+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Receptor-recognition and antiviral mechanisms of retrovirus-derived human proteins. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 31, Issue 9, Page 1368-1376, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Apr 26, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Shashank Khare / Miryam I Villalba / Juan C Canul-Tec / Arantza Balsebre Cajiao / Anand Kumar / Marija Backovic / Felix A Rey / Els Pardon / Jan Steyaert / Camilo Perez / Nicolas Reyes /     |
| PubMed Abstract | Human syncytin-1 and suppressyn are cellular proteins of retroviral origin involved in cell-cell fusion events to establish the maternal-fetal interface in the placenta. In cell culture, they ...Human syncytin-1 and suppressyn are cellular proteins of retroviral origin involved in cell-cell fusion events to establish the maternal-fetal interface in the placenta. In cell culture, they restrict infections from members of the largest interference group of vertebrate retroviruses, and are regarded as host immunity factors expressed during development. At the core of the syncytin-1 and suppressyn functions are poorly understood mechanisms to recognize a common cellular receptor, the membrane transporter ASCT2. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human ASCT2 in complexes with the receptor-binding domains of syncytin-1 and suppressyn. Despite their evolutionary divergence, the two placental proteins occupy similar positions in ASCT2, and are stabilized by the formation of a hybrid β-sheet or 'clamp' with the receptor. Structural predictions of the receptor-binding domains of extant retroviruses indicate overlapping binding interfaces and clamping sites with ASCT2, revealing a competition mechanism between the placental proteins and the retroviruses. Our work uncovers a common ASCT2 recognition mechanism by a large group of endogenous and disease-causing retroviruses, and provides high-resolution views on how placental human proteins exert morphological and immunological functions. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:38671230 PubMed:38671230 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.31 - 3.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-17189, PDB-8oud: EMDB-17192, PDB-8ouh: EMDB-17193, PDB-8oui: EMDB-17194, PDB-8ouj: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NA: 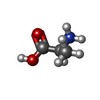 ChemComp-ALA:  ChemComp-Y01:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Neutral aminoacid transmembrane transporter activity / ASCT2 / Complex / Nanobody / PROTEIN TRANSPORT / Small neutral amino acid transporter / Syncytin-1 / Receptor binding domain / Small neural amino acid transporter / Suppressyn |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
