[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8glp: mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct f... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8glp | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria (Consensus LSU focused refined structure) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Human 80S / tRNA / mRNA tRNA selection | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationembryonic brain development / translation at presynapse / exit from mitosis / optic nerve development / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / regulation of translation involved in cellular response to UV / negative regulation of protein neddylation / negative regulation of formation of translation preinitiation complex / axial mesoderm development / regulation of G1 to G0 transition ...embryonic brain development / translation at presynapse / exit from mitosis / optic nerve development / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / regulation of translation involved in cellular response to UV / negative regulation of protein neddylation / negative regulation of formation of translation preinitiation complex / axial mesoderm development / regulation of G1 to G0 transition / retinal ganglion cell axon guidance / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / ribosomal protein import into nucleus / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / positive regulation of base-excision repair / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / protein-DNA complex disassembly / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / positive regulation of gastrulation / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / 90S preribosome assembly / nucleolus organization / IRE1-RACK1-PP2A complex / positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / TNFR1-mediated ceramide production / alpha-beta T cell differentiation / GAIT complex / negative regulation of RNA splicing / negative regulation of DNA repair / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / TORC2 complex binding / G1 to G0 transition / supercoiled DNA binding / NF-kappaB complex / cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / neural crest cell differentiation / oxidized purine DNA binding / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / middle ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hydrogen peroxide / negative regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / erythrocyte homeostasis / negative regulation of phagocytosis / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / cytoplasmic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / protein kinase A binding / homeostatic process / ion channel inhibitor activity / laminin receptor activity / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / pigmentation / Translation initiation complex formation / positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / macrophage chemotaxis / lung morphogenesis / cellular response to actinomycin D / fibroblast growth factor binding / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation / monocyte chemotaxis / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / TOR signaling / BH3 domain binding / Protein hydroxylation / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / iron-sulfur cluster binding / mTORC1-mediated signalling / regulation of cell division / Peptide chain elongation / cellular response to ethanol / positive regulation of protein binding / positive regulation of GTPase activity / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / blastocyst development / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Viral mRNA Translation / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein binding / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / protein localization to nucleus / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Holm, M. / Natchiar, K.S. / Rundlet, E.J. / Myasnikov, A.G. / Watson, Z.L. / Altman, R.B. / Blanchard, S.C. | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: mRNA decoding in human is kinetically and structurally distinct from bacteria. Authors: Mikael Holm / S Kundhavai Natchiar / Emily J Rundlet / Alexander G Myasnikov / Zoe L Watson / Roger B Altman / Hao-Yuan Wang / Jack Taunton / Scott C Blanchard /   Abstract: In all species, ribosomes synthesize proteins by faithfully decoding messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotide sequences using aminoacyl-tRNA substrates. Current knowledge of the decoding mechanism derives ...In all species, ribosomes synthesize proteins by faithfully decoding messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotide sequences using aminoacyl-tRNA substrates. Current knowledge of the decoding mechanism derives principally from studies on bacterial systems. Although key features are conserved across evolution, eukaryotes achieve higher-fidelity mRNA decoding than bacteria. In human, changes in decoding fidelity are linked to ageing and disease and represent a potential point of therapeutic intervention in both viral and cancer treatment. Here we combine single-molecule imaging and cryogenic electron microscopy methods to examine the molecular basis of human ribosome fidelity to reveal that the decoding mechanism is both kinetically and structurally distinct from that of bacteria. Although decoding is globally analogous in both species, the reaction coordinate of aminoacyl-tRNA movement is altered on the human ribosome and the process is an order of magnitude slower. These distinctions arise from eukaryote-specific structural elements in the human ribosome and in the elongation factor eukaryotic elongation factor 1A (eEF1A) that together coordinate faithful tRNA incorporation at each mRNA codon. The distinct nature and timing of conformational changes within the ribosome and eEF1A rationalize how increased decoding fidelity is achieved and potentially regulated in eukaryotic species. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8glp.cif.gz 8glp.cif.gz | 5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8glp.ent.gz pdb8glp.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8glp.json.gz 8glp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gl/8glp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gl/8glp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gl/8glp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gl/8glp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40205MC 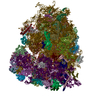 8g5yC  8g5zC  8g60C 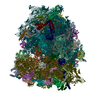 8g61C  8g6jC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 6 types, 6 molecules S2L8L5L7mRPt
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 603580.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 50171.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 555853 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 555853 |
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 1640884.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #4: RNA chain | Mass: 38691.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 23898 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 23898 |
| #80: RNA chain | Mass: 19128.443 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #81: RNA chain | Mass: 24848.943 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
+40S ribosomal protein ... , 30 types, 30 molecules SBSASDSJSESCSGSFSHSWSISQSUSKSOSXSMSSSdSNSLSRSPSTSVSYSZSaSbSc
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules SeSfSg
| #35: Protein | Mass: 14415.724 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62861 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62861 |
|---|---|
| #36: Protein | Mass: 18004.041 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62979 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62979 |
| #37: Protein | Mass: 35115.652 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63244 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63244 |
+60S ribosomal protein ... , 42 types, 42 molecules LALBLCLJLHLELGLOLLLVLMLaLNLILDLQLRLSLTLPLULXLYLWLZLrLhLbLFLc...
-Non-polymers , 10 types, 8765 molecules 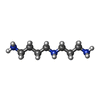
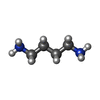















| #82: Chemical | ChemComp-SPD / #83: Chemical | ChemComp-PUT / #84: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #85: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #86: Chemical | ChemComp-ANM / | #87: Chemical | ChemComp-3H3 / | #88: Chemical | #89: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #90: Chemical | ChemComp-MET / | #91: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human ribosome / Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#80 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: -1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: -500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 79 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19_4092: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 1.67 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 845750 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj




























































