+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii F-ATPase rotary subunits γ and ε, unveiling novel compound targets. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | FASEB J, Vol. 38, Issue 20, Page e70131, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Oct 28, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Khoa Cong Minh Le / Chui Fann Wong / Volker Müller / Gerhard Grüber /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Priority 1: critical WHO pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii depends on ATP synthesis and ATP:ADP homeostasis and its bifunctional FF-ATP synthase. While synthesizing ATP, it regulates ATP cleavage by ...Priority 1: critical WHO pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii depends on ATP synthesis and ATP:ADP homeostasis and its bifunctional FF-ATP synthase. While synthesizing ATP, it regulates ATP cleavage by its inhibitory ε subunit to prevent wasteful ATP consumption. We determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of the ATPase active A. baumannii F-αßγε mutant in four distinct conformational states, revealing four transition states and structural transformation of the ε's C-terminal domain, forming the switch of an ATP hydrolysis off- and an ATP synthesis on-state based. These alterations go in concert with altered motions and interactions in the catalytic- and rotary subunits of this engine. These A. baumannii interacting sites provide novel pathogen-specific targets for inhibitors, with the aim of ATP depletion and/or ATP synthesis and growth inhibition. Furthermore, the presented diversity to other bacterial F-ATP synthases extends the view of structural elements regulating such a catalyst. |
 External links External links |  FASEB J / FASEB J /  PubMed:39467208 / PubMed:39467208 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.89 - 3.18 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-60117, PDB-8zi0: EMDB-60118, PDB-8zi1: EMDB-60119, PDB-8zi2: EMDB-60120, PDB-8zi3: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-PO4: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / ATP hydrolysis / F1-ATPase |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



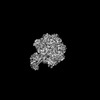
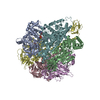

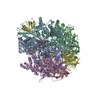

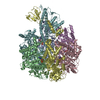

 acinetobacter baumannii ab5075 (bacteria)
acinetobacter baumannii ab5075 (bacteria)