[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10515: Phosphorylated turkey beta1 adrenoceptor with bound agonist formo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10515 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Phosphorylated turkey beta1 adrenoceptor with bound agonist formoterol coupled to arrestin-2 in lipid nanodisc. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / Arrestin / Complex / Nanodisc / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbeta1-adrenergic receptor activity / positive regulation of heart contraction / angiotensin receptor binding / regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / norepinephrine-epinephrine-mediated vasodilation involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure ...beta1-adrenergic receptor activity / positive regulation of heart contraction / angiotensin receptor binding / regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / norepinephrine-epinephrine-mediated vasodilation involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / : / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / stress fiber assembly / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / pseudopodium / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / clathrin-coated pit / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / enzyme inhibitor activity / GTPase activator activity / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / G protein-coupled receptor binding / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / endocytic vesicle membrane / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / protein transport / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / cytoplasmic vesicle / molecular adaptor activity / G alpha (s) signalling events / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / early endosome / transcription coactivator activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / protein ubiquitination / Golgi membrane / lysosomal membrane / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / signal transduction / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleoplasm / membrane / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Phage display vector pTDisp (others) Homo sapiens (human) / Phage display vector pTDisp (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee Y / Tate CG | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Molecular basis of β-arrestin coupling to formoterol-bound β-adrenoceptor. Authors: Yang Lee / Tony Warne / Rony Nehmé / Shubhi Pandey / Hemlata Dwivedi-Agnihotri / Madhu Chaturvedi / Patricia C Edwards / Javier García-Nafría / Andrew G W Leslie / Arun K Shukla / Christopher G Tate /     Abstract: The β-adrenoceptor (βAR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that couples to the heterotrimeric G protein G. G-protein-mediated signalling is terminated by phosphorylation of the C terminus of ...The β-adrenoceptor (βAR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that couples to the heterotrimeric G protein G. G-protein-mediated signalling is terminated by phosphorylation of the C terminus of the receptor by GPCR kinases (GRKs) and by coupling of β-arrestin 1 (βarr1, also known as arrestin 2), which displaces G and induces signalling through the MAP kinase pathway. The ability of synthetic agonists to induce signalling preferentially through either G proteins or arrestins-known as biased agonism-is important in drug development, because the therapeutic effect may arise from only one signalling cascade, whereas the other pathway may mediate undesirable side effects. To understand the molecular basis for arrestin coupling, here we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the βAR-βarr1 complex in lipid nanodiscs bound to the biased agonist formoterol, and the crystal structure of formoterol-bound βAR coupled to the G-protein-mimetic nanobody Nb80. βarr1 couples to βAR in a manner distinct to that of G coupling to βAR-the finger loop of βarr1 occupies a narrower cleft on the intracellular surface, and is closer to transmembrane helix H7 of the receptor when compared with the C-terminal α5 helix of G. The conformation of the finger loop in βarr1 is different from that adopted by the finger loop of visual arrestin when it couples to rhodopsin. βAR coupled to βarr1 shows considerable differences in structure compared with βAR coupled to Nb80, including an inward movement of extracellular loop 3 and the cytoplasmic ends of H5 and H6. We observe weakened interactions between formoterol and two serine residues in H5 at the orthosteric binding site of βAR, and find that formoterol has a lower affinity for the βAR-βarr1 complex than for the βAR-G complex. The structural differences between these complexes of βAR provide a foundation for the design of small molecules that could bias signalling in the β-adrenoceptors. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020Title: Molecular determinants of beta-arrestin coupling to formoterol-bound beta1-adrenoceptor. Authors: Lee Y / Warne T / Nehme R / Pandey S / Dwivedi-Agnihotri H / Edwards PC / Garcia-Nafria J / Leslie AGW / Shukla AK / Tate CG | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10515.map.gz emd_10515.map.gz | 4.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10515-v30.xml emd-10515-v30.xml emd-10515.xml emd-10515.xml | 31.5 KB 31.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10515_fsc.xml emd_10515_fsc.xml | 8.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10515.png emd_10515.png | 56 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_10515_msk_1.map emd_10515_msk_1.map | 52.7 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10515.cif.gz emd-10515.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_10515_half_map_1.map.gz emd_10515_half_map_1.map.gz emd_10515_half_map_2.map.gz emd_10515_half_map_2.map.gz | 40.7 MB 40.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10515 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10515 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10515 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10515 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6tkoMC  6iblC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10342 (Title: Cryo-EM structure of the formoterol-bound turkey beta1 adrenoceptor coupled to beta-arrestin-1 with bound Fab30 in lipid nanodisc EMPIAR-10342 (Title: Cryo-EM structure of the formoterol-bound turkey beta1 adrenoceptor coupled to beta-arrestin-1 with bound Fab30 in lipid nanodiscData size: 4.0 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs [micrographs - multiframe] Data #3: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs [micrographs - multiframe] Data #4: Nanodisc subtracted particles [picked particles - multiframe - processed] Data #5: Nanodisc-reinstated particles [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10515.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10515.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
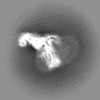
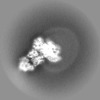
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
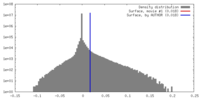
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_10515_msk_1.map emd_10515_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
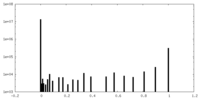
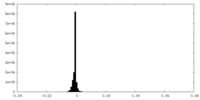
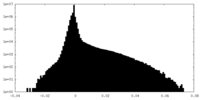
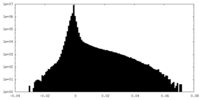
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: RELION auto-refinement half map 2. Half maps were...
| File | emd_10515_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RELION auto-refinement half map 2. Half maps were locally filtered between refinement iterations using SIDESPLITTER. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: RELION auto-refinement half map 1. Half maps were...
| File | emd_10515_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RELION auto-refinement half map 1. Half maps were locally filtered between refinement iterations using SIDESPLITTER. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Formoterol-bound beta1-adrenoceptor coupled to beta-arrestin-1 st...
+Supramolecule #1: Formoterol-bound beta1-adrenoceptor coupled to beta-arrestin-1 st...
+Supramolecule #2: Beta-1 adrenergic receptor
+Supramolecule #3: Beta-arrestin-1
+Supramolecule #4: Fab30 heavy chain
+Supramolecule #5: Fab30 light chain
+Macromolecule #1: Beta-1 adrenergic receptor
+Macromolecule #2: Beta-arrestin-1
+Macromolecule #3: Fab30 heavy chain
+Macromolecule #4: Fab30 light chain
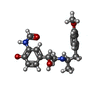
+Macromolecule #5: ~{N}-[5-[(1~{R})-2-[[(2~{R})-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]amino...
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Blotted for 2-3 seconds before plunging. Liquid ethane maintained at 92.15 K.. | ||||||||||||
| Details | This sample was monodisperse. |
- Electron microscopy #1
Electron microscopy #1
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Temperature | Min: 70.0 K / Max: 70.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum SE / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Details | Data collected with a stage-tilt of 30deg; two non-overlapping exposures per hole and multi-hole image-shift data acquisition strategies (3x3 holes per stage shift). |
| Image recording | Image recording ID: 1 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Electron microscopy #1~
Electron microscopy #1~
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Temperature | Min: 70.0 K / Max: 70.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum SE / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Details | Data collected with a stage-tilt of 30deg; two non-overlapping exposures per hole using image-shift. |
| Image recording | Image recording ID: 2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | Initial placement was done manually in Coot, followed by rigid-body refinement in PHENIX and jelly-body refinement in REFMAC5. Manual remodeling was performed in Coot and iterated with real space refinement in PHENIX. Chemical restraints for formoterol were calculated in eLBOW using AM1 optimisation. | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER / Overall B value: 80.6 / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-6tko: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



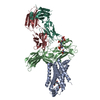

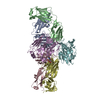

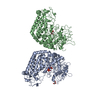














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)

































 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)