+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis for λN-dependent processive transcription antitermination. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Microbiol, Vol. 2, Page 17062, Year 2017 |
| Publish date | Apr 28, 2017 |
 Authors Authors | Nelly Said / Ferdinand Krupp / Ekaterina Anedchenko / Karine F Santos / Olexandr Dybkov / Yong-Heng Huang / Chung-Tien Lee / Bernhard Loll / Elmar Behrmann / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke / Justus Loerke / Henning Urlaub / Christian M T Spahn / Gert Weber / Markus C Wahl /  |
| PubMed Abstract | λN-mediated processive antitermination constitutes a paradigmatic transcription regulatory event, during which phage protein λN, host factors NusA, NusB, NusE and NusG, and an RNA nut site render ...λN-mediated processive antitermination constitutes a paradigmatic transcription regulatory event, during which phage protein λN, host factors NusA, NusB, NusE and NusG, and an RNA nut site render elongating RNA polymerase termination-resistant. The structural basis of the process has so far remained elusive. Here we describe a crystal structure of a λN-NusA-NusB-NusE-nut site complex and an electron cryo-microscopic structure of a complete transcription antitermination complex, comprising RNA polymerase, DNA, nut site RNA, all Nus factors and λN, validated by crosslinking/mass spectrometry. Due to intrinsic disorder, λN can act as a multiprotein/RNA interaction hub, which, together with nut site RNA, arranges NusA, NusB and NusE into a triangular complex. This complex docks via the NusA N-terminal domain and the λN C-terminus next to the RNA exit channel on RNA polymerase. Based on the structures, comparative crosslinking analyses and structure-guided mutagenesis, we hypothesize that λN mounts a multipronged strategy to reprogram the transcriptional machinery, which may include (1) the λN C terminus clamping the RNA exit channel, thus stabilizing the DNA:RNA hybrid; (2) repositioning of NusA and RNAP elements, thus redirecting nascent RNA and sequestering the upstream branch of a terminator hairpin; and (3) hindering RNA engagement of termination factor ρ and/or obstructing ρ translocation on the transcript. |
 External links External links |  Nat Microbiol / Nat Microbiol /  PubMed:28452979 PubMed:28452979 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.143 - 9.8 Å |
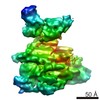
| Structure data | EMDB-3561: map of the RNA polymerase lambda-based antitermination complex solved by cryo-EM  PDB-5lm7: 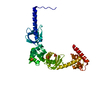 PDB-5lm9: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Transcription regulation antitermination Nus proteins Phage lambda N protein / Transcription factor / Antitermination Termination / Nus proteins / TRANSCRIPTION/DNA/RNA / DNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE / BACTERIAL TRANSCRIPTION / TERNARY ELONGATION COMPLEX / ANTITERMINATION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA-RNA complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 escherichia phage lambda (virus)
escherichia phage lambda (virus)