+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20327 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
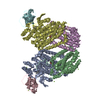
| Title | Spastin Hexamer in complex with substrate peptide | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | AAA+ ATPase / Microtubule Severing / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytokinetic process / microtubule-severing ATPase / microtubule severing ATPase activity / microtubule severing / positive regulation of microtubule depolymerization / endoplasmic reticulum tubular network / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / nuclear membrane reassembly / mitotic nuclear membrane reassembly / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III ...cytokinetic process / microtubule-severing ATPase / microtubule severing ATPase activity / microtubule severing / positive regulation of microtubule depolymerization / endoplasmic reticulum tubular network / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / nuclear membrane reassembly / mitotic nuclear membrane reassembly / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / membrane fission / anterograde axonal transport / microtubule bundle formation / exit from mitosis / protein hexamerization / mitotic spindle disassembly / axonal transport of mitochondrion / positive regulation of cytokinesis / mitotic cytokinesis / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / alpha-tubulin binding / beta-tubulin binding / lipid droplet / axon cytoplasm / axonogenesis / protein homooligomerization / spindle pole / cytoplasmic vesicle / midbody / nuclear membrane / microtubule binding / microtubule / endosome / axon / centrosome / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / ATP hydrolysis activity / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Han H / Schubert HL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2020 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2020Title: Structure of spastin bound to a glutamate-rich peptide implies a hand-over-hand mechanism of substrate translocation. Authors: Han Han / Heidi L Schubert / John McCullough / Nicole Monroe / Michael D Purdy / Mark Yeager / Wesley I Sundquist / Christopher P Hill /  Abstract: Many members of the AAA+ ATPase family function as hexamers that unfold their protein substrates. These AAA unfoldases include spastin, which plays a critical role in the architecture of eukaryotic ...Many members of the AAA+ ATPase family function as hexamers that unfold their protein substrates. These AAA unfoldases include spastin, which plays a critical role in the architecture of eukaryotic cells by driving the remodeling and severing of microtubules, which are cytoskeletal polymers of tubulin subunits. Here, we demonstrate that a human spastin binds weakly to unmodified peptides from the C-terminal segment of human tubulin α1A/B. A peptide comprising alternating glutamate and tyrosine residues binds more tightly, which is consistent with the known importance of glutamylation for spastin microtubule severing activity. A cryo-EM structure of the spastin-peptide complex at 4.2 Å resolution revealed an asymmetric hexamer in which five spastin subunits adopt a helical, spiral staircase configuration that binds the peptide within the central pore, whereas the sixth subunit of the hexamer is displaced from the peptide/substrate, as if transitioning from one end of the helix to the other. This configuration differs from a recently published structure of spastin from , which forms a six-subunit spiral without a transitioning subunit. Our structure resembles other recently reported AAA unfoldases, including the meiotic clade relative Vps4, and supports a model in which spastin utilizes a hand-over-hand mechanism of tubulin translocation and microtubule remodeling. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20327.map.gz emd_20327.map.gz | 5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20327-v30.xml emd-20327-v30.xml emd-20327.xml emd-20327.xml | 18.5 KB 18.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20327.png emd_20327.png | 72 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20327.cif.gz emd-20327.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20327 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20327 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20327 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20327 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6pekMC  6penMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10382 (Title: Structure of spastin bound to a glutamate-rich peptide implies a hand-over-hand mechanism of substrate translocation. EMPIAR-10382 (Title: Structure of spastin bound to a glutamate-rich peptide implies a hand-over-hand mechanism of substrate translocation.Data size: 1.8 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame movies of ADPBeFx-bound Spastin [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20327.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20327.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.056 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
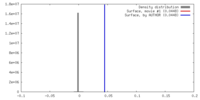
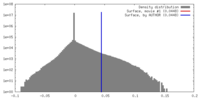
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Spastin Hexamer in complex with substrate peptide
| Entire | Name: Spastin Hexamer in complex with substrate peptide |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Spastin Hexamer in complex with substrate peptide
| Supramolecule | Name: Spastin Hexamer in complex with substrate peptide / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Spastin
| Macromolecule | Name: Spastin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: microtubule-severing ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.498328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAAKRSSGAA PAPASASAPA PVPGGEAERV RVFHKQAFEY ISIALRIDED EKAGQKEQAV EWYKKGIEEL EKGIAVIVTG QGEQCERAR RLQAKMMTNL VMAKDRLQLL ESGAVPKRKD PLTHTSNSLP RSKTVMKTGS AGLSGHHRAP SYSGLSMVSG V KQGSGPAP ...String: MAAKRSSGAA PAPASASAPA PVPGGEAERV RVFHKQAFEY ISIALRIDED EKAGQKEQAV EWYKKGIEEL EKGIAVIVTG QGEQCERAR RLQAKMMTNL VMAKDRLQLL ESGAVPKRKD PLTHTSNSLP RSKTVMKTGS AGLSGHHRAP SYSGLSMVSG V KQGSGPAP TTHKGTPKTN RTNKPSTPTT ATRKKKDLKN FRNVDSNLAN LIMNEIVDNG TAVKFDDIAG QDLAKQALQE IV ILPSLRP ELFTGLRAPA RGLLLFGPPG NGKTMLAKAV AAESNATFFN ISAASLTSKY VGEGEKLVRA LFAVARELQP SII FIDEVD SLLCERREGE HDASRRLKTE FLIEFDGVQS AGDDRVLVMG ATNRPQELDE AVLRRFIKRV YVSLPNEETR LLLL KNLLC KQGSPLTQKE LAQLARMTDG YSGSDLTALA KDAALGPIRE LKPEQVKNMS ASEMRNIRLS DFTESLKKIK RSVSP QTLE AYIRWNKDFG DTTV UniProtKB: Spastin |
-Macromolecule #2: substrate peptide, TYR-GLU-TYR-GLU-TYR-GLU-TYR-GLU
| Macromolecule | Name: substrate peptide, TYR-GLU-TYR-GLU-TYR-GLU-TYR-GLU / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.479453 KDa |
| Sequence | String: EYEYEYEYEY |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: BEF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 66.007 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-BEF: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 57.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




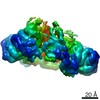
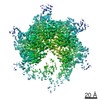

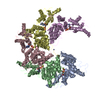
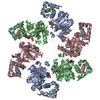
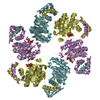





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)