+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Kainate receptor channel opening and gating mechanism. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 630, Issue 8017, Page 762-768, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | May 22, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Shanti Pal Gangwar / Maria V Yelshanskaya / Kirill D Nadezhdin / Laura Y Yen / Thomas P Newton / Muhammed Aktolun / Maria G Kurnikova / Alexander I Sobolevsky /  |
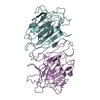
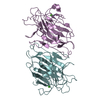
| PubMed Abstract | Kainate receptors, a subclass of ionotropic glutamate receptors, are tetrameric ligand-gated ion channels that mediate excitatory neurotransmission. Kainate receptors modulate neuronal circuits and ...Kainate receptors, a subclass of ionotropic glutamate receptors, are tetrameric ligand-gated ion channels that mediate excitatory neurotransmission. Kainate receptors modulate neuronal circuits and synaptic plasticity during the development and function of the central nervous system and are implicated in various neurological and psychiatric diseases, including epilepsy, depression, schizophrenia, anxiety and autism. Although structures of kainate receptor domains and subunit assemblies are available, the mechanism of kainate receptor gating remains poorly understood. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of the kainate receptor GluK2 in the presence of the agonist glutamate and the positive allosteric modulators lectin concanavalin A and BPAM344. Concanavalin A and BPAM344 inhibit kainate receptor desensitization and prolong activation by acting as a spacer between the amino-terminal and ligand-binding domains and a stabilizer of the ligand-binding domain dimer interface, respectively. Channel opening involves the kinking of all four pore-forming M3 helices. Our structures reveal the molecular basis of kainate receptor gating, which could guide the development of drugs for treatment of neurological disorders. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:38778115 / PubMed:38778115 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.36 - 6.66 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-44123: Cryo-EM density of GluK2 amino-terminal domain (GluK2-ATD) from the open-state structure of kainate receptor GluK2 in complex with agonist glutamate and positive allosteric modulator BPAM344 bound to ConA EMDB-44124, PDB-9b33: EMDB-44125, PDB-9b34:  EMDB-44126: Open state of kainate receptor GluK2 in complex with agonist glutamate and positive allosteric modulator BPAM344 bound to two concanavalin A dimers  EMDB-44127: Open state of kainate receptor GluK2 in complex with agonist glutamate and positive allosteric modulator BPAM344 bound to one concanavalin A dimer EMDB-44128, PDB-9b35: EMDB-44129, PDB-9b36: EMDB-44130, PDB-9b37: EMDB-44131, PDB-9b38: EMDB-44132, PDB-9b39: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-CA: 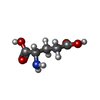 ChemComp-GLU: 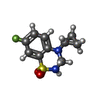 ChemComp-2J9:  ChemComp-POV:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-NAG: 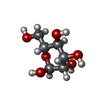 ChemComp-MAN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / kainate receptor / GluK2 / positive allosteric modulator / BPAM344 / open / concanavalin A / ConA / glutamate / LBD-TMD / ligand-binding domain / transmembrane domain / pseudo 4-fold symmetrical / LBD / asymmetric |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers