[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8zi0: Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8zi0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
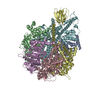
| Title | Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase rotary subunits gamma and epsilon and novel compound targets - Conformation 1 | ||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase ...) x 4 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / ATP hydrolysis / F1-ATPase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.18 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Le, K.C.M. / Wong, C.F. / Gruber, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 1items Singapore, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2024 Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM reveals transition states of the Acinetobacter baumannii F-ATPase rotary subunits γ and ε, unveiling novel compound targets. Authors: Khoa Cong Minh Le / Chui Fann Wong / Volker Müller / Gerhard Grüber /   Abstract: Priority 1: critical WHO pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii depends on ATP synthesis and ATP:ADP homeostasis and its bifunctional FF-ATP synthase. While synthesizing ATP, it regulates ATP cleavage by ...Priority 1: critical WHO pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii depends on ATP synthesis and ATP:ADP homeostasis and its bifunctional FF-ATP synthase. While synthesizing ATP, it regulates ATP cleavage by its inhibitory ε subunit to prevent wasteful ATP consumption. We determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of the ATPase active A. baumannii F-αßγε mutant in four distinct conformational states, revealing four transition states and structural transformation of the ε's C-terminal domain, forming the switch of an ATP hydrolysis off- and an ATP synthesis on-state based. These alterations go in concert with altered motions and interactions in the catalytic- and rotary subunits of this engine. These A. baumannii interacting sites provide novel pathogen-specific targets for inhibitors, with the aim of ATP depletion and/or ATP synthesis and growth inhibition. Furthermore, the presented diversity to other bacterial F-ATP synthases extends the view of structural elements regulating such a catalyst. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8zi0.cif.gz 8zi0.cif.gz | 613.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8zi0.ent.gz pdb8zi0.ent.gz | 501.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8zi0.json.gz 8zi0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/8zi0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/8zi0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/8zi0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zi/8zi0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  60117MC  8zi1C 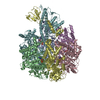 8zi2C  8zi3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 4 types, 8 molecules ABCDEFeg
| #1: Protein | Mass: 55452.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria)Gene: atpA, A1S_0153 / Plasmid: pET29b / Production host:  References: UniProt: A3M142, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 50327.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria)Gene: atpD, A0141_RS12845, A0141_RS20960, A7M90_08515, Aba7835_18750, ABCAM1_0171, ABR2091_0172, ABUW_3732, ACX61_17955, APD17_18800, AUO97_06425, AYR68_18055, B7L45_18625, B9W25_04445, B9X95_01225, ...Gene: atpD, A0141_RS12845, A0141_RS20960, A7M90_08515, Aba7835_18750, ABCAM1_0171, ABR2091_0172, ABUW_3732, ACX61_17955, APD17_18800, AUO97_06425, AYR68_18055, B7L45_18625, B9W25_04445, B9X95_01225, C2U32_15270, CAS83_08025, CBE85_14440, CBL15_17790, CSB70_3894, CTZ19_18505, CV954_019160, D8O08_000340, DLI71_10780, DOL94_02915, E1A86_02070, E1A87_05115, EA706_05505, EA720_009770, EA722_10620, EGM95_19710, F2P40_12655, F4T85_15180, FDN00_02380, FE003_18670, FJU42_13260, FJV09_08800, FR761_02120, G3N53_14495, GNY86_14295, GSE42_00720, HB367_12615, HBK86_18980, HIN86_18910, IAG11_01885, IMO23_00745, ITE13_08765, JHZ39_002240, P9867_05895, SAMEA104305318_03329, SAMEA4394745_01410 Plasmid: pET29b / Production host:  References: UniProt: V5VHQ6, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 13838.840 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: deletion 134-139 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Subunit epsilon with truncated C-terminus domain, deletion I134-Q139 Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria)Gene: atpC, A0141_RS12850, A0141_RS20965, A7M90_08520, Aba7835_18745, ABCAM1_0172, ABR2091_0173, ABUW_3731, ACX61_17950, APD17_18795, AUO97_06420, AYR68_18050, B7L45_18620, B9W25_04440, B9X95_01230, ...Gene: atpC, A0141_RS12850, A0141_RS20965, A7M90_08520, Aba7835_18745, ABCAM1_0172, ABR2091_0173, ABUW_3731, ACX61_17950, APD17_18795, AUO97_06420, AYR68_18050, B7L45_18620, B9W25_04440, B9X95_01230, C2U32_15275, CAS83_08020, CBE85_14435, CBL15_17785, CSB70_3895, CTZ19_18500, CV954_019155, D8O08_000335, DLI71_10775, DOL94_02920, E1A86_02075, E1A87_05110, EA686_08570, EA706_05510, EA720_009765, EA722_10625, EGM95_19705, F2P40_12650, F4T85_15175, FDN00_02385, FE003_18665, FJU42_13255, FJV09_08795, FR761_02125, G3N53_14500, GNY86_14290, GSE42_00725, HB367_12610, HBK86_18985, HIN86_18905, IMO23_00750, JHZ39_002241, P9867_05900, SAMEA104305318_03328, SAMEA4394745_01411 Plasmid: pET29b / Production host:  #4: Protein | | Mass: 32135.037 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria)Gene: atpG, A1S_0154 / Plasmid: pET29b / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 9 molecules 






| #5: Chemical | | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #7: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Acinetobacter baumannii F1-ATPase recombinant protein with truncation mutation at subunit epsilon CTD, 134-139 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.37 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 / Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 160000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 6.02 sec. / Electron dose: 68.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 8635 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 829861 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.18 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 47078 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7YRY Accession code: 7YRY Details: The initial model is from the CryoEM structure of AbF1-ATPase Wild Type form. Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj