+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Architecture and assembly mechanism of native glycine receptors. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nature, Vol. 599, Issue 7885, Page 513-517, Year 2021 |
| 掲載日 | 2021年9月23日 |
 著者 著者 | Hongtao Zhu / Eric Gouaux /  |
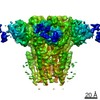
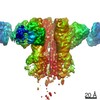
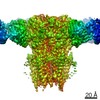
| PubMed 要旨 | Glycine receptors (GlyRs) are pentameric, 'Cys-loop' receptors that form chloride-permeable channels and mediate fast inhibitory signalling throughout the central nervous system. In the spinal cord ...Glycine receptors (GlyRs) are pentameric, 'Cys-loop' receptors that form chloride-permeable channels and mediate fast inhibitory signalling throughout the central nervous system. In the spinal cord and brainstem, GlyRs regulate locomotion and cause movement disorders when mutated. However, the stoichiometry of native GlyRs and the mechanism by which they are assembled remain unclear, despite extensive investigation. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of native GlyRs from pig spinal cord and brainstem, revealing structural insights into heteromeric receptors and their predominant subunit stoichiometry of 4α:1β. Within the heteromeric pentamer, the β(+)-α(-) interface adopts a structure that is distinct from the α(+)-α(-) and α(+)-β(-) interfaces. Furthermore, the β-subunit contains a unique phenylalanine residue that resides within the pore and disrupts the canonical picrotoxin site. These results explain why inclusion of the β-subunit breaks receptor symmetry and alters ion channel pharmacology. We also find incomplete receptor complexes and, by elucidating their structures, reveal the architectures of partially assembled α-trimers and α-tetramers. |
 リンク リンク |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:34555840 / PubMed:34555840 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.7 - 12.0 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-23910, PDB-7mlu: EMDB-23911, PDB-7mlv: 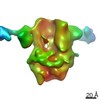 EMDB-23912: EMDB-23913, PDB-7mly: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-NAG: 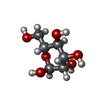 ChemComp-MAN: 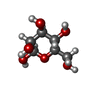 ChemComp-BMA: 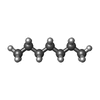 ChemComp-HP6: 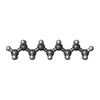 ChemComp-DD9:  ChemComp-LNK:  ChemComp-MYS:  ChemComp-D10:  ChemComp-NBU:  ChemComp-GLY:  ChemComp-D12:  ChemComp-OCT:  ChemComp-HEX:  ChemComp-UND: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN / glycine receptor / ion channel / homomeric pentamer / homomeric tetramer / heteromeric pentamer |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について