[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
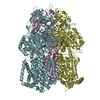
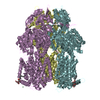
Yorodumi- PDB-6vkt: Cryo-electron microscopy structures of a gonococcal multidrug eff... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vkt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
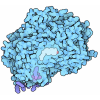
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structures of a gonococcal multidrug efflux pump illuminate a mechanism of erythromycin drug recognition | ||||||
 Components Components | Efflux pump membrane transporter | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Efflux / pump / erythromycin | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationefflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / response to toxic substance / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lyu, M. / Moseng, M.A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2020 Journal: mBio / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM Structures of a Gonococcal Multidrug Efflux Pump Illuminate a Mechanism of Drug Recognition and Resistance. Authors: Meinan Lyu / Mitchell A Moseng / Jennifer L Reimche / Concerta L Holley / Vijaya Dhulipala / Chih-Chia Su / William M Shafer / Edward W Yu /  Abstract: is an obligate human pathogen and causative agent of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) gonorrhea. The most predominant and clinically important multidrug efflux system in is the ultiple ... is an obligate human pathogen and causative agent of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) gonorrhea. The most predominant and clinically important multidrug efflux system in is the ultiple ransferrable esistance (Mtr) pump, which mediates resistance to a number of different classes of structurally diverse antimicrobial agents, including clinically used antibiotics (e.g., β-lactams and macrolides), dyes, detergents and host-derived antimicrobials (e.g., cationic antimicrobial peptides and bile salts). Recently, it has been found that gonococci bearing mosaic-like sequences within the gene can result in amino acid changes that increase the MtrD multidrug efflux pump activity, probably by influencing antimicrobial recognition and/or extrusion to elevate the level of antibiotic resistance. Here, we report drug-bound solution structures of the MtrD multidrug efflux pump carrying a mosaic-like sequence using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy, with the antibiotics bound deeply inside the periplasmic domain of the pump. Through this structural approach coupled with genetic studies, we identify critical amino acids that are important for drug resistance and propose a mechanism for proton translocation. has become a highly antimicrobial-resistant Gram-negative pathogen. Multidrug efflux is a major mechanism that uses to counteract the action of multiple classes of antibiotics. It appears that gonococci bearing mosaic-like sequences within the gene , encoding the most predominant and clinically important transporter of any gonococcal multidrug efflux pump, significantly elevate drug resistance and enhance transport function. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of MtrD carrying a mosaic-like sequence that allow us to understand the mechanism of drug recognition. Our work will ultimately inform structure-guided drug design for inhibiting these critical multidrug efflux pumps. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vkt.cif.gz 6vkt.cif.gz | 534.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vkt.ent.gz pdb6vkt.ent.gz | 441.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vkt.json.gz 6vkt.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6vkt_validation.pdf.gz 6vkt_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6vkt_full_validation.pdf.gz 6vkt_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.7 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6vkt_validation.xml.gz 6vkt_validation.xml.gz | 98.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6vkt_validation.cif.gz 6vkt_validation.cif.gz | 142.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vkt https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vkt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vkt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vkt | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21229MC 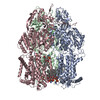 6vksC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
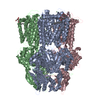
| Deposited unit | 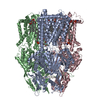
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
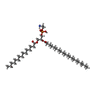
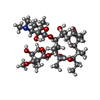
| #1: Protein | Mass: 111643.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) / Gene: mtrD, E8M65_05860, E8M67_05810, E8M69_06545 / Production host: Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) / Gene: mtrD, E8M65_05860, E8M67_05810, E8M69_06545 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-PTY / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ERY / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MtrD efflux pump with bound erythromycin / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
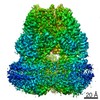
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.72 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1507208 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj