+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural mechanism of GTPase-powered ribosome-tRNA movement. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 12, Issue 1, Page 5933, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Oct 11, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Valentyn Petrychenko / Bee-Zen Peng / Ana C de A P Schwarzer / Frank Peske / Marina V Rodnina / Niels Fischer /  |
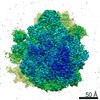
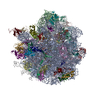
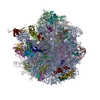
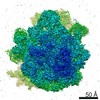
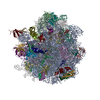
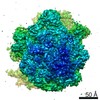
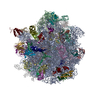
| PubMed Abstract | GTPases are regulators of cell signaling acting as molecular switches. The translational GTPase EF-G stands out, as it uses GTP hydrolysis to generate force and promote the movement of the ribosome ...GTPases are regulators of cell signaling acting as molecular switches. The translational GTPase EF-G stands out, as it uses GTP hydrolysis to generate force and promote the movement of the ribosome along the mRNA. The key unresolved question is how GTP hydrolysis drives molecular movement. Here, we visualize the GTPase-powered step of ongoing translocation by time-resolved cryo-EM. EF-G in the active GDP-Pi form stabilizes the rotated conformation of ribosomal subunits and induces twisting of the sarcin-ricin loop of the 23 S rRNA. Refolding of the GTPase switch regions upon Pi release initiates a large-scale rigid-body rotation of EF-G pivoting around the sarcin-ricin loop that facilitates back rotation of the ribosomal subunits and forward swiveling of the head domain of the small subunit, ultimately driving tRNA forward movement. The findings demonstrate how a GTPase orchestrates spontaneous thermal fluctuations of a large RNA-protein complex into force-generating molecular movement. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:34635670 / PubMed:34635670 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.35 - 9.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-13458, PDB-7pjs: EMDB-13459, PDB-7pjt: EMDB-13460, PDB-7pju: EMDB-13461, PDB-7pjv: EMDB-13462, PDB-7pjw: EMDB-13463, PDB-7pjx: EMDB-13464, PDB-7pjy: EMDB-13465, PDB-7pjz: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-NA: 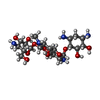 ChemComp-AM2:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-GDP:  ChemComp-PO4: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / EF-G / robosome / 70S / apramycin / translocation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers