+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural basis of second-generation HIV integrase inhibitor action and viral resistance. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Science, Vol. 367, Issue 6479, Page 806-810, Year 2020 |
| 掲載日 | 2020年2月14日 |
 著者 著者 | Nicola J Cook / Wen Li / Dénes Berta / Magd Badaoui / Allison Ballandras-Colas / Andrea Nans / Abhay Kotecha / Edina Rosta / Alan N Engelman / Peter Cherepanov /    |
| PubMed 要旨 | Although second-generation HIV integrase strand-transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) are prescribed throughout the world, the mechanistic basis for the superiority of these drugs is poorly understood. We ...Although second-generation HIV integrase strand-transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) are prescribed throughout the world, the mechanistic basis for the superiority of these drugs is poorly understood. We used single-particle cryo-electron microscopy to visualize the mode of action of the advanced INSTIs dolutegravir and bictegravir at near-atomic resolution. Glutamine-148→histidine (Q148H) and glycine-140→serine (G140S) amino acid substitutions in integrase that result in clinical INSTI failure perturb optimal magnesium ion coordination in the enzyme active site. The expanded chemical scaffolds of second-generation compounds mediate interactions with the protein backbone that are critical for antagonizing viruses containing the Q148H and G140S mutations. Our results reveal that binding to magnesium ions underpins a fundamental weakness of the INSTI pharmacophore that is exploited by the virus to engender resistance and provide a structural framework for the development of this class of anti-HIV/AIDS therapeutics. |
 リンク リンク |  Science / Science /  PubMed:32001525 / PubMed:32001525 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.81 - 3.36 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-10041, PDB-6rwl: EMDB-10042, PDB-6rwm: EMDB-10043, PDB-6rwn: EMDB-10044, PDB-6rwo: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-MG: 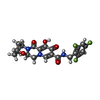 ChemComp-KLQ:  ChemComp-CL:  ChemComp-HOH: 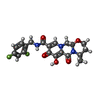 ChemComp-DLU: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | RECOMBINATION / retroviral integrase / lentivirus / strand transfer inhibior / protein-DNA complex |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について





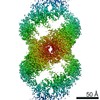
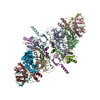

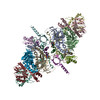
 simian immunodeficiency virus (サル免疫不全ウイルス)
simian immunodeficiency virus (サル免疫不全ウイルス)