[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6z2k: The structure of the tetrameric HDAC1/MIDEAS/DNTTIP1 MiDAC deacet... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6z2k | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The structure of the tetrameric HDAC1/MIDEAS/DNTTIP1 MiDAC deacetylase complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / HDAC1 MIDEAS ELMSAN1 DNTTIP1 TDIF1 histone deacetylase MiDAC | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationLoss of MECP2 binding ability to 5mC-DNA / Krueppel-associated box domain binding / Repression of WNT target genes / MECP2 regulates transcription of neuronal ligands / protein lysine delactylase activity / p75NTR negatively regulates cell cycle via SC1 / epidermal cell differentiation / histone decrotonylase activity / fungiform papilla formation / NuRD complex ...Loss of MECP2 binding ability to 5mC-DNA / Krueppel-associated box domain binding / Repression of WNT target genes / MECP2 regulates transcription of neuronal ligands / protein lysine delactylase activity / p75NTR negatively regulates cell cycle via SC1 / epidermal cell differentiation / histone decrotonylase activity / fungiform papilla formation / NuRD complex / regulation of cell fate specification / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of stem cell population maintenance / endoderm development / histone deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by p107 (RBL1) and p130 (RBL2) in complex with HDAC1 / histone deacetylase / regulation of stem cell differentiation / protein deacetylation / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in apoptosis / STAT3 nuclear events downstream of ALK signaling / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / protein lysine deacetylase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds; In linear amides / histone deacetylase activity / embryonic digit morphogenesis / positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / DNA methylation-dependent constitutive heterochromatin formation / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / G1/S-Specific Transcription / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / histone deacetylase complex / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / eyelid development in camera-type eye / Sin3-type complex / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / E-box binding / oligodendrocyte differentiation / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / G0 and Early G1 / host-mediated suppression of viral transcription / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / hair follicle placode formation / NF-kappaB binding / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / Transcriptional regulation of brown and beige adipocyte differentiation by EBF2 / nucleosome binding / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Acetylation / heterochromatin / cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / transcription repressor complex / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / negative regulation of cell migration / negative regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / transcription corepressor binding / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / hippocampus development / HDACs deacetylate histones / circadian regulation of gene expression / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / promoter-specific chromatin binding / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / SMAD2/SMAD3:SMAD4 heterotrimer regulates transcription / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / histone deacetylase binding / neuron differentiation / p53 binding / transcription corepressor activity / heterochromatin formation / chromosome / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / chromatin organization / transcription regulator complex / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / Potential therapeutics for SARS / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / chromatin remodeling / negative regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fairall, L. / Saleh, A. / Ragan, T.J. / Millard, C.J. / Savva, C.G. / Schwabe, J.W.R. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: The MiDAC histone deacetylase complex is essential for embryonic development and has a unique multivalent structure. Authors: Robert E Turnbull / Louise Fairall / Almutasem Saleh / Emma Kelsall / Kyle L Morris / T J Ragan / Christos G Savva / Aditya Chandru / Christopher J Millard / Olga V Makarova / Corinne J ...Authors: Robert E Turnbull / Louise Fairall / Almutasem Saleh / Emma Kelsall / Kyle L Morris / T J Ragan / Christos G Savva / Aditya Chandru / Christopher J Millard / Olga V Makarova / Corinne J Smith / Alan M Roseman / Andrew M Fry / Shaun M Cowley / John W R Schwabe /  Abstract: MiDAC is one of seven distinct, large multi-protein complexes that recruit class I histone deacetylases to the genome to regulate gene expression. Despite implications of involvement in cell cycle ...MiDAC is one of seven distinct, large multi-protein complexes that recruit class I histone deacetylases to the genome to regulate gene expression. Despite implications of involvement in cell cycle regulation and in several cancers, surprisingly little is known about the function or structure of MiDAC. Here we show that MiDAC is important for chromosome alignment during mitosis in cancer cell lines. Mice lacking the MiDAC proteins, DNTTIP1 or MIDEAS, die with identical phenotypes during late embryogenesis due to perturbations in gene expression that result in heart malformation and haematopoietic failure. This suggests that MiDAC has an essential and unique function that cannot be compensated by other HDAC complexes. Consistent with this, the cryoEM structure of MiDAC reveals a unique and distinctive mode of assembly. Four copies of HDAC1 are positioned at the periphery with outward-facing active sites suggesting that the complex may target multiple nucleosomes implying a processive deacetylase function. #1:  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2015 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2015Title: Structural and functional characterization of a cell cycle associated HDAC1/2 complex reveals the structural basis for complex assembly and nucleosome targeting. Authors: Toshimasa Itoh / Louise Fairall / Frederick W Muskett / Charles P Milano / Peter J Watson / Nadia Arnaudo / Almutasem Saleh / Christopher J Millard / Mohammed El-Mezgueldi / Fabrizio Martino ...Authors: Toshimasa Itoh / Louise Fairall / Frederick W Muskett / Charles P Milano / Peter J Watson / Nadia Arnaudo / Almutasem Saleh / Christopher J Millard / Mohammed El-Mezgueldi / Fabrizio Martino / John W R Schwabe /  Abstract: Recent proteomic studies have identified a novel histone deacetylase complex that is upregulated during mitosis and is associated with cyclin A. This complex is conserved from nematodes to man and ...Recent proteomic studies have identified a novel histone deacetylase complex that is upregulated during mitosis and is associated with cyclin A. This complex is conserved from nematodes to man and contains histone deacetylases 1 and 2, the MIDEAS corepressor protein and a protein called DNTTIP1 whose function was hitherto poorly understood. Here, we report the structures of two domains from DNTTIP1. The amino-terminal region forms a tight dimerization domain with a novel structural fold that interacts with and mediates assembly of the HDAC1:MIDEAS complex. The carboxy-terminal domain of DNTTIP1 has a structure related to the SKI/SNO/DAC domain, despite lacking obvious sequence homology. We show that this domain in DNTTIP1 mediates interaction with both DNA and nucleosomes. Thus, DNTTIP1 acts as a dimeric chromatin binding module in the HDAC1:MIDEAS corepressor complex. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6z2k.cif.gz 6z2k.cif.gz | 790.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6z2k.ent.gz pdb6z2k.ent.gz | 662 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6z2k.json.gz 6z2k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/6z2k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/6z2k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/6z2k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/6z2k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11042MC  6z2jC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 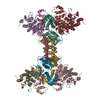
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 12 molecules CEKIABGHFDLJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 55178.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HDAC1, RPD3L1 / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HDAC1, RPD3L1 / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13547, histone deacetylase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13547, histone deacetylase#2: Protein | Mass: 14381.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DNTTIP1, C20orf167, TDIF1 / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DNTTIP1, C20orf167, TDIF1 / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H147 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H147#3: Protein | Mass: 19794.771 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MIDEAS, C14orf117, C14orf43, ELMSAN1 / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MIDEAS, C14orf117, C14orf43, ELMSAN1 / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q6PJG2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q6PJG2 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 16 molecules 

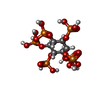


| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #6: Chemical | ChemComp-IHP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Tetrameric complex of the MiDAC deacetylase complex containing HDAC1, the ELM2-SANT domain of MIDEAS and the dimerisation domain of DNTTIP1 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.357 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293F Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.45 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 30 mA for 30 sec / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil, UltrAuFoil, R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: Blot time 3 sec, blot force 10. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Calibrated magnification: 129629 X / Nominal defocus max: 500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 100 K / Temperature (min): 100 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 60 sec. / Electron dose: 36 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 2752 |
| EM imaging optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 14 µm / Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3260: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 151434 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D2 (2x2 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 63222 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






































