+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
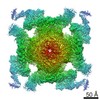
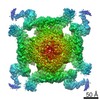
| Title | Pig R615C RyR1 in complex with CaM, EGTA (class 1, open) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | RyR1, FKBP12.6, CaM | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | receptor / calcium / channel / complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-ISOMERASE-CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / CaM pathway / response to redox state / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers ...: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / CaM pathway / response to redox state / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / negative regulation of heart rate / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / 'de novo' protein folding / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / FK506 binding / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / smooth muscle contraction / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of cytokinesis / protein maturation / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / peptidylprolyl isomerase / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Woll KW / Haji-Ghassemi O | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Pathological conformations of disease mutant Ryanodine Receptors revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Kellie A Woll / Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Filip Van Petegem /  Abstract: Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and ...Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) are massive channels that release Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Hundreds of mutations are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and arrhythmias. Here, we explore the first MH mutation identified in humans by providing cryo-EM snapshots of the pig homolog, R615C, showing that it affects an interface between three solenoid regions. We also show the impact of apo-calmodulin (apoCaM) and how it can induce opening by bending of the bridging solenoid, mediated by its N-terminal lobe. For R615C RyR1, apoCaM binding abolishes a pathological 'intermediate' conformation, distributing the population to a mixture of open and closed channels, both different from the structure without apoCaM. Comparisons show that the mutation primarily affects the closed state, inducing partial movements linked to channel activation. This shows that disease mutations can cause distinct pathological conformations of the RyR and facilitate channel opening by disrupting interactions between different solenoid regions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22018.map.gz emd_22018.map.gz | 54.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22018-v30.xml emd-22018-v30.xml emd-22018.xml emd-22018.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22018.png emd_22018.png | 214.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22018.cif.gz emd-22018.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22018 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22018 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22018 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22018 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6x35MC  6w1nC  6x32C  6x33C  6x34C  6x36C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22018.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22018.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RyR1, FKBP12.6, CaM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-calmodulin complex
| Entire | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-calmodulin complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-calmodulin complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor-FKBP1B-calmodulin complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: ryanodine receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: FKBP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: FKBP1B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: Calmodulin
| Supramolecule | Name: Calmodulin / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.939562 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SNAGVEIETI SPGDGRTFPK KGQTCVVHYT GMLQNGKKFD SSRDRNKPFK FRIGKQEVIK GFEEGAAQMS LGQRAKLTCT PDVAYGATG HPGVIPPNAT LIFDVELLNL E UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine Receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine Receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 423.654469 KDa |
| Sequence | String: QFLRTDDEVV LQCNATVLKE QLKLCLAAEG FGNRLCFLEP TSNAQNVPPD LAICCFVLEQ SLSVRALQEM LANGHRTLLY GHAILLRHA HSGMYLSCLT TSRSMTDKLA FDVGLQEDAT GEACWWTTHP ASKQRSEGEK VRVGDDLILV SVSSERYLHL S TASGELQV ...String: QFLRTDDEVV LQCNATVLKE QLKLCLAAEG FGNRLCFLEP TSNAQNVPPD LAICCFVLEQ SLSVRALQEM LANGHRTLLY GHAILLRHA HSGMYLSCLT TSRSMTDKLA FDVGLQEDAT GEACWWTTHP ASKQRSEGEK VRVGDDLILV SVSSERYLHL S TASGELQV DASFMQTLWN MNPICSGCEE GYVTGGHVLR LFHGHMDECL TISPADQRRL VYYEGGSVCT HARSLWRLEP LR ISWSGSH LRWGQPLRIR HVTTGRYLAL IEDQGLVVVD ASKAHTKATS FCFRISKEKL KRDVEGMGPP EIKYGESLCF VQH VASGLW LTYAALKKKA ILHQEGHMDD ALSLTRCQQE ESQAARMIYS TAGLYNHFIK GLDSFSGKPR PAGTALPLEG VILS LQDLI GYFEPPSEEL QHEEKQSKLR SLRNRQSLFQ EEGMLSLVLN CIDRLNVYTT AAHFAEFAGE EAAESWKEIV NLLYE ILAS LIRGNRANCA LFSNNLDWLV SKLDRLEASS GILEVLYCVL IESPEVLNII QENHIKSIIS LLDKHGRNHK VLDVLC SLC VCNGVAVCSN QDLITENLLP GRELLLQTNL INYVTSIRPN IFVGRAEGTT QYSKWYFEVM VDEVVPFLTA QATHLRV GW ALTEGYSPYP GGGEGWGGNG VGDDLYSYGF DGLHLWTGHV PRLVTSPGQH LLAPEDVVSC CLDLSVPSIS FRINGCPV Q GVFEAFNLNG LFFPVVSFSA GVKVRFLLGG RHGEFKFLPP PGYAPCHEAV LPRERLRLEP IKEYRREGPR GPHLVGPSR CLSHTDFVPC PLPPHLERIR EKLAENIHEL WALTRIEQGW TYGPVRDDNK RLHPCLVDFH SLPEPERNYN LQMSGETLKT LLALGCHVG MADEKAEDNL RKTKLPKTYM MSNGYKPAPL DLSHVRLTPA QTTLVDRLAE NGHNVWARDR VAQGWSYSAV Q DIPARRNP RLVPYRLLDE ATKRSNRDSL CQAVRTLLGY GRVRIFRAEK SYAVQSGRWY FEFEAVTTGE MRVGWARPEL RP DVELGAD ELAYVFNGHR GQRWHLGSEL FGRPWQSGDV VGCMIDLTEN TIIFTLNGEV LMSDSGSETA FRDIEVGDGF LPV CSLGPG QVGHLNLGQD VSSLRFFAIC GLQEGFEPFA INMQRPVTTW FSKSLPQFEA VPLEHPHYEV SRVDGTVDTP PCLR LTHRS LVEMLFLRLS LPVQFHQLNT TTYYYSVRVF AGQEPSCVWV GWVTPDYHQH DMNFDLTKVR AVTVTMGDNI HSSLK CSNC YMVWGGDFVS HTDLVIGCLV DLATGLMTFT ANGKESNTFF QVEPNTKLFP AVFVLPTHQN VIQFELGKQK NIMPLS AAM FLSERKNPAP QCPPRLEMQM LMPVSWSRMP NHFLRVETRR AGERLGWAVQ CQEPLTMMAL HIPEENRCMD ILELSER LD LQQFHSHTLR LYRAVCALGN NRVAHALCSH VDQAQLLHAL EDAHLPGPLR AGYYDLLISI HLESACRSRR SMLSEYIV P LTPETRAITL FPPRHGLPGV GVTTSLRPPH HFSAPCFVAA LPEAPARLSP SIPLEALRDK ALRMLGEAVR DGGQHARDP VGGSVEFQFV PVLKLVSTLL VMGIFGDEDV KQILKMIEPE VEEGLLQMKL PESVKLQMCN LLEYFCDQEL QHRVESLAAF AERYVDKLQ ANQRDRYGIL MKAFTMTAAE TARRTREFRS PPQEQINMLL HFKPLPDEIR QDLLEFHQDL LTHCGIQLQS L QELVSHTV VRWAQEDFVQ SPELVRAMFS LLHRQYDGLG ELLRALPRAY TISPSSVEDT MSLLECLGQI RSLLIVQMGP QE ENLMIQS IGNIMNNKVF YQHPNLMRAL GMHETVMEVM VNVLGRFPKM VTSCCRFLCY FCRISRQNQR SMFDHLSYLL ENS GSTPLD VAAASVIDNN ELALALQEQD LEKVVSYLAG CGLQSCPMLL AKGYPDIGWN PCGGERYLDF LRFAVFVNGE SVEE NANVV VRLLIRKPEC FGPALRLLAT IEEAIGHAIM SFYAALIDLL GRCAPEMHLI QAGKGEALRI RAILRSLVPL DDLVG IISL PLQIPLMSAS FVPDHKASMV LFLDRVYGIE FLLHVLDVGF EMALALNRYL CLAVLPLITK CAPLFAMVDS MLHTVY RLS RGRSLTKAQR DVIEECLMAL CRYIRPSMLQ HLLRRLVF(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)DPR PVETLNVIIP EKLDSFINKF AEYTHEKWAF DKIQNNWSYG EN IDEELKT HPMLRPYKTF SEKDKEIYRW PIKESLKAMI AWEWTIEKAR EGEYNPQPPD LSGVTLSREL QAMAEQLAEN YHN TWGRKK KQELEAKGGG THPLLVPYDT LTAKEKARDR EKAQELLKFL QMNGYAVTR(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)EFSVLCR DLYALYPLLI RYVDNNRAHW LTEPNPSAEE LFRMVGEI F IYWSKSHNFK REEQNFVV(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) RRAVVACFRM TPLYNLPTHR ACNMFLESYK AAWILTEDHS FEDRMIDDL SKAGEQEEEE EEVEEKKPDP LHQLVLHFSR TALTEKSKLD EDYLYMAYAD IMAKSCHLEE SFEEKEMEKQ R LLYQQARL HNRGAAEMVL QMISACKGET GAMVSSTLKL GISILNGGNA DVQQKMLDYL KDKKEVGFFQ SIQALMQTCS VL DLNAFER QNKAEGLGMV NEDGTVIGEK VMADDEFTQD LFRFLQLLCE GHNNDFQNYL RTQTGNTTTI NIIICTVDYL LRL QESISD FYWYYSGKDV IEEQGKRNFS KAMSVAKQVF NSLTEYIQGP CTGNQQSLAH SRLWDAVVGF LHVFAHMMMK LAQD SSQIE LLKELLDLQK DMVVMLLSLL EGNVVNGMIA RQMVDMLVES SSNVEMILKF FDMFLKLKDI VGSEAFQDYV TDPRG LISK KDFQK(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)EEFANRFQE PARDIGFNVA VLLTNLSEHV PHDPRLRNFL EL AESILEY FRPYLGRIEI MGASRRIERI YFEISETNRA QWEMPQVKES KRQFIFDVVN EGGESEKMEL FVSFCEDTIF EMQ (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)EVQRVKFL NYLSRNFYTL RFLALFLAFA INFILLFYKV SDSPPVYYFL EESTGYMEPA LRCLSLLHTL VAFLCII GY NCLKVPLVIF KREKELARKL EFDGLYITEQ PEDDDVKGQW DRLVLNTPSF PSNYWDKFVK RKVLDKHGDI YGRERIAE G LLTWLMSIDV KYQIWKFGVI FTDNSFLYLG WYMVMSLLGH YNNFFFAAHL LDIAMGVKTL RTILSSVTHN GKQLVMTVG LLAVVVYLYT VVAFNFFRKF YNKSEDEDEP DMKCDDMMTC YLFHMYVGVR AGGGIGDEIE DPAGDEYELY RVVFDITFFF FVIVILLAI IQGLIIDAFG ELRDQQEQVR EDMETKCFIC GIGSDYFDTT PHRFETHTLE EHNLANYMFF LMYLINKDET E HTGQESYV WKMYQERCWD FFPAGDCFRK QYEDQL |
-Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.723365 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTA UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: PHENIX (ver. dev-3714) / Number images used: 25122 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















