[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21229: Cryo-electron microscopy structures of a gonococcal multidrug eff... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21229 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
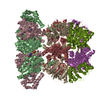
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structures of a gonococcal multidrug efflux pump illuminate a mechanism of erythromycin drug recognition | |||||||||
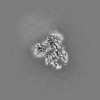
 Map data Map data | Structure of a gonococcal multidrug efflux pump | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Efflux / pump / erythromycin / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationefflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / response to toxic substance / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lyu M / Moseng MA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2020 Journal: mBio / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM Structures of a Gonococcal Multidrug Efflux Pump Illuminate a Mechanism of Drug Recognition and Resistance. Authors: Meinan Lyu / Mitchell A Moseng / Jennifer L Reimche / Concerta L Holley / Vijaya Dhulipala / Chih-Chia Su / William M Shafer / Edward W Yu /  Abstract: is an obligate human pathogen and causative agent of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) gonorrhea. The most predominant and clinically important multidrug efflux system in is the ultiple ... is an obligate human pathogen and causative agent of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) gonorrhea. The most predominant and clinically important multidrug efflux system in is the ultiple ransferrable esistance (Mtr) pump, which mediates resistance to a number of different classes of structurally diverse antimicrobial agents, including clinically used antibiotics (e.g., β-lactams and macrolides), dyes, detergents and host-derived antimicrobials (e.g., cationic antimicrobial peptides and bile salts). Recently, it has been found that gonococci bearing mosaic-like sequences within the gene can result in amino acid changes that increase the MtrD multidrug efflux pump activity, probably by influencing antimicrobial recognition and/or extrusion to elevate the level of antibiotic resistance. Here, we report drug-bound solution structures of the MtrD multidrug efflux pump carrying a mosaic-like sequence using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy, with the antibiotics bound deeply inside the periplasmic domain of the pump. Through this structural approach coupled with genetic studies, we identify critical amino acids that are important for drug resistance and propose a mechanism for proton translocation. has become a highly antimicrobial-resistant Gram-negative pathogen. Multidrug efflux is a major mechanism that uses to counteract the action of multiple classes of antibiotics. It appears that gonococci bearing mosaic-like sequences within the gene , encoding the most predominant and clinically important transporter of any gonococcal multidrug efflux pump, significantly elevate drug resistance and enhance transport function. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of MtrD carrying a mosaic-like sequence that allow us to understand the mechanism of drug recognition. Our work will ultimately inform structure-guided drug design for inhibiting these critical multidrug efflux pumps. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21229.map.gz emd_21229.map.gz | 138.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21229-v30.xml emd-21229-v30.xml emd-21229.xml emd-21229.xml | 10.4 KB 10.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21229.png emd_21229.png | 143.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21229.cif.gz emd-21229.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21229 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21229 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21229 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21229 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6vktMC  6vksC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21229.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 163.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21229.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 163.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of a gonococcal multidrug efflux pump | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : MtrD efflux pump with bound erythromycin
| Entire | Name: MtrD efflux pump with bound erythromycin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: MtrD efflux pump with bound erythromycin
| Supramolecule | Name: MtrD efflux pump with bound erythromycin / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Efflux pump membrane transporter
| Macromolecule | Name: Efflux pump membrane transporter / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 111.643969 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAKFFIDRPI FAWVISIFII AAGIFGIKSL PVSQYPSVAA PTITLHAIYP GASAQVMEGS VLSVIERNMN GVEGLDYMST SADSSGSGS VSLTFTPDTD ENLAQVEVQN KLSEVLSTLP ATVQQYGVTV SKARSNFLMI VMLSSDVQST EEMNDYAQRN V VPELQRIE ...String: MAKFFIDRPI FAWVISIFII AAGIFGIKSL PVSQYPSVAA PTITLHAIYP GASAQVMEGS VLSVIERNMN GVEGLDYMST SADSSGSGS VSLTFTPDTD ENLAQVEVQN KLSEVLSTLP ATVQQYGVTV SKARSNFLMI VMLSSDVQST EEMNDYAQRN V VPELQRIE GVGQVRLFGA QRAMRIWVDP KKLQNYNLSF ADVGSALSAQ NIQISAGSIG SLPAVRGQTV TATVTAQGQL GT AEEFGNV ILRANTDGSN IYLKDVAKVG LGMEDYSSST RLNGVNTTGM AVMLSNSGNA MATAKAVKER LAVLEKYFPQ GMS WKTPYD TSKFVEISIE KVIHTLIEAM VLVFVVMYLF LQNIRYTLIP TIVVPISLLG GFAFISYMGM SINVLTMFAM ILVI GIVVD DAIVVVENVE RIMAGEGLPP KEATKKAMGQ ISGAVIGITA VLISVFVPLA MFSGAAGNIY KQFALTMASS IAFSA FLAL TLTPALCATM LKTIPKGHHE EKKGFFGWFN KKFDSWTHGY EGRVAKVLRK TFRMMVVYIG LAVVGVFLFM RLPTSF LPT EDQGFVMVSV QLPAGATKER TDATLAQVTQ LAKSIPEIEN IITVSGFSFS GSGQNMAMGF AILKDWNERT ASGSDAV AV AGKLTGMMMG TLKDGFGIAV VPPPILELGN GSGLSINLQD RNNTGHTALL AKRNELIQKM RASGLFDPST VRAGGLED S PQLKIDINRA AAAAQGVSFA DIRTALASAL SSSYVSDFPN QGRLQRVMVQ ADGDARMQPA DILNLTVPNS SGIAVPLSS IATVSWQMGT EQSVRFNGYP AMELSGSPAT GVSTGQAMEA VQKMVDELGS GYSLEWGGQS REEAKGGSQT IALYALAAVA VFLVLAALY ESWSIPLAVL LVMPLGLAGA AAGVTGRNLF EGLLGSVPSF ANDIYFQVGF VTVMGLSAKN AILIIEFAKD L QAQGKSAV EAALEAARLR FRPIIMTSFA FILGVVPLYI AGGASSASQR AIGTTVFWGM LIGTLLSVFL VPLFYVVVRK FF KETAHE UniProtKB: UNIPROTKB: A0A4T9VBR9 |
-Macromolecule #2: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 23 / Formula: PTY |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 734.039 Da |
| Chemical component information | 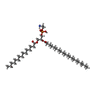 ChemComp-PTY: |
-Macromolecule #3: ERYTHROMYCIN A
| Macromolecule | Name: ERYTHROMYCIN A / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ERY |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 733.927 Da |
| Chemical component information | 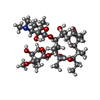 ChemComp-ERY: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.72 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 1507208 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



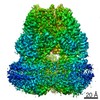
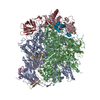
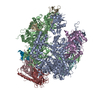
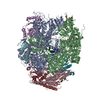
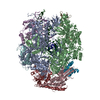
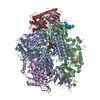
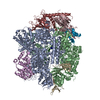

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)