+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | HflX-mediated drug resistance through ribosome splitting and rRNA disordering in mycobacteria. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 122, Issue 6, Page e2419826122, Year 2025 |
| 掲載日 | 2025年2月11日 |
 著者 著者 | Soneya Majumdar / Amuliya Kashyap / Ravi K Koripella / Manjuli R Sharma / Kelley Hurst-Hess / Swati R Manjari / Nilesh K Banavali / Pallavi Ghosh / Rajendra K Agrawal /  |
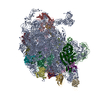
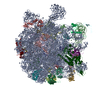
| PubMed 要旨 | HflX is a highly conserved ribosome-associated GTPase implicated in rescuing stalled ribosomes and mediating antibiotic resistance in several bacteria, including macrolide-lincosamide antibiotic ...HflX is a highly conserved ribosome-associated GTPase implicated in rescuing stalled ribosomes and mediating antibiotic resistance in several bacteria, including macrolide-lincosamide antibiotic resistance in mycobacteria. Mycobacterial HflXs carry a distinct N-terminal extension (NTE) and a small insertion, as compared to their eubacterial homologs. Here, we present several high-resolution cryo-EM structures of mycobacterial HflX in complex with the 70S ribosome and its 50S subunit, with and without antibiotics. These structures reveal a distinct mechanism for HflX-mediated ribosome splitting and antibiotic resistance in mycobacteria. Our findings indicate that the NTE of mycobacterial HflX induces persistent disordering of multiple 23S rRNA helices, facilitating the dissociation of the 70S ribosome and generating an inactive pool of 50S subunits. During this process, HflX undergoes a large conformational change that stabilizes its NTE. Mycobacterial HflX also acts as an anti-association factor by binding to predissociated 50S subunits. Our structures show that a mycobacteria-specific insertion in HflX reaches far into the peptidyl transferase center (PTC), such that it would overlap with the ribosome-bound macrolide antibiotics. However, in the presence of antibiotics, this insertion retracts, adjusts around, and interacts with the antibiotic molecules. These results suggest that mycobacterial HflX is agnostic to antibiotic presence in the PTC. It mediates antibiotic resistance by splitting antibiotic-stalled 70S ribosomes and inactivating the resulting 50S subunits. |
 リンク リンク |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:39913204 / PubMed:39913204 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.63 - 4.96 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-43267, PDB-8vio: EMDB-43294, PDB-8vk0: EMDB-43305, PDB-8vk7: EMDB-43317, PDB-8vki: EMDB-43333, PDB-8vkw: EMDB-43409, PDB-8vpk: EMDB-43476, PDB-8vr4: EMDB-43477, PDB-8vr8: EMDB-43484, PDB-8vrl:  EMDB-43778: Structure of HflX mediated, inactive Mycobacterium smegmatis 50S ribosomal subunit  EMDB-43791: Mycobacterium smegmatis 70S ribosome bound to P-tRNA  EMDB-44044: Pre-dissociated Mycobacterium smegmatis 50S ribosomal subunit-HflX-GMPPCP complex |
| 化合物 | 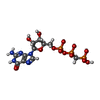 ChemComp-GCP: 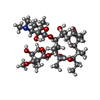 ChemComp-ERY: 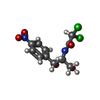 ChemComp-CLM: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | RIBOSOME / ribosome splitting / Mycobacterium smegmatis 70S / HflX / TRANSLATION / Mycobacterium smegmatis 50S / disordered 23S rRNA helices / erythromycin / chloramphenicol |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について





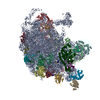
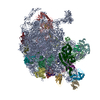


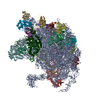
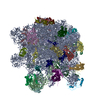


 mycolicibacterium smegmatis mc2 155 (バクテリア)
mycolicibacterium smegmatis mc2 155 (バクテリア)