+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6v00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
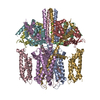
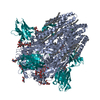
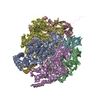
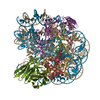
| Title | structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE3-CaM complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / potassium channel / KCNQ1 / CaM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / regulation of gastric acid secretion ...negative regulation of membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / regulation of gastric acid secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / iodide transport / Phase 3 - rapid repolarisation / membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / negative regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane / Phase 2 - plateau phase / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion export across plasma membrane / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / renal sodium ion absorption / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization / auditory receptor cell development / protein phosphatase 1 binding / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion homeostasis / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / non-motile cilium assembly / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / cardiac muscle cell contraction / intestinal absorption / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / inner ear morphogenesis / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / neuronal cell body membrane / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / sodium ion transport / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / renal absorption / autophagosome membrane docking / ciliary base / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / regulation of heart contraction / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / inner ear development / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / monoatomic ion channel complex / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / action potential / cochlea development / Calcineurin activates NFAT / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / social behavior / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / potassium channel regulator activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Anaplasma marginale (bacteria) Anaplasma marginale (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mackinnon, R. / Sun, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structural Basis of Human KCNQ1 Modulation and Gating. Authors: Ji Sun / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: KCNQ1, also known as Kv7.1, is a voltage-dependent K channel that regulates gastric acid secretion, salt and glucose homeostasis, and heart rhythm. Its functional properties are regulated in a tissue- ...KCNQ1, also known as Kv7.1, is a voltage-dependent K channel that regulates gastric acid secretion, salt and glucose homeostasis, and heart rhythm. Its functional properties are regulated in a tissue-specific manner through co-assembly with beta subunits KCNE1-5. In non-excitable cells, KCNQ1 forms a complex with KCNE3, which suppresses channel closure at negative membrane voltages that otherwise would close it. Pore opening is regulated by the signaling lipid PIP2. Using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), we show that KCNE3 tucks its single-membrane-spanning helix against KCNQ1, at a location that appears to lock the voltage sensor in its depolarized conformation. Without PIP2, the pore remains closed. Upon addition, PIP2 occupies a site on KCNQ1 within the inner membrane leaflet, which triggers a large conformational change that leads to dilation of the pore's gate. It is likely that this mechanism of PIP2 activation is conserved among Kv7 channels. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6v00.cif.gz 6v00.cif.gz | 428.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6v00.ent.gz pdb6v00.ent.gz | 323.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6v00.json.gz 6v00.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v0/6v00 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v0/6v00 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v0/6v00 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v0/6v00 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20966MC  6uzzC  6v01C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 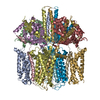
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63258.574 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNQ1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNQ1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P51787 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P51787#2: Protein | Mass: 16852.545 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DP23 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DP23#3: Protein | Mass: 40095.168 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Anaplasma marginale (bacteria), (gene. exp.) Anaplasma marginale (bacteria), (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: mCherry, KCNE3 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: X5DSL3, UniProt: Q9Y6H6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: X5DSL3, UniProt: Q9Y6H6#4: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: KCNQ1-CaM complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 94 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 39074 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj