac myosin binding protein C mode 2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of mysoin binding protein C | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | myosin binding protein C / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbasal body patch / C zone / regulation of muscle filament sliding / striated muscle myosin thick filament / tight junction assembly / regulation of striated muscle contraction / A band / cardiac myofibril / profilin binding / protein localization to bicellular tight junction ...basal body patch / C zone / regulation of muscle filament sliding / striated muscle myosin thick filament / tight junction assembly / regulation of striated muscle contraction / A band / cardiac myofibril / profilin binding / protein localization to bicellular tight junction / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Gap junction degradation / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / dense body / regulation of stress fiber assembly / Striated Muscle Contraction / regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction / M band / Adherens junctions interactions / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / structural constituent of muscle / regulation of focal adhesion assembly / sarcomere organization / positive regulation of wound healing / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / apical junction complex / myosin heavy chain binding / myosin binding / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / myofibril / filamentous actin / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / Recycling pathway of L1 / ATPase activator activity / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / heart morphogenesis / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / cardiac muscle contraction / phagocytic vesicle / titin binding / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / sarcomere / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / actin filament / cell motility / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / cellular response to type II interferon / platelet aggregation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / cell-cell junction / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / actin cytoskeleton / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / actin binding / angiogenesis / blood microparticle / cytoskeleton / cell adhesion / positive regulation of cell migration / axon / hydrolase activity / focal adhesion / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / synapse / positive regulation of gene expression / protein kinase binding / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 11.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Galkin VE / Schroeder GF | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2018 Journal: Structure / Year: 2018Title: N-Terminal Domains of Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Cooperatively Activate the Thin Filament. Authors: Cristina Risi / Betty Belknap / Eva Forgacs-Lonart / Samantha P Harris / Gunnar F Schröder / Howard D White / Vitold E Galkin /   Abstract: Muscle contraction relies on interaction between myosin-based thick filaments and actin-based thin filaments. Myosin binding protein C (MyBP-C) is a key regulator of actomyosin interactions. Recent ...Muscle contraction relies on interaction between myosin-based thick filaments and actin-based thin filaments. Myosin binding protein C (MyBP-C) is a key regulator of actomyosin interactions. Recent studies established that the N'-terminal domains (NTDs) of MyBP-C can either activate or inhibit thin filaments, but the mechanism of their collective action is poorly understood. Cardiac MyBP-C (cMyBP-C) harbors an extra NTD, which is absent in skeletal isoforms of MyBP-C, and its role in regulation of cardiac contraction is unknown. Here we show that the first two domains of human cMyPB-C (i.e., C0 and C1) cooperate to activate the thin filament. We demonstrate that C1 interacts with tropomyosin via a positively charged loop and that this interaction, stabilized by the C0 domain, is required for thin filament activation by cMyBP-C. Our data reveal a mechanism by which cMyBP-C can modulate cardiac contraction and demonstrate a function of the C0 domain. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7781.map.gz emd_7781.map.gz | 2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7781-v30.xml emd-7781-v30.xml emd-7781.xml emd-7781.xml | 17 KB 17 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7781.png emd_7781.png | 137.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7781.cif.gz emd-7781.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7781 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7781 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7781 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7781 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6cxjMC  4346C  7780C  6cxiC  6g2tC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7781.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 7.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7781.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 7.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of mysoin binding protein C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of cardiac myo...
| Entire | Name: cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of cardiac myosin binding protein C mode 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of cardiac myo...
| Supramolecule | Name: cardiac thin filament decorated with C0C1 fragment of cardiac myosin binding protein C mode 2 type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: actin
| Supramolecule | Name: actin / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: myosin binding protein C
| Supramolecule | Name: myosin binding protein C / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: tropomyosin
| Supramolecule | Name: tropomyosin / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, cytoplasmic 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.838766 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MEEEIAALVI DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSGDGV T HTVPIYEG ...String: MEEEIAALVI DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSGDGV T HTVPIYEG YALPHAILRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFTTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFEQEMA TAASSSSLEK SY ELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PEALFQPSFL GMESCGIHET TFNSIMKCDV DIRKDLYANT VLSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKEI TAL APSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ISKQEYDESG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type
| Macromolecule | Name: Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.180806 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDDPIGLFVM RPQDGEVTVG GSITFSARVA GASLLKPPVV KWFKGKWVDL SSKVGQHLQL HDSYDRASKV YLFELHITDA QPAFTGSYR CEVSTKDKFD CSNFNLTVHE UniProtKB: Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type |
-Macromolecule #3: Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type
| Macromolecule | Name: Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.70606 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPGKKPVS AFSKKPRSVE VAAGSPAVFE AETERAGVKV RWQRGGSDIS ASNKYGLATE GTRHTLTVRE VGPADQGSYA VIAGSSKVK FDLKVIEAEK AE UniProtKB: Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type |
-Macromolecule #4: Tropomyosin
| Macromolecule | Name: Tropomyosin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Details: model / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.826337 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: LACEY / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 15 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 294 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 27.5 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: -166.6 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 11.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER / Software - details: IHRSR / Number images used: 5830 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: cylinder density map |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE / Software - Name: SPIDER |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6cxj: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


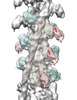

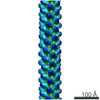
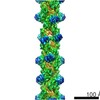
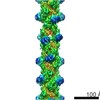
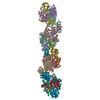
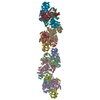
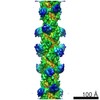
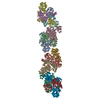





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















