[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20927: Clostridium difficile binary toxin translocase CDTb tetradecamer ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20927 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
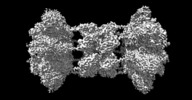
| Title | Clostridium difficile binary toxin translocase CDTb tetradecamer in symmetric conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | toxin translocase | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CDTb / translocase / tetradecamer / TOXIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein homooligomerization / transferase activity / extracellular region / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Clostridioides difficile (bacteria) Clostridioides difficile (bacteria) | |||||||||
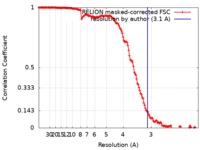
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu X / Pozharski E | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the cell-binding component of the binary toxin reveals a di-heptamer macromolecular assembly. Authors: Xingjian Xu / Raquel Godoy-Ruiz / Kaylin A Adipietro / Christopher Peralta / Danya Ben-Hail / Kristen M Varney / Mary E Cook / Braden M Roth / Paul T Wilder / Thomas Cleveland / Alexander ...Authors: Xingjian Xu / Raquel Godoy-Ruiz / Kaylin A Adipietro / Christopher Peralta / Danya Ben-Hail / Kristen M Varney / Mary E Cook / Braden M Roth / Paul T Wilder / Thomas Cleveland / Alexander Grishaev / Heather M Neu / Sarah L J Michel / Wenbo Yu / Dorothy Beckett / Richard R Rustandi / Catherine Lancaster / John W Loughney / Adam Kristopeit / Sianny Christanti / Jessica W Olson / Alexander D MacKerell / Amedee des Georges / Edwin Pozharski / David J Weber /  Abstract: Targeting infection is challenging because treatment options are limited, and high recurrence rates are common. One reason for this is that hypervirulent strains often have a binary toxin termed ...Targeting infection is challenging because treatment options are limited, and high recurrence rates are common. One reason for this is that hypervirulent strains often have a binary toxin termed the toxin, in addition to the enterotoxins TsdA and TsdB. The toxin has an enzymatic component, termed CDTa, and a pore-forming or delivery subunit termed CDTb. CDTb was characterized here using a combination of single-particle cryoelectron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, NMR, and other biophysical methods. In the absence of CDTa, 2 di-heptamer structures for activated CDTb (1.0 MDa) were solved at atomic resolution, including a symmetric (CDTb; 3.14 Å) and an asymmetric form (CDTb; 2.84 Å). Roles played by 2 receptor-binding domains of activated CDTb were of particular interest since the receptor-binding domain 1 lacks sequence homology to any other known toxin, and the receptor-binding domain 2 is completely absent in other well-studied heptameric toxins (i.e., anthrax). For CDTb, a Ca binding site was discovered in the first receptor-binding domain that is important for its stability, and the second receptor-binding domain was found to be critical for host cell toxicity and the di-heptamer fold for both forms of activated CDTb. Together, these studies represent a starting point for developing structure-based drug-design strategies to target the most severe strains of . | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
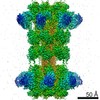
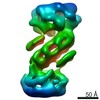
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20927.map.gz emd_20927.map.gz | 227 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20927-v30.xml emd-20927-v30.xml emd-20927.xml emd-20927.xml | 10.8 KB 10.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_20927_fsc.xml emd_20927_fsc.xml | 14.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_20927.png emd_20927.png | 127.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20927.cif.gz emd-20927.cif.gz | 5.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20927 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20927 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20927 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20927 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_20927_validation.pdf.gz emd_20927_validation.pdf.gz | 596.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_20927_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_20927_full_validation.pdf.gz | 595.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_20927_validation.xml.gz emd_20927_validation.xml.gz | 13.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_20927_validation.cif.gz emd_20927_validation.cif.gz | 18.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20927 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20927 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20927 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20927 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6uwtMC  6uwiC  6uwoC  6uwrC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20927.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20927.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | toxin translocase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CDTb tetradecamer
| Entire | Name: CDTb tetradecamer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CDTb tetradecamer
| Supramolecule | Name: CDTb tetradecamer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Clostridioides difficile (bacteria) Clostridioides difficile (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.05 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: ADP-ribosyltransferase binding component
| Macromolecule | Name: ADP-ribosyltransferase binding component / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 14 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Clostridioides difficile (bacteria) Clostridioides difficile (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 74.679086 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: LMSDWEDEDL DTDNDNIPDS YERNGYTIKD LIAVKWEDSF AEQGYKKYVS NYLESNTAGD PYTDYEKASG SFDKAIKTEA RDPLVAAYP IVGVGMEKLI ISTNEHASTD QGKTVSRATT NSKTESNTAG VSVNVGYQNG FTANVTTNYS HTTDNSTAVQ D SNGESWNT ...String: LMSDWEDEDL DTDNDNIPDS YERNGYTIKD LIAVKWEDSF AEQGYKKYVS NYLESNTAGD PYTDYEKASG SFDKAIKTEA RDPLVAAYP IVGVGMEKLI ISTNEHASTD QGKTVSRATT NSKTESNTAG VSVNVGYQNG FTANVTTNYS HTTDNSTAVQ D SNGESWNT GLSINKGESA YINANVRYYN TGTAPMYKVT PTTNLVLDGD TLSTIKAQEN QIGNNLSPGD TYPKKGLSPL AL NTMDQFS SRLIPINYDQ LKKLDAGKQI KLETTQVSGN FGTKNSSGQI VTEGNSWSDY ISQIDSISAS IILDTENESY ERR VTAKNL QDPEDKTPEL TIGEAIEKAF GATKKDGLLY FNDIPIDESC VELIFDDNTA NKIKDSLKTL SDKKIYNVKL ERGM NILIK TPTYFTNFDD YNNYPSTWSN VNTTNQDGLQ GSANKLNGET KIKIPMSELK PYKRYVFSGY SKDPLTSNSI IVKIK AKEE KTDYLVPEQG YTKFSYEFET TEKDSSNIEI TLIGSGTTYL DNLSITELNS TPEILDEPEV KIPTDQEIMD AHKIYF ADL NFNPSTGNTY INGMYFAPTQ TNKEALDYIQ KYRVEATLQY SGFKDIGTKD KEMRNYLGDP NQPKTNYVNL RSYFTGG EN IMTYKKLRIY AITPDDRELL VLSVD UniProtKB: ADP-ribosyltransferase binding component |
-Macromolecule #2: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 28 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 56.9 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)