[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
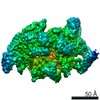
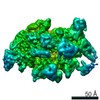
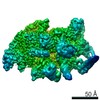
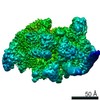
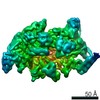
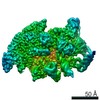
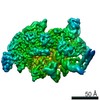
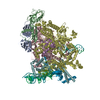
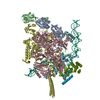
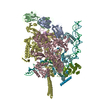
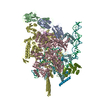
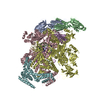
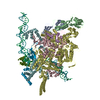
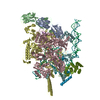
Yorodumi- PDB-6vw0: Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNAP S456L mutant open promoter complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vw0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNAP S456L mutant open promoter complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSFERASE/DNA / initiation / transcription bubble / open promoter complex / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to water / bacterial-type RNA polymerase holo enzyme binding / Antimicrobial action and antimicrobial resistance in Mtb / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / rRNA transcription / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / peptidoglycan-based cell wall / : ...response to water / bacterial-type RNA polymerase holo enzyme binding / Antimicrobial action and antimicrobial resistance in Mtb / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / rRNA transcription / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / peptidoglycan-based cell wall / : / : / : / : / : / : / DNA-templated transcription initiation / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / nucleic acid binding / protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.59 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lilic, M. / Boyaci, H. / Chen, J. / Darst, S.A. / Campbell, E.A. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: The antibiotic sorangicin A inhibits promoter DNA unwinding in a rifampicin-resistant RNA polymerase. Authors: Mirjana Lilic / James Chen / Hande Boyaci / Nathaniel Braffman / Elizabeth A Hubin / Jennifer Herrmann / Rolf Müller / Rachel Mooney / Robert Landick / Seth A Darst / Elizabeth A Campbell /   Abstract: Rifampicin (Rif) is a first-line therapeutic used to treat the infectious disease tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by the pathogen (). The emergence of Rif-resistant (Rif) presents a need for new ...Rifampicin (Rif) is a first-line therapeutic used to treat the infectious disease tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by the pathogen (). The emergence of Rif-resistant (Rif) presents a need for new antibiotics. Rif targets the enzyme RNA polymerase (RNAP). Sorangicin A (Sor) is an unrelated inhibitor that binds in the Rif-binding pocket of RNAP. Sor inhibits a subset of Rif RNAPs, including the most prevalent clinical Rif RNAP substitution found in infected patients (S456>L of the β subunit). Here, we present structural and biochemical data demonstrating that Sor inhibits the wild-type RNAP by a similar mechanism as Rif: by preventing the translocation of very short RNAs. By contrast, Sor inhibits the Rif S456L enzyme at an earlier step, preventing the transition of a partially unwound promoter DNA intermediate to the fully opened DNA and blocking the template-strand DNA from reaching the active site in the RNAP catalytic center. By defining template-strand blocking as a mechanism for inhibition, we provide a mechanistic drug target in RNAP. Our finding that Sor inhibits the wild-type and mutant RNAPs through different mechanisms prompts future considerations for designing antibiotics against resistant targets. Also, we show that Sor has a better pharmacokinetic profile than Rif, making it a suitable starting molecule to design drugs to be used for the treatment of TB patients with comorbidities who require multiple medications. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vw0.cif.gz 6vw0.cif.gz | 690.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vw0.ent.gz pdb6vw0.ent.gz | 541 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vw0.json.gz 6vw0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6vw0_validation.pdf.gz 6vw0_validation.pdf.gz | 950.2 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6vw0_full_validation.pdf.gz 6vw0_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1002.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6vw0_validation.xml.gz 6vw0_validation.xml.gz | 90 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6vw0_validation.cif.gz 6vw0_validation.cif.gz | 143.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vw0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vw0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vw0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vw0 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21409MC  6vvsC  6vvtC  6vvvC  6vvxC  6vvyC  6vvzC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 37745.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A5U8D3, UniProt: P9WGZ1*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #2: Protein | | Mass: 130096.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: S456L Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: V9Z879, UniProt: P9WGY9*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #3: Protein | | Mass: 148202.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A5U053, UniProt: P9WGY7*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #4: Protein | | Mass: 11776.996 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: rpoZ, ERS007672_03979, ERS007703_04032, ERS007720_04749, ERS027652_00548, ERS027654_02543, ERS027656_03959, ERS124361_02246 Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A0T9N9K3, UniProt: P9WGY5*PLUS, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules F
| #5: Protein | Mass: 58169.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-RNA polymerase-binding ... , 2 types, 2 molecules JM
| #6: Protein | Mass: 12993.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 17933.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules OP
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 27907.809 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 27618.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #10: Chemical | | #11: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNAP S456L mutant open promoter complex Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#9 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 71 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3246: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.59 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 55833 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj








































