[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-22844: Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the heavy metal efflux pump... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22844 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
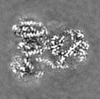
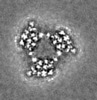
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the heavy metal efflux pump CusA in a homogeneous binding copper(1) state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | efflux / pump / heavy metal. copper / silver / closed / open / transport / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsilver ion transport / silver ion transmembrane transporter activity / plasma membrane copper ion transport / copper ion transmembrane transport / response to silver ion / silver ion transmembrane transport / copper ion transmembrane transporter activity / copper ion export / detoxification of copper ion / response to copper ion ...silver ion transport / silver ion transmembrane transporter activity / plasma membrane copper ion transport / copper ion transmembrane transport / response to silver ion / silver ion transmembrane transport / copper ion transmembrane transporter activity / copper ion export / detoxification of copper ion / response to copper ion / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / response to toxic substance / copper ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Moseng MA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2021 Journal: mBio / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM Structures of CusA Reveal a Mechanism of Metal-Ion Export. Authors: Mitchell A Moseng / Meinan Lyu / Tanadet Pipatpolkai / Przemyslaw Glaza / Corey C Emerson / Phoebe L Stewart / Phillip J Stansfeld / Edward W Yu /   Abstract: Gram-negative bacteria utilize the resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) superfamily of efflux pumps to expel a variety of toxic compounds from the cell. The CusA membrane protein, which ...Gram-negative bacteria utilize the resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) superfamily of efflux pumps to expel a variety of toxic compounds from the cell. The CusA membrane protein, which recognizes and extrudes biocidal Cu(I) and Ag(I) ions, belongs to the heavy-metal efflux (HME) subfamily of RND efflux pumps. We here report four structures of the trimeric CusA heavy-metal efflux pump in the presence of Cu(I) using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). We discover that different CusA protomers within the trimer are able to bind Cu(I) ions simultaneously. Our structural data combined with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations allow us to propose a mechanism for ion transport where each CusA protomer functions independently within the trimer. The bacterial RND superfamily of efflux pumps mediate resistance to a variety of biocides, including Cu(I) and Ag(I) ions. Here we report four cryo-EM structures of the trimeric CusA pump in the presence of Cu(I). Combined with MD simulations, our data indicate that each CusA protomer within the trimer recognizes and extrudes Cu(I) independently. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22844.map.gz emd_22844.map.gz | 12.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22844-v30.xml emd-22844-v30.xml emd-22844.xml emd-22844.xml | 10.9 KB 10.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22844.png emd_22844.png | 185.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22844.cif.gz emd-22844.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22844 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22844 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 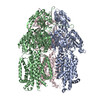 7kf6MC 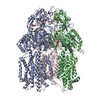 7kf5C  7kf7C  7kf8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22844.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 13.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22844.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 13.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CusA in symmetric copper binding form
| Entire | Name: CusA in symmetric copper binding form |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CusA in symmetric copper binding form
| Supramolecule | Name: CusA in symmetric copper binding form / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Cation efflux system protein CusA
| Macromolecule | Name: Cation efflux system protein CusA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 115.833945 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGHHHHHHMI EWIIRRSVAN RFLVLMGALF LSIWGTWTII NTPVDALPDL SDVQVIIKTS YPGQAPQIVE NQVTYPLTTT MLSVPGAKT VRGFSQFGDS YVYVIFEDGT DPYWARSRVL EYLNQVQGKL PAGVSAELGP DATGVGWIYE YALVDRSGKH D LADLRSLQ ...String: MGHHHHHHMI EWIIRRSVAN RFLVLMGALF LSIWGTWTII NTPVDALPDL SDVQVIIKTS YPGQAPQIVE NQVTYPLTTT MLSVPGAKT VRGFSQFGDS YVYVIFEDGT DPYWARSRVL EYLNQVQGKL PAGVSAELGP DATGVGWIYE YALVDRSGKH D LADLRSLQ DWFLKYELKT IPDVAEVASV GGVVKEYQVV IDPQRLAQYG ISLAEVKSAL DASNQEAGGS SIELAEAEYM VR ASGYLQT LDDFNHIVLK ASENGVPVYL RDVAKVQIGP EMRRGIAELN GEGEVAGGVV ILRSGKNARE VIAAVKDKLE TLK SSLPEG VEIVTTYDRS QLIDRAIDNL SGKLLEEFIV VAVVCALFLW HVRSALVAII SLPLGLCIAF IVMHFQGLNA NIMS LGGIA IAVGAMVDAA IVMIENAHKR LEEWQHQHPD ATLDNKTRWQ VITDASVEVG PALFISLLII TLSFIPIFTL EGQEG RLFG PLAFTKTYAM AGAALLAIVV IPILMGYWIR GKIPPESSNP LNRFLIRVYH PLLLKVLHWP KTTLLVAALS VLTVLW PLN KVGGEFLPQI NEGDLLYMPS TLPGISAAEA ASMLQKTDKL IMSVPEVARV FGKTGKAETA TDSAPLEMVE TTIQLKP QE QWRPGMTMDK IIEELDNTVR LPGLANLWVP PIRNRIDMLS TGIKSPIGIK VSGTVLADID AMAEQIEEVA RTVPGVAS A LAERLEGGRY INVEINREKA ARYGMTVADV QLFVTSAVGG AMVGETVEGI ARYPINLRYP QSWRDSPQAL RQLPILTPM KQQITLADVA DIKVSTGPSM LKTENARPTS WIYIDARDRD MVSVVHDLQK AIAEKVQLKP GTSVAFSGQF ELLERANHKL KLMVPMTLM IIFVLLYLAF RRVGEALLII SSVPFALVGG IWLLWWMGFH LSVATGTGFI ALAGVAAEFG VVMLMYLRHA I EAVPSLNN PQTFSEQKLD EALYHGAVLR VRPKAMTVAV IIAGLLPILW GTGAGSEVMS RIAAPMIGGM ITAPLLSLFI IP AAYKLMW LHRHRVRK UniProtKB: Cation efflux system protein CusA |
-Macromolecule #2: COPPER (I) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: COPPER (I) ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: CU1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.546 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CU1: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.5 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 3452 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7kf6: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)