[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6jr3: Crystal structure of insulin hexamer fitted into cryo EM density ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6jr3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of insulin hexamer fitted into cryo EM density map where each dimer was kept as rigid body | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HORMONE / Insulin fibrillation / Natural polyphenols / Anti-Amyloid activity / Insulin hexamer / Bioavailability | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst ...negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / alpha-beta T cell activation / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / negative regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / transport vesicle / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / positive regulation of glycolytic process / positive regulation of cytokine production / endosome lumen / acute-phase response / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein secretion / insulin receptor binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / wound healing / positive regulation of neuron projection development / hormone activity / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / vasodilation / cognition / glucose metabolic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / cell-cell signaling / glucose homeostasis / regulation of protein localization / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell growth / protease binding / secretory granule lumen / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of cell migration / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / Amyloid fiber formation / receptor ligand activity / Golgi membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / extracellular space / extracellular region / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 14.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sengupta, J. / Pathak, B.K. / Bhakta, S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  India, 3items India, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Comput Aided Mol Des / Year: 2020 Journal: J Comput Aided Mol Des / Year: 2020Title: Resveratrol as a nontoxic excipient stabilizes insulin in a bioactive hexameric form. Authors: Bani Kumar Pathak / Debajyoti Das / Sayan Bhakta / Partha Chakrabarti / Jayati Sengupta /  Abstract: Insulin aggregation is the leading cause of considerable reduction in the amount of active drug molecules in liquid formulations manufactured for diabetes management. Phenolic compounds, such as ...Insulin aggregation is the leading cause of considerable reduction in the amount of active drug molecules in liquid formulations manufactured for diabetes management. Phenolic compounds, such as phenol and m-cresol, are routinely used to stabilize insulin in a hexameric form during its commercial preparation. However, long term usage of commercial insulin results in various adverse secondary responses, for which toxicity of the phenolic excipients is primarily responsible. In this study we aimed to find out a nontoxic insulin stabilizer. To that end, we have selected resveratrol, a natural polyphenol, as a prospective nontoxic insulin stabilizer because of its structural similarity with commercially used phenolic compounds. Atomic force microscopy visualization of resveratrol-treated human insulin revealed that resveratrol has a unique ability to arrest hINS in a soluble oligomeric form having discrete spherical morphology. Most importantly, resveratrol-treated insulin is nontoxic for HepG2 cells and it effectively maintains low blood glucose in a mouse model. Cryo-electron microscopy revealed 3D morphology of resveratrol-stabilized insulin that strikingly resembles crystal structures of insulin hexamer formulated with m-cresol. Significantly, we found that, in a condition inductive to amyloid fibrillation at physiological pH, resveratrol is capable of stabilizing insulin more efficiently than m-cresol. Thus, this study describes resveratrol as an effective nontoxic natural molecule that can be used for stabilizing insulin in a bioactive oligomeric form during its commercial formulation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6jr3.cif.gz 6jr3.cif.gz | 18.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6jr3.ent.gz pdb6jr3.ent.gz | 8.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6jr3.json.gz 6jr3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/6jr3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/6jr3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/6jr3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/6jr3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 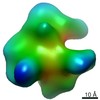 9878MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2383.698 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host:  #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3433.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Insulin oligomer and Resveratrol complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 10 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: SPIDER / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 14.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 11000 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1EV6 Accession code: 1EV6 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj