+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 617, Issue 7959, Page 200-207, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Apr 5, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Mikael Holm / S Kundhavai Natchiar / Emily J Rundlet / Alexander G Myasnikov / Zoe L Watson / Roger B Altman / Hao-Yuan Wang / Jack Taunton / Scott C Blanchard /   |
| PubMed Abstract | In all species, ribosomes synthesize proteins by faithfully decoding messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotide sequences using aminoacyl-tRNA substrates. Current knowledge of the decoding mechanism derives ...In all species, ribosomes synthesize proteins by faithfully decoding messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotide sequences using aminoacyl-tRNA substrates. Current knowledge of the decoding mechanism derives principally from studies on bacterial systems. Although key features are conserved across evolution, eukaryotes achieve higher-fidelity mRNA decoding than bacteria. In human, changes in decoding fidelity are linked to ageing and disease and represent a potential point of therapeutic intervention in both viral and cancer treatment. Here we combine single-molecule imaging and cryogenic electron microscopy methods to examine the molecular basis of human ribosome fidelity to reveal that the decoding mechanism is both kinetically and structurally distinct from that of bacteria. Although decoding is globally analogous in both species, the reaction coordinate of aminoacyl-tRNA movement is altered on the human ribosome and the process is an order of magnitude slower. These distinctions arise from eukaryote-specific structural elements in the human ribosome and in the elongation factor eukaryotic elongation factor 1A (eEF1A) that together coordinate faithful tRNA incorporation at each mRNA codon. The distinct nature and timing of conformational changes within the ribosome and eEF1A rationalize how increased decoding fidelity is achieved and potentially regulated in eukaryotic species. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:37020024 / PubMed:37020024 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 1.67 - 2.94 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-29757, PDB-8g5y: EMDB-29758, PDB-8g5z: EMDB-29759, PDB-8g60: EMDB-29760, PDB-8g61:  EMDB-29766: mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria (60S Focus refined map)  EMDB-29768: mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria (40S Focus refined map) EMDB-29771, PDB-8g6j:  EMDB-29782: mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria (80S consensus refined structure) EMDB-40205, PDB-8glp: |
| Chemicals | 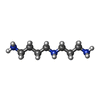 ChemComp-SPD: 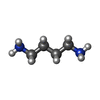 ChemComp-PUT:  ChemComp-K:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ANM:  ChemComp-3H3:  ChemComp-ZN: 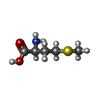 ChemComp-MET:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-PHE:  ChemComp-GSP:  ChemComp-ZIY:  ChemComp-3HE:  ChemComp-HMT:  ChemComp-YRB: 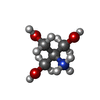 ChemComp-TRS: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Human 80S / tRNA / mRNA eEF1A / eIF5A / tRNA selection / mRNA tRNA selection |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers









 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
