+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22017 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
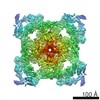
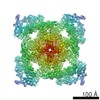
| Title | Pig R615C RyR1 EGTA (all classes, open) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | RyR1, FKBP12.6 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | receptor / calcium / channel / complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-ISOMERASE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / response to redox state / negative regulation of heart rate / 'de novo' protein folding / FK506 binding ...: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / response to redox state / negative regulation of heart rate / 'de novo' protein folding / FK506 binding / smooth muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Ion homeostasis / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein maturation / peptidylprolyl isomerase / calcium channel regulator activity / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / protein refolding / transmembrane transporter binding / signaling receptor binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Woll KW / Haji-Ghassemi O | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Pathological conformations of disease mutant Ryanodine Receptors revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Kellie A Woll / Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Filip Van Petegem /  Abstract: Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and ...Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and arrhythmias. Here, we explore the first MH mutation identified in humans by providing cryo-EM snapshots of the pig homolog, R615C, showing that it affects an interface between three solenoid regions. We also show the impact of apo-calmodulin (apoCaM) and how it can induce opening by bending of the bridging solenoid, mediated by its N-terminal lobe. For R615C RyR1, apoCaM binding abolishes a pathological 'intermediate' conformation, distributing the population to a mixture of open and closed channels, both different from the structure without apoCaM. Comparisons show that the mutation primarily affects the closed state, inducing partial movements linked to channel activation. This shows that disease mutations can cause distinct pathological conformations of the RyR and facilitate channel opening by disrupting interactions between different solenoid regions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22017.map.gz emd_22017.map.gz | 398.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22017-v30.xml emd-22017-v30.xml emd-22017.xml emd-22017.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22017.png emd_22017.png | 185.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22017.cif.gz emd-22017.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_22017_additional_1.map.gz emd_22017_additional_1.map.gz emd_22017_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22017_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22017_half_map_2.map.gz emd_22017_half_map_2.map.gz | 36.7 MB 390.4 MB 390.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22017 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22017 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22017 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22017 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6x34MC  6w1nC  6x32C  6x33C  6x35C  6x36C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22017.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22017.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RyR1, FKBP12.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
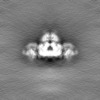
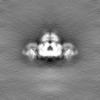
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
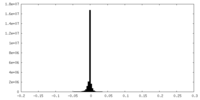
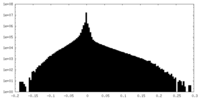
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Density modified map generated from PHENIX Resolve
| File | emd_22017_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density modified map generated from PHENIX Resolve | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
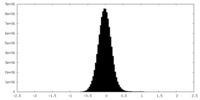
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_22017_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
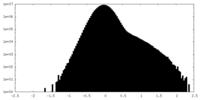
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_22017_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex
| Entire | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: ryanodine receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: FKBP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: FKBP1B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.538191 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GVEIETISPG DGRTFPKKGQ TCVVHYTGML QNGKKFDSSR DRNKPFKFRI GKQEVIKGFE EGAAQMSLGQ RAKLTCTPDV AYGATGHPG VIPPNATLIF DVELLNL UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine Receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine Receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 414.496875 KDa |
| Sequence | String: FLRTDDEVVL QCNATVLKEQ LKLCLAAEGF GNRLCFLEPT SNAQNVPPDL AICCFVLEQS LSVRALQEML ANGHRTLLYG HAILLRHAH SGMYLSCLTT SRSMTDKLAF DVGLQEDATG EACWWTTHPA SKQRSEGEKV RVGDDLILVS VSSERYLHLS T ASGELQVD ...String: FLRTDDEVVL QCNATVLKEQ LKLCLAAEGF GNRLCFLEPT SNAQNVPPDL AICCFVLEQS LSVRALQEML ANGHRTLLYG HAILLRHAH SGMYLSCLTT SRSMTDKLAF DVGLQEDATG EACWWTTHPA SKQRSEGEKV RVGDDLILVS VSSERYLHLS T ASGELQVD ASFMQTLWNM NPICSGCEEG YVTGGHVLRL FHGHMDECLT ISPADSDDQR RLVYYEGGSV CTHARSLWRL EP LRISWSG SHLRWGQPLR IRHVTTGRYL ALIEDQGLVV DASKAHTKAT SFCFRISKEK LKRDVEGMGP PEIKYGESLC FVQ HVASGL WLTYAALKKK AILHQEGHMD DALSLTRCQQ EESQAARMIY STAGLYNHFI KGLDSFSGKP RGSGAPAGTA LPLE GVILS LQDLIGYFEP PSEELQHEEK QSKLRSLRNR QSLFQEEGML SLVLNCIDRL NVYTTAAHFA EFAGEEAAES WKEIV NLLY EILASLIRGN RANCALFSNN LDWLVSKLDR LEASSGILEV LYCVLIESPE VLNIIQENHI KSIISLLDKH GRNHKV LDV LCSLCVCNGV AVCSNQDLIT ENLLPGRELL LQTNLINYVT SIRPNIFVGR AEGTTQYSKW YFEVMVDEVV PFLTAQA TH LRVGWALTEG YSPYPGGGEG WGGNGVGDDL YSYGFDGLHL WTGHVPRLVT SPGQHLLAPE DVVSCCLDLS VPSISFRI N GCPVQGVFEA FNLNGLFFPV VSFSAGVKVR FLLGGRHGEF KFLPPPGYAP CHEAVLPRER LRLEPIKEYR REGPRGPHL VGPSRCLSHT DFVPCPLPPH LERIREKLAE NIHELWALTR IEQGWTYGPV RDDNKRLHPC LVDFHSLPEP ERNYNLQMSG ETLKTLLAL GCHVGMADEK AEDNLRKTKL PKTYMMSNGY KPAPLDAQTT LVDRLAENGH NVWARDRVAQ GWSYSAVQDI P ARRNPRLV PYRLLDEATK RSNRDSLCQA VRTLLGYGYN IERVRIFRAE KSYAVQSGRW YFEFEAVTTG EMRVGWARPE LR PDVELGA DELAYVFNGH RGQRWHLGSE LFGRPWQSGD VVGCMIDLTE NTIIFTLNGE VLMSDSGSET AFRDIEVGDG FLP VCSLGP GQVGHLNLGQ DVSSLRFFAI CGLQEGFEPF AINMQRPVTT WFSKSLPQFE AVPLEHPHYE VSRVDGTVDT PPCL RLTHR SLVEMLFLRL SLPVQFHQLN TTTYYYSVRV FAGQEPSCVW VGWVTPDYHQ HDMNFDLTKV RAVTVTMGDN IHSSL KCSN CYMVWGGDFV SHTDLVIGCL VDLATGLMTF TANGKESNTF FQVEPNTKLF PAVFVLPTHQ NVIQFELGKQ KNIMPL SAA MFLSERKNPA PQCPPRLEMQ MLMPVSWSRM PNHFLRVETR RAGERLGWAV PLTMMALHIP EENRCMDILE LSERLDL QQ FHSHTLRLYR AVCALGNNRV AHALCSHVDQ AQLLHALEDA HLPGPLRAGY YDLLISIHLE SACRSRRSML SEYIVPLT P ETRAITLFPP RHGLPGVGVT TSLRPPHHFS APCFVAALPE APARLSPSIP LEALRDKALR MLGEAVRDGG QHARDPVGG SVEFQFVPVL KLVSTLLVMG IFGDEDVKQI LKMIEPEVEE GLLQMKLPES VKLQMCNLLE YFCDQELQHR VESLAAFAER YVDKLQANQ RDRYGILMKA FTMTAAETAR RTREFRSPPQ EQINMLLHFK PLPDEIRQDL LEFHQDLLTH CGIQLQSLQE L VSHTVVRW AQEDFVQSPE LVRAMFSLLH RQYDGLGELL RALPRAYTIS PSSVEDTMSL LECLGQIRSL LIVQMGPQEE NL MIQSIGN IMNNKVFYQH PNLMRALGMH ETVMEVMVNV LRFPKMVTSC CRFLCYFCRI SRQNQRSMFD HLSYLLENSG STP LDVAAA SVIDNNELAL ALQEQDLEKV VSYLAGCGLQ SCPMLLAKGY PDIGWNPCGG ERYLDFLRFA VFVNGESVEE NANV VVRLL IRKPECFGPA LRLLATIEEA IAIMSFYAAL IDLLGRCAPE MHLIQAGKGE ALRIRAILRS LVPLDDLVGI ISLPL QIPT MSASFVPDHK ASMVLFLDRV YGFLLHVLDV GFALALNRYL CLAVLPLITK CAPLFAMVDS MLHTVYRLSR GRSLTK AQR DVIEECLMAL CRYIRPSMLQ HLLRRLVF(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)DPR PVETLNVIIP EKLDSFINKF AEYTHEKWAF DKIQNNWSYG ENIDEELKTH PM LRPYKTF SEKDKEIYRW PIKESLKAMI AWEWTIEKAR EGEYNPQPPD LSGVTLSREL QAMAEQLAEN YHNTWGRKKK QEL EAKGGG THPLLVPYDT LTAKEKARDR EKAQELLKFL QMNGYAVTR(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)EFSVLCRDL YALYPLLIRY VDNNRAHWLT E PNPSAEEL FRMVGEIFIY WSKSKHNFKR EEQNFVV(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)P LYNLPTHRAC NMFLESYKAA WILT EDHSF EDRMIDDLSK AKKPDPLHQL VLHFSRTALT EKSKLDEDYL YMAYADIMAK SCHLSFEEKE MEKQRLLYQQ ARLHN RGAA EMVLQMISAC KGETGAMVSS TLKLGISILN GGNADVQQKM LDYLKDKKEV GFFQSIQALM QTCSVLDLNA FERQNK AEG LGEKVMADDE FTQDLFRFLQ LLCEGHNNDF QNYLRTQTGN TTTINIIICT VDYLLRLQES ISDFYWYYSG KDVIEEQ GK RNFSKAMSVA KQVFNSLTEY IQGPCTGNQQ SLAHSRLWDA VVGFLHVFAH MMMKLAQDSS QIELLKELLD LQKDMVVM L LSLLEGNVVN GMIARQMVDM LVESSSNVEM ILKFFDMFLK LKDIVGSEAF QDYVTDPRGL ISKKDFQK(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)EFANR FQEPARDIGF NVAVLLTNLS EHVPHDPRLR NFLELAESIL EYFRPYLGRI EIMGA SRRI ERIYFEISET NRAQWEMPQV KESKRQFIFD VVNEGGESEK MELFVSFCED TIFEEVQRVK FLNYLSRNFY TLRFLA LFL AFAINFILLF YKVSDSPVYY FLEESTGYME PALRCLSLLH TLVAFLCIIG YNCLKVPLVI FKREKELARK LEFDGLY IT EQPVKGQWDR LVLNTPSFPS NYWDKFVKRK VLDKHGDIYG RERIAEGLLT WLMSIDVKYQ IWKFGVIFTD NSFLYLGW Y MVMSLLGHYN NFFFAAHLLD IAMGVKTLRT ILSSVTHNGK QLVMTVGLLA VVVYLYTVVA FNFFRKFYNK SEDEDEPDM KCDDMMTCYL FHMYVGVRAG GGIGDEIEDP AGDEYELYRV VFDITFFFFV IVILLAIIQG LIIDAFGELR DQQEQVREDM ETKCFICGI GSDYFDTTPH RFETHTLEEH NLANYMFFLM YLINKDETEH TGQESYVWKM YQERCWDFFP AGDCFRKQ |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: PHENIX (ver. dev-3714) / Number images used: 58822 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)