+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of the cell-binding component of the binary toxin reveals a di-heptamer macromolecular assembly. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 117, Issue 2, Page 1049-1058, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Jan 14, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Xingjian Xu / Raquel Godoy-Ruiz / Kaylin A Adipietro / Christopher Peralta / Danya Ben-Hail / Kristen M Varney / Mary E Cook / Braden M Roth / Paul T Wilder / Thomas Cleveland / Alexander Grishaev / Heather M Neu / Sarah L J Michel / Wenbo Yu / Dorothy Beckett / Richard R Rustandi / Catherine Lancaster / John W Loughney / Adam Kristopeit / Sianny Christanti / Jessica W Olson / Alexander D MacKerell / Amedee des Georges / Edwin Pozharski / David J Weber /  |
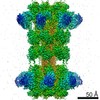
| PubMed Abstract | Targeting infection is challenging because treatment options are limited, and high recurrence rates are common. One reason for this is that hypervirulent strains often have a binary toxin termed ...Targeting infection is challenging because treatment options are limited, and high recurrence rates are common. One reason for this is that hypervirulent strains often have a binary toxin termed the toxin, in addition to the enterotoxins TsdA and TsdB. The toxin has an enzymatic component, termed CDTa, and a pore-forming or delivery subunit termed CDTb. CDTb was characterized here using a combination of single-particle cryoelectron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, NMR, and other biophysical methods. In the absence of CDTa, 2 di-heptamer structures for activated CDTb (1.0 MDa) were solved at atomic resolution, including a symmetric (CDTb; 3.14 Å) and an asymmetric form (CDTb; 2.84 Å). Roles played by 2 receptor-binding domains of activated CDTb were of particular interest since the receptor-binding domain 1 lacks sequence homology to any other known toxin, and the receptor-binding domain 2 is completely absent in other well-studied heptameric toxins (i.e., anthrax). For CDTb, a Ca binding site was discovered in the first receptor-binding domain that is important for its stability, and the second receptor-binding domain was found to be critical for host cell toxicity and the di-heptamer fold for both forms of activated CDTb. Together, these studies represent a starting point for developing structure-based drug-design strategies to target the most severe strains of . |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:31896582 / PubMed:31896582 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.3 - 3.7 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-20926, PDB-6uwr: EMDB-20927, PDB-6uwt:  PDB-6uwi:  PDB-6uwo: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TOXIN / Translocase / RBD2 / CDTb / binary toxin / tetradecamer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 clostridioides difficile (bacteria)
clostridioides difficile (bacteria)