[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-60117: Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
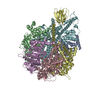
| Title | Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase rotary subunits gamma and epsilon and novel compound targets - Conformation 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ATP hydrolysis / F1-ATPase / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.18 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Le KCM / Wong CF / Gruber G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 1 items Singapore, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2024 Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii F-ATPase rotary subunits γ and ε, unveiling novel compound targets. Authors: Khoa Cong Minh Le / Chui Fann Wong / Volker Müller / Gerhard Grüber /   Abstract: Priority 1: critical WHO pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii depends on ATP synthesis and ATP:ADP homeostasis and its bifunctional FF-ATP synthase. While synthesizing ATP, it regulates ATP cleavage by ...Priority 1: critical WHO pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii depends on ATP synthesis and ATP:ADP homeostasis and its bifunctional FF-ATP synthase. While synthesizing ATP, it regulates ATP cleavage by its inhibitory ε subunit to prevent wasteful ATP consumption. We determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of the ATPase active A. baumannii F-αßγε mutant in four distinct conformational states, revealing four transition states and structural transformation of the ε's C-terminal domain, forming the switch of an ATP hydrolysis off- and an ATP synthesis on-state based. These alterations go in concert with altered motions and interactions in the catalytic- and rotary subunits of this engine. These A. baumannii interacting sites provide novel pathogen-specific targets for inhibitors, with the aim of ATP depletion and/or ATP synthesis and growth inhibition. Furthermore, the presented diversity to other bacterial F-ATP synthases extends the view of structural elements regulating such a catalyst. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_60117.map.gz emd_60117.map.gz | 122.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-60117-v30.xml emd-60117-v30.xml emd-60117.xml emd-60117.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_60117_fsc.xml emd_60117_fsc.xml | 13.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_60117.png emd_60117.png | 67.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_60117_msk_1.map emd_60117_msk_1.map | 244.1 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-60117.cif.gz emd-60117.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_60117_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60117_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60117_half_map_2.map.gz emd_60117_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.8 MB 226.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60117 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60117 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60117 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60117 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 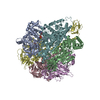 8zi0MC  8zi1C  8zi2C  8zi3C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_60117.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_60117.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.858 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_60117_msk_1.map emd_60117_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_60117_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase recombinant protein with trunca...
| Entire | Name: Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase recombinant protein with truncation mutation at subunit epsilon CTD, 134-139 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase recombinant protein with trunca...
| Supramolecule | Name: Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase recombinant protein with truncation mutation at subunit epsilon CTD, 134-139 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 370 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP synthase subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.452906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQQLNPSEIS ALIKQRIGDL DTSATAKNEG TIVMVSDGIV RIHGLADAMY GEMIEFDGGL FGMALNLEQD SVGAVVLGNY LSLQEGQKA RCTGRVLEVP VGPELLGRVV DALGNPIDGK GPIDAKLTDA VEKVAPGVIW RQSVDQPVQT GYKSVDTMIP V GRGQRELI ...String: MQQLNPSEIS ALIKQRIGDL DTSATAKNEG TIVMVSDGIV RIHGLADAMY GEMIEFDGGL FGMALNLEQD SVGAVVLGNY LSLQEGQKA RCTGRVLEVP VGPELLGRVV DALGNPIDGK GPIDAKLTDA VEKVAPGVIW RQSVDQPVQT GYKSVDTMIP V GRGQRELI IGDRQTGKTA MAIDAIIAQK NSGIKCVYVA IGQKQSTIAN VVRKLEETGA MAYTTVVAAA AADPAAMQYL AP YSGCTMG EYFRDRGEDA LIIYDDLSKQ AVAYRQISLL LRRPPGREAY PGDVFYLHSR LLERASRVSA EYVEKFTNGA VTG KTGSLT ALPIIETQAG DVSAFVPTNV ISITDGQIFL ETSLFNAGIR PAVNAGISVS RVGGSAQTKI IKKLSGGIRT ALAQ YRELA AFAQFASDLD EATRKQLEHG QRVTELMKQK QYAPYSIADQ AVSVYASNEG YMADVEVKKI VDFDAALIAY FRSEY APLM KQIDETGDYN KDIEAAIKAG IESFKATQTY UniProtKB: ATP synthase subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: ATP synthase subunit beta
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase subunit beta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.32718 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSSGRIIQII GAVIDVEFER TSVPKIYDAL QVDGTETTLE VQQQLGDGVV RTIAMGSTEG LKRGLTVTST NAPISVPVGT ATLGRIMDV LGRPIDEAGP VATEERLPIH RQAPSYAEQA ASTDLLETGI KVIDLLCPFA KGGKVGLFGG AGVGKTVNMM E LINNIAKA ...String: MSSGRIIQII GAVIDVEFER TSVPKIYDAL QVDGTETTLE VQQQLGDGVV RTIAMGSTEG LKRGLTVTST NAPISVPVGT ATLGRIMDV LGRPIDEAGP VATEERLPIH RQAPSYAEQA ASTDLLETGI KVIDLLCPFA KGGKVGLFGG AGVGKTVNMM E LINNIAKA HSGLSVFAGV GERTREGNDF YHEMKDSNVL DKVAMVYGQM NEPPGNRLRV ALTGLTMAEY FRDEKDENGK GR DVLLFVD NIYRYTLAGT EVSALLGRMP SAVGYQPTLA EEMGVLQERI TSTKSGSITS IQAVYVPADD LTDPSPATTF AHL DATVVL SRDIASSGIY PAIDPLDSTS RQLDPLVVGQ EHYEIARAVQ NVLQRYKELK DIIAILGMDE LAEEDKLVVY RARK IQRFF SQPFHVAEVF TGAPGKLVPL KETIRGFKGL LAGEYDHIPE QAFYMVGGID EVIAKAEKL UniProtKB: ATP synthase subunit beta |
-Macromolecule #3: ATP synthase epsilon chain
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase epsilon chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: Subunit epsilon with truncated C-terminus domain, deletion I134-Q139 Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.83884 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MATMQCDVVS VKESIYSGAV TMLIAKGAGG ELGILPGHAP LVTLLQPGPI RVLLENGTEE IVYVSGGVLE VQPHVVTVLA DTAIRADNL DEAAILEARK NAEQLLANQK SDLDSAAALA ALAETAAQLE TIRK UniProtKB: ATP synthase epsilon chain |
-Macromolecule #4: ATP synthase gamma chain
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase gamma chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 32.135037 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MANLKEIRAK VASIKSTQKI TRAMQMVAAS KMRRAQERMA QGRPYADNMR RVIAHLVQAN PEYKHRYMVD RPVKRVGYII VSSDRGLAG GLNINLFKKV VQHVKAQQEQ SIEVQFALIG QKAVSFFKNY GGKVLGATTQ IGDAPSLEQL TGSVQVMLDA F DKGELDRI ...String: MANLKEIRAK VASIKSTQKI TRAMQMVAAS KMRRAQERMA QGRPYADNMR RVIAHLVQAN PEYKHRYMVD RPVKRVGYII VSSDRGLAG GLNINLFKKV VQHVKAQQEQ SIEVQFALIG QKAVSFFKNY GGKVLGATTQ IGDAPSLEQL TGSVQVMLDA F DKGELDRI YLVSNGFVNA MTQKPKVEQL VPLAPAEEGD DLNRTYGWDY IYEPEAEELL NGLLVRYIES MVYQGVIENV AC EQSARMV AMKAATDNAG QLIKDLQLIY NKLRQAAITQ EISEIVGGAA AV UniProtKB: ATP synthase gamma chain |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #6: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #8: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.5 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 8635 / Average exposure time: 6.02 sec. / Average electron dose: 68.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 160000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model Details: The initial model is from the CryoEM structure of AbF1-ATPase Wild Type form. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-8zi0: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)