[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
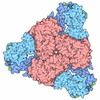
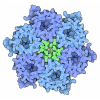
Yorodumi- PDB-5lp3: Three tetrameric rings of Isoaspartyl Dipeptidase fitted in an EM... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5lp3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Three tetrameric rings of Isoaspartyl Dipeptidase fitted in an EM volume. | ||||||
 Components Components | Isoaspartyl dipeptidase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Designed protein filament / Isoaspartyl Dipeptidase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Omega peptidases / beta-aspartyl-peptidase activity / metallopeptidase activity / proteolysis / zinc ion binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 10.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Garcia-Seisdedos, H. / Empereur-Mot, C. / Elad, N. / Levy, E.D. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2017 Journal: Nature / Year: 2017Title: Proteins evolve on the edge of supramolecular self-assembly. Authors: Hector Garcia-Seisdedos / Charly Empereur-Mot / Nadav Elad / Emmanuel D Levy /  Abstract: The self-association of proteins into symmetric complexes is ubiquitous in all kingdoms of life. Symmetric complexes possess unique geometric and functional properties, but their internal symmetry ...The self-association of proteins into symmetric complexes is ubiquitous in all kingdoms of life. Symmetric complexes possess unique geometric and functional properties, but their internal symmetry can pose a risk. In sickle-cell disease, the symmetry of haemoglobin exacerbates the effect of a mutation, triggering assembly into harmful fibrils. Here we examine the universality of this mechanism and its relation to protein structure geometry. We introduced point mutations solely designed to increase surface hydrophobicity among 12 distinct symmetric complexes from Escherichia coli. Notably, all responded by forming supramolecular assemblies in vitro, as well as in vivo upon heterologous expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Remarkably, in four cases, micrometre-long fibrils formed in vivo in response to a single point mutation. Biophysical measurements and electron microscopy revealed that mutants self-assembled in their folded states and so were not amyloid-like. Structural examination of 73 mutants identified supramolecular assembly hot spots predictable by geometry. A subsequent structural analysis of 7,471 symmetric complexes showed that geometric hot spots were buffered chemically by hydrophilic residues, suggesting a mechanism preventing mis-assembly of these regions. Thus, point mutations can frequently trigger folded proteins to self-assemble into higher-order structures. This potential is counterbalanced by negative selection and can be exploited to design nanomaterials in living cells. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5lp3.cif.gz 5lp3.cif.gz | 782.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5lp3.ent.gz pdb5lp3.ent.gz | 653.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5lp3.json.gz 5lp3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lp/5lp3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lp/5lp3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lp/5lp3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lp/5lp3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4094MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41167.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: P39377, Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Omega peptidases Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Isoaspartyl Dipeptidase / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Plasmid: pET-30a(+) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 297 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI 20 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / C2 aperture diameter: 30 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 32 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 38786 Details: Particles were manually selected from filaments only | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D4 (2x4 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 10.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 17277 / Details: 2 CLASSES WERE MERGED IN THE FINAL RECONSTRUCTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj