+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21513 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Pig Ryanodine Receptor (WT) in 5mM EGTA condition | |||||||||
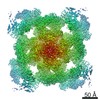
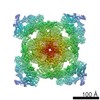
 Map data Map data | Final map from cryoSPARC | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | receptor / calcium / channel / complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-ISOMERASE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / response to redox state / negative regulation of heart rate / 'de novo' protein folding / FK506 binding ...: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / response to redox state / negative regulation of heart rate / 'de novo' protein folding / FK506 binding / smooth muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Ion homeostasis / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein maturation / peptidylprolyl isomerase / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium channel regulator activity / calcium-mediated signaling / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / protein refolding / transmembrane transporter binding / signaling receptor binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Woll KW / Haji-Ghassemi O | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Pathological conformations of disease mutant Ryanodine Receptors revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Kellie A Woll / Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Filip Van Petegem /  Abstract: Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and ...Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and arrhythmias. Here, we explore the first MH mutation identified in humans by providing cryo-EM snapshots of the pig homolog, R615C, showing that it affects an interface between three solenoid regions. We also show the impact of apo-calmodulin (apoCaM) and how it can induce opening by bending of the bridging solenoid, mediated by its N-terminal lobe. For R615C RyR1, apoCaM binding abolishes a pathological 'intermediate' conformation, distributing the population to a mixture of open and closed channels, both different from the structure without apoCaM. Comparisons show that the mutation primarily affects the closed state, inducing partial movements linked to channel activation. This shows that disease mutations can cause distinct pathological conformations of the RyR and facilitate channel opening by disrupting interactions between different solenoid regions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21513.map.gz emd_21513.map.gz | 398.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21513-v30.xml emd-21513-v30.xml emd-21513.xml emd-21513.xml | 25.1 KB 25.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21513.png emd_21513.png | 200.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21513.cif.gz emd-21513.cif.gz | 8.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_21513_additional_1.map.gz emd_21513_additional_1.map.gz emd_21513_additional_2.map.gz emd_21513_additional_2.map.gz emd_21513_half_map_1.map.gz emd_21513_half_map_1.map.gz emd_21513_half_map_2.map.gz emd_21513_half_map_2.map.gz | 38.4 MB 57.5 MB 390.4 MB 390.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21513 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21513 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21513 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21513 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6w1nMC  6x32C  6x33C  6x34C  6x35C  6x36C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21513.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21513.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
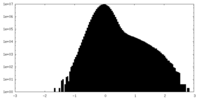
| Annotation | Final map from cryoSPARC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.37083 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Density modified map obtained from PHENIX Resolve
| File | emd_21513_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density modified map obtained from PHENIX Resolve | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
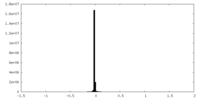
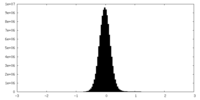
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: composite map made from focused (masked) refinements conducted...
| File | emd_21513_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | composite map made from focused (masked) refinements conducted in RELION | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
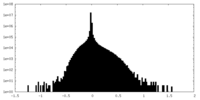
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_21513_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
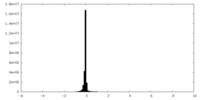
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_21513_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
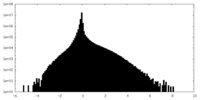
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex
| Entire | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: ryanodine receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: FKBP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: FKBP1B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.939562 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SNAGVEIETI SPGDGRTFPK KGQTCVVHYT GMLQNGKKFD SSRDRNKPFK FRIGKQEVIK GFEEGAAQMS LGQRAKLTCT PDVAYGATG HPGVIPPNAT LIFDVELLNL E UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine Receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine Receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 510.786406 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MGDGGEGEDE VQFLRTDDEV VLQCNATVLK EQLKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE PTSNAQNVPP DLAICCFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEAG VESSQGGGHR TLLYGHAILL RHAHSGMYLS CLTTSRSMTD KLAFDVGLQE DATGEACWWT THPASKQRSE G EKVRVGDD ...String: MGDGGEGEDE VQFLRTDDEV VLQCNATVLK EQLKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE PTSNAQNVPP DLAICCFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEAG VESSQGGGHR TLLYGHAILL RHAHSGMYLS CLTTSRSMTD KLAFDVGLQE DATGEACWWT THPASKQRSE G EKVRVGDD LILVSVSSER YLHLSTASGE LQVDASFMQT LWNMNPICSG CEEGYVTGGH VLRLFHGHMD ECLTISPADS DD QRRLVYY EGGSVCTHAR SLWRLEPLRI SWSGSHLRWG QPLRIRHVTT GRYLALIEDQ GLVVVDASKA HTKATSFCFR ISK EKLDTA PKRDVEGMGP PEIKYGESLC FVQHVASGLW LTYAAPDPKA LRLGVLKKKA ILHQEGHMDD ALSLTRCQQE ESQA ARMIY STAGLYNHFI KGLDSFSGKP RGSGAPAGTA LPLEGVILSL QDLIGYFEPP SEELQHEEKQ SKLRSLRNRQ SLFQE EGML SLVLNCIDRL NVYTTAAHFA EFAGEEAAES WKEIVNLLYE ILASLIRGNR ANCALFSNNL DWLVSKLDRL EASSGI LEV LYCVLIESPE VLNIIQENHI KSIISLLDKH GRNHKVLDVL CSLCVCNGVA VRSNQDLITE NLLPGRELLL QTNLINY VT SIRPNIFVGR AEGTTQYSKW YFEVMVDEVV PFLTAQATHL RVGWALTEGY SPYPGGGEGW GGNGVGDDLY SYGFDGLH L WTGHVPRLVT SPGQHLLAPE DVVSCCLDLS VPSISFRING CPVQGVFEAF NLNGLFFPVV SFSAGVKVRF LLGGRHGEF KFLPPPGYAP CHEAVLPRER LRLEPIKEYR REGPRGPHLV GPSRCLSHTD FVPCPVDTVQ IVLPPHLERI REKLAENIHE LWALTRIEQ GWTYGPVRDD NKRLHPCLVD FHSLPEPERN YNLQMSGETL KTLLALGCHV GMADEKAEDN LRKTKLPKTY M MSNGYKPA PLDLSHVRLT PAQTTLVDRL AENGHNVWAR DRVAQGWSYS AVQDIPARRN PRLVPYRLLD EATKRSNRDS LC QAVRTLL GYGYNIEPPD QEPSQVESQS RWDRVRIFRA EKSYAVQSGR WYFEFEAVTT GEMRVGWARP ELRPDVELGA DEL AYVFNG HRGQRWHLGS ELFGRPWQSG DVVGCMIDLT ENTIIFTLNG EVLMSDSGSE TAFRDIEVGD GFLPVCSLGP GQVG HLNLG QDVSSLRFFA ICGLQEGFEP FAINMQRPVT TWFSKSLPQF EAVPLEHPHY EVSRVDGTVD TPPCLRLTHR TWGSQ NSLV EMLFLRLSLP VQFHQHFRCT AGATPLAPPG LQPPAEDEAR AAEPDPDYEN LRRSAGRWGE AEGGKEGTAK EGAPGG TAQ AGVEAQPPRA ENEKDATTEK NKKRGFLFKA KKAAMMTQPP ATPTLPRLPH EVVPADDRDD PDIILNTTTY YYSVRVF AG QEPSCVWVGW VTPDYHQHDM NFDLTKVRAV TVTMGDEQGN IHSSLKCSNC YMVWGGDFVS PGQQGRISHT DLVIGCLV D LATGLMTFTA NGKESNTFFQ VEPNTKLFPA VFVLPTHQNV IQFELGKQKN IMPLSAAMFL SERKNPAPQC PPRLEMQML MPVSWSRMPN HFLRVETRRA GERLGWAVQC QEPLTMMALH IPEENRCMDI LELSERLDLQ QFHSHTLRLY RAVCALGNNR VAHALCSHV DQAQLLHALE DAHLPGPLRA GYYDLLISIH LESACRSRRS MLSEYIVPLT PETRAITLFP PGKRTENGPR R HGLPGVGV TTSLRPPHHF SAPCFVAALP AVGAAEAPAR LSPSIPLEAL RDKALRMLGE AVRDGGQHAR DPVGGSVEFQ FV PVLKLVS TLLVMGIFGD EDVKQILKMI EPEVFTEEEE EEEEEEEEEE EDEEEKEEDE EEEAREKEDE EKEEEETAEG EKE EYLEEG LLQMKLPESV KLQMCNLLEY FCDQELQHRV ESLAAFAERY VDKLQANQRD RYGILMKAFT MTAAETARRT REFR SPPQE QINMLLHFKD GEDEEDCPLP DEIRQDLLEF HQDLLTHCGI QLEGEEEEPE EEATLGSRLM SLLEKVRLVK KKEEK SEEE PPAEESKLQS LQELVSHTVV RWAQEDFVQS PELVRAMFSL LHRQYDGLGE LLRALPRAYT ISPSSVEDTM SLLECL GQI RSLLIVQMGP QEENLMIQSI GNIMNNKVFY QHPNLMRALG MHETVMEVMV NVLGGGESKE IRFPKMVTSC CRFLCYF CR ISRQNQRSMF DHLSYLLENS GIGLGMQGST PLDVAAASVI DNNELALALQ EQDLEKVVSY LAGCGLQSCP MLLAKGYP D IGWNPCGGER YLDFLRFAVF VNGESVEENA NVVVRLLIRK PECFGPALRG EGGSGLLATI EEAIRISEDP ARDGPGVRR DRRREHFGEE PPEENRVHLG HAIMSFYAAL IDLLGRCAPE MHLIQAGKGE ALRIRAILRS LVPLDDLVGI ISLPLQIPTL GKDGALVQP KMSASFVPDH KASMVLFLDR VYGIENQDFL LHVLDVGFLP DMRAAASLDT ATFSTTEMAL ALNRYLCLAV L PLITKCAP LFAGTEHRAI MVDSMLHTVY RLSRGRSLTK AQRDVIEECL MALCRYIRPS MLQHLLRRLV FDVP(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)DPRPVET LNVIIPEK L DSFINKFAEY THEKWAFDKI QNNWSYGENI DEELKTHPML RPYKTFSEKD KEIYRWPIKE SLKAMIAWEW TIEKAREGE EEKTEKKKTR KISQSAQTYD AREGYNPQPP DLSGVTLSRE LQAMAEQLAE NYHNTWGRKK KQELEAKGGG THPLLVPYDT LTAKEKARD REKAQELLKF LQMNGYAVTR (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)PLLIRYV DNNRAHWLTE PNPSAEELFR MVGEIFIYWS K(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) SLRWQMALYR GLPGREEDA DDPEKIVRRV QEVSAVLYHL EQMEHPYKSK (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)MTPLYNLP THRACNM FL ESYKAAWILT EDHSFEDRMI DDLSKAGEQE EEEEEVEEKK PDPLHQLVLH FSRTALTEKS KLDEDYLYMA YADIMAKS C HLEEGGENGE AQEEVEVSFE EKEMEKQRLL YQQARLHNRG AAEMVLQMIS ACKGETGAMV SSTLKLGISI LNGGNADVQ QKMLDYLKDK KEVGFFQSIQ ALMQTCSVLD LNAFERQNKA EGLGMVNEDG TVINRQNGEK VMADDEFTQD LFRFLQLLCE GHNNDFQNY LRTQTGNTTT INIIICTVDY LLRLQESISD FYWYYSGKDV IEEQGKRNFS KAMSVAKQVF NSLTEYIQGP C TGNQQSLA HSRLWDAVVG FLHVFAHMMM KLAQDSSQIE LLKELLDLQK DMVVMLLSLL EGNVVNGMIA RQMVDMLVES SS NVEMILK FFDMFLKLKD IVGSEAFQDY VTDPRGLISK KDFQK(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)EEFANRFQ EPARDIGFNV AVLLTNLSEH VPHDPRLRNF LELAESILEY FRPYLGRIEI MGASRRIERI YFEISETNRA QWEMPQVKES KRQFIFDVV NEGGESEKME LFVSFCEDTI FEMQIAAQIS EPEGEPEEDE DEGAGLAEAG AEGAEEGAVG PEGAAGTAAA G LTARLAAA TSRALRGLSY RSLRRRVRRL RRLTAREAAT ALAALLWAAL AHAGAAGAGA AAGALRLLWG SLFGGGLVEG AK KVTVTEL LAGMPDPTGD EVHGEQPAGP GGEADGEGAG EGAGEAWEGA GDEEVAVQEA GPGGADGAVA VAEGGPFRPE GAG GLGDMG DTTPAEPPTP EGSPIIKRKL GVDGEEEELP PEPEPEPEPE PEKADAENGE KEEVPKPPPE PPKKTAPPPP PPKK EEGGS GGLEFWGELE VQRVKFLNYL SRNFYTLRFL ALFLAFAINF ILLFYKVSDS PPGEDDMEGS AAGDLSGAGS GGGSG WGSG AGEEVEGDED ENMVYYFLEE STGYMEPALR CLSLLHTLVA FLCIIGYNCL KVPLVIFKRE KELARKLEFD GLYITE QPE DDDVKGQWDR LVLNTPSFPS NYWDKFVKRK VLDKHGDIYG RERIAELLGM DLATLEITAH NERKPEPPPG LLTWLMS ID VKYQIWKFGV IFTDNSFLYL GWYMVMSLLG HYNNFFFAAH LLDIAMGVKT LRTILSSVTH NGKQLVMTVG LLAVVVYL Y TVVAFNFFRK FYNKSEDEDE PDMKCDDMMT CYLFHMYVGV RAGGGIGDEI EDPAGDEYEL YRVVFDITFF FFVIVILLA IIQGLIIDAF GELRDQQEQV REDMETKCFI CGIGSDYFDT TPHRFETHTL EEHNLANYMF FLMYLINKDE TEHTGQESYV WKMYQERCW DFFPAGDCFR KQYEDQLS |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C4 (4 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: PHENIX (ver. dev-3714) / Number images used: 52289 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




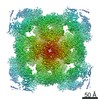











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)