[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-22016: Wt pig RyR1 in complex with apoCaM, EGTA condition (class 3, open) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22016 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Wt pig RyR1 in complex with apoCaM, EGTA condition (class 3, open) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | RyR1, FKBP12.6, CaM | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | receptor / calcium / channel / complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-ISOMERASE-CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / CaM pathway / response to redox state / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers ...: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / CaM pathway / response to redox state / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / negative regulation of heart rate / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / 'de novo' protein folding / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / FK506 binding / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / smooth muscle contraction / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / regulation of cytokinesis / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / spindle microtubule / protein maturation / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / peptidylprolyl isomerase / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / spindle pole / Signaling by RAF1 mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Woll KW / Haji-Ghassemi O | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Pathological conformations of disease mutant Ryanodine Receptors revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Kellie A Woll / Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Filip Van Petegem /  Abstract: Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and ...Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and arrhythmias. Here, we explore the first MH mutation identified in humans by providing cryo-EM snapshots of the pig homolog, R615C, showing that it affects an interface between three solenoid regions. We also show the impact of apo-calmodulin (apoCaM) and how it can induce opening by bending of the bridging solenoid, mediated by its N-terminal lobe. For R615C RyR1, apoCaM binding abolishes a pathological 'intermediate' conformation, distributing the population to a mixture of open and closed channels, both different from the structure without apoCaM. Comparisons show that the mutation primarily affects the closed state, inducing partial movements linked to channel activation. This shows that disease mutations can cause distinct pathological conformations of the RyR and facilitate channel opening by disrupting interactions between different solenoid regions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22016.map.gz emd_22016.map.gz | 57.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22016-v30.xml emd-22016-v30.xml emd-22016.xml emd-22016.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22016.png emd_22016.png | 209.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22016.cif.gz emd-22016.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22016 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22016 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22016 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22016 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6x33MC  6w1nC  6x32C  6x34C  6x35C  6x36C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22016.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22016.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RyR1, FKBP12.6, CaM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-Calmodulin complex
| Entire | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-Calmodulin complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-Calmodulin complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-Calmodulin complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: ryanodine receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: FKBP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: FKBP1B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: Calmodulin
| Supramolecule | Name: Calmodulin / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.667305 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GVEIETISPG DGRTFPKKGQ TCVVHYTGML QNGKKFDSSR DRNKPFKFRI GKQEVIKGFE EGAAQMSLGQ RAKLTCTPDV AYGATGHPG VIPPNATLIF DVELLNLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine Receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine Receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 425.09225 KDa |
| Sequence | String: QFLRTDDEVV LQCNATVLKE QLKLCLAAEG FGNRLCFLEP TSNAQNVPPD LAICCFVLEQ SLSVRALQEM LANGHRTLLY GHAILLRHA HSGMYLSCLT TSRSMTDKLA FDVGLQEDAT GEACWWTTHP ASKQRSEGEK VRVGDDLILV SVSSERYLHL S TASGELQV ...String: QFLRTDDEVV LQCNATVLKE QLKLCLAAEG FGNRLCFLEP TSNAQNVPPD LAICCFVLEQ SLSVRALQEM LANGHRTLLY GHAILLRHA HSGMYLSCLT TSRSMTDKLA FDVGLQEDAT GEACWWTTHP ASKQRSEGEK VRVGDDLILV SVSSERYLHL S TASGELQV DASFMQTLWN MNPICSGCEE GYVTGGHVLR LFHGHMDECL TISPADSDDQ RRLVYYEGGS VCTHARSLWR LE PLRISWS GSHLRWGQPL RIRHVTTGRY LALIEDQGLV VVDASKAHTK ATSFCFRISK EKLKRDVEGM GPPEIKYGES LCF VQHVAS GLWLTYAALK KKAILHQEGH MDDALSLTRC QQEESQAARM IYSTAGLYNH FIKGLDSFSG KPRGSGAPAG TALP LEGVI LSLQDLIGYF EPPSEELQHE EKQSKLRSLR NRQSLFQEEG MLSLVLNCID RLNVYTTAAH FAEFAGEEAA ESWKE IVNL LYEILASLIR GNRANCALFS NNLDWLVSKL DRLEASSGIL EVLYCVLIES PEVLNIIQEN HIKSIISLLD KHGRNH KVL DVLCSLCVCN GVAVRSNQDL ITENLLPGRE LLLQTNLINY VTSIRPNIFV GRAEGTTQYS KWYFEVMVDE VVPFLTA QA THLRVGWALT EGYSPYPGGG EGWGGNGVGD DLYSYGFDGL HLWTGHVPRL VTSPGQHLLA PEDVVSCCLD LSVPSISF R INGCPVQGVF EAFNLNGLFF PVVSFSAGVK VRFLLGGRHG EFKFLPPPGY APCHEAVLPR ERLRLEPIKE YRREGPRGP HLVGPSRCLS HTDFVPCHLE RIREKLAENI HELWALTRIE QGWTYGPVRD DNKRLHPCLV DFHSLPEPER NYNLQMSGET LKTLLALGC HVGMADEKAE DNLRKTKLPK TYMMSNGYKP APLDLSHVRL TPAQTTLVDR LAENGHNVWA RDRVAQGWSY S AVQDIPAR RNPRLVPYRL LDEATKRSNR DSLCQAVRTL LGYGYNIERV RIFRAEKSYA VQSGRWYFEF EAVTTGEMRV GW ARPELRP DVELGADELA YVFNGHRGQR WHLGSELFGR PWQSGDVVGC MIDLTENTII FTLNGEVLMS DSGSETAFRD IEV GDGFLP VCSLGPGQVG HLNLGQDVSS LRFFAICGLQ EGFEPFAINM QRPVTTWFSK SLPQFEAVPL EHPHYEVSRV DGTV DTPPC LRLTHRSLVE MLFLRLSLPV QFHQLNTTTY YYSVRVFAGQ EPSCVWVGWV TPDYHQHDMN FDLTKVRAVT VTMGD NIHS SLKCSNCYMV WGGDFVSHTD LVIGCLVDLA TGLMTFTANG KESNTFFQVE PNTKLFPAVF VLPTHQNVIQ FELGKQ KNI MPLSAAMFLS ERKNPAPQCP PRLEMQMLMP VSWSRMPNHF LRVETRRAGE RLGWAVQCQE PLTMMALHIP EENRCMD IL ELSERLDLQQ FHSHTLRLYR AVCALGNNRV AHALCSHVDQ AQLLHALEDA HLPGPLRAGY YDLLISIHLE SACRSRRS M LSEYIVPLTP ETRAITLFPP RHGLPGVGVT TSLRPPHHFS APCFVAALPE APARLSPSIP LEALRDKALR MLGEAVRDG GQHARDPVGG SVEFQFVPVL KLVSTLLVMG IFGDEDVKQI LKMIEPEVEE GLLQMKLPES VKLQMCNLLE YFCDQELQHR VESLAAFAE RYVDKLQANQ RDRYGILMKA FTMTAAETAR RTREFRSPPQ EQINMLLHFK PLPDEIRQDL LEFHQDLLTH C GIQLQSLQ ELVSHTVVRW AQEDFVQSPE LVRAMFSLLH RQYDGLGELL RALPRAYTIS PSSVEDTMSL LECLGQIRSL LI VQMGPQE ENLMIQSIGN IMNNKVFYQH PNLMRALGMH ETVMEVMVNV LRFPKMVTSC CRFLCYFCRI SRQNQRSMFD HLS YLLENS GGMQGSTPLD VAAASVIDNN ELALALQEQD LEKVVSYLAG CGLQSCPMLL AKGYPDIGWN PCGGERYLDF LRFA VFVNG ESVEENANVV VRLLIRKPEC FGPALRGEGG SGLLATIEEA IHLGHAIMSF YAALIDLLGR CAPEMHLIQA GKGEA LRIR AILRSLVPLD DLVGIISLPL QIPMSASFVP DHKASMVLFL DRVYGIENQD FLLHVLDVGF LPDMRAAALA LNRYLC LAV LPLITKCAPL FAMVDSMLHT VYRLSRGRSL TKAQRDVIEE CLMALCRYIR PSMLQHLLRR LVF(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)DPRPVETL NVIIPEKLDS FI NKFAEYT HEKWAFDKIQ NNWSYGENID EELKTHPMLR PYKTFSEKDK EIYRWPIKES LKAMIAWEWT IEKAREGEYN PQP PDLSGV TLSRELQAMA EQLAENYHNT WGRKKKQELE AKGGGTHPLL VPYDTLTAKE KARDREKAQE LLKFLQMNGY AVTR (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)F SVLCRDLYAL YPLL IRYVD NNRAHWLTEP NPSAEELFRM VGEIFIYWSK SHNFKREEQN FVV(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)HKLLS KQRRR AVVA CFRMTPLYNL PTHRACNMFL ESYKAAWILT EDHSFEDRMI DDLSKAGEQE EEEEEVEEKK PDPLHQLVLH FSRTAL TEK SKLDEDYLYM AYADIMAKSC HLEESFEEKE MEKQRLLYQQ ARLHNRGAAE MVLQMISACK GETGAMVSST LKLGISI LN GGNADVQQKM LDYLKDKKEV GFFQSIQALM QTCSVLDLNA FERQNKAEGL GMVNEDGTVI GEKVMADDEF TQDLFRFL Q LLCEGHNNDF QNYLRTQTGN TTTINIIICT VDYLLRLQES ISDFYWYYSG KDVIEEQGKR NFSKAMSVAK QVFNSLTEY IQGPCTGNQQ SLAHSRLWDA VVGFLHVFAH MMMKLAQDSS QIELLKELLD LQKDMVVMLL SLLEGNVVNG MIARQMVDML VESSSNVEM ILKFFDMFLK LKDIVGSEAF QDYVTDPRGL ISKKDFQK(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)EFA NR FQEPARDIGF NVAVLLTNLS EHVPHDPRLR NFLELAESIL EYFRPYLGRI EIMGASRRIE RIYFEISETN RAQWEMPQ V KESKRQFIFD VVNEKMELFV SFCEDTIFEM QIAAQ(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)EVQRVKF LNYLSRNFYT LRFLALFLAF AINFILLF Y KVSDSPPVYY FLEESTGYME PALRCLSLLH TLVAFLCIIG YNCLKVPLVI FKREKELARK LEFDGLYITE QPEDDDVKG QWDRLVLNTP SFPSNYWDKF VKRKVLDKHG DIYGRERIAE IDVKYQIWKF GVIFTDNSFL YLGWYMVMSL LGHYNNFFFA AHLLDIAMG VKTLRTILSS VTHNGKQLVM TVGLLAVVVY LYTVVAFNFF RKFYNKMKCD DMMTCYLFHM YVGVRAGGGI G DEIEDPAG DEYELYRVVF DITFFFFVIV ILLAIIQGLI IDAFGELRDQ QEQVREDMET KCFICGIGSD YFDTTPHRFE TH TLEEHNL ANYMFFLMYL INKDETEHTG QESYVWKMYQ ERCWDFFPAG DCFRKQYEDQ L |
-Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.723365 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTA UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: PHENIX (ver. dev-3714) / Number images used: 25122 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




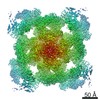

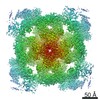



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)