[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5v5c: VQIINK, Structure of the amyloid-spine from microtubule associate... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5v5c | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | VQIINK, Structure of the amyloid-spine from microtubule associated protein tau Repeat 2 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Microtubule-associated protein tau Tau protein Tau protein | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN /  Amyloid / tau / Amyloid / tau /  Alzheimer's Disease / Alzheimer's Disease /  tauopathy / tauopathy /  MAPT MAPT | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule /  axonal transport / histone-dependent DNA binding / axonal transport / histone-dependent DNA binding /  neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of diacylglycerol kinase activity / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of diacylglycerol kinase activity / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion /  neurofibrillary tangle / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / microtubule lateral binding / neurofibrillary tangle / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / microtubule lateral binding /  tubulin complex ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / tubulin complex ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule /  axonal transport / histone-dependent DNA binding / axonal transport / histone-dependent DNA binding /  neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of diacylglycerol kinase activity / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of diacylglycerol kinase activity / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion /  neurofibrillary tangle / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / microtubule lateral binding / neurofibrillary tangle / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / microtubule lateral binding /  tubulin complex / tubulin complex /  phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / main axon / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / negative regulation of kinase activity / negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation / generation of neurons / regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of protein localization / rRNA metabolic process / internal protein amino acid acetylation / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / main axon / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / negative regulation of kinase activity / negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation / generation of neurons / regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of protein localization / rRNA metabolic process / internal protein amino acid acetylation /  regulation of mitochondrial fission / regulation of mitochondrial fission /  lipoprotein particle binding / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / axonal transport of mitochondrion / axon development / lipoprotein particle binding / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / axonal transport of mitochondrion / axon development /  central nervous system neuron development / central nervous system neuron development /  regulation of microtubule polymerization / regulation of microtubule polymerization /  microtubule polymerization / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / microtubule polymerization / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential /  dynactin binding / glial cell projection / dynactin binding / glial cell projection /  apolipoprotein binding / protein polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission / apolipoprotein binding / protein polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission /  axolemma / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / positive regulation of axon extension / supramolecular fiber organization / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / axolemma / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / positive regulation of axon extension / supramolecular fiber organization / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization /  stress granule assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / regulation of cellular response to heat / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / axon cytoplasm / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / somatodendritic compartment / stress granule assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / regulation of cellular response to heat / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / axon cytoplasm / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / somatodendritic compartment /  synapse assembly / synapse assembly /  phosphatidylinositol binding / nuclear periphery / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / protein phosphatase 2A binding / phosphatidylinositol binding / nuclear periphery / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / protein phosphatase 2A binding /  regulation of autophagy / astrocyte activation / synapse organization / microglial cell activation / response to lead ion / regulation of autophagy / astrocyte activation / synapse organization / microglial cell activation / response to lead ion /  Hsp90 protein binding / Hsp90 protein binding /  regulation of synaptic plasticity / PKR-mediated signaling / protein homooligomerization / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / regulation of synaptic plasticity / PKR-mediated signaling / protein homooligomerization / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule /  memory / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / memory / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to reactive oxygen species /  SH3 domain binding / neuron projection development / activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / microtubule cytoskeleton / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / SH3 domain binding / neuron projection development / activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / microtubule cytoskeleton / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity /  single-stranded DNA binding / cell-cell signaling / cellular response to heat / single-stranded DNA binding / cell-cell signaling / cellular response to heat /  cell body / cell body /  actin binding / actin binding /  growth cone / protein-folding chaperone binding / growth cone / protein-folding chaperone binding /  double-stranded DNA binding / double-stranded DNA binding /  microtubule binding / microtubule binding /  microtubule / amyloid fibril formation / sequence-specific DNA binding / microtubule / amyloid fibril formation / sequence-specific DNA binding /  dendritic spine / learning or memory / neuron projection / nuclear speck / dendritic spine / learning or memory / neuron projection / nuclear speck /  membrane raft / membrane raft /  axon / negative regulation of gene expression / axon / negative regulation of gene expression /  dendrite / neuronal cell body / DNA damage response / dendrite / neuronal cell body / DNA damage response /  protein kinase binding / protein kinase binding /  enzyme binding / enzyme binding /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  DNA binding DNA bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY / ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY /  electron crystallography / electron crystallography /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / molecular replacement /  cryo EM / Resolution: 1.25 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 1.25 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Seidler, P.M. / Sawaya, M.R. / Rodriguez, J.A. / Eisenberg, D.S. / Cascio, D. / Boyer, D.R. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Chem / Year: 2018Title: Structure-based inhibitors of tau aggregation. Authors: P M Seidler / D R Boyer / J A Rodriguez / M R Sawaya / D Cascio / K Murray / T Gonen / D S Eisenberg /  Abstract: Aggregated tau protein is associated with over 20 neurological disorders, which include Alzheimer's disease. Previous work has shown that tau's sequence segments VQIINK and VQIVYK drive its ...Aggregated tau protein is associated with over 20 neurological disorders, which include Alzheimer's disease. Previous work has shown that tau's sequence segments VQIINK and VQIVYK drive its aggregation, but inhibitors based on the structure of the VQIVYK segment only partially inhibit full-length tau aggregation and are ineffective at inhibiting seeding by full-length fibrils. Here we show that the VQIINK segment is the more powerful driver of tau aggregation. Two structures of this segment determined by the cryo-electron microscopy method micro-electron diffraction explain its dominant influence on tau aggregation. Of practical significance, the structures lead to the design of inhibitors that not only inhibit tau aggregation but also inhibit the ability of exogenous full-length tau fibrils to seed intracellular tau in HEK293 biosensor cells into amyloid. We also raise the possibility that the two VQIINK structures represent amyloid polymorphs of tau that may account for a subset of prion-like strains of tau. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5v5c.cif.gz 5v5c.cif.gz | 13.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5v5c.ent.gz pdb5v5c.ent.gz | 5.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5v5c.json.gz 5v5c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v5/5v5c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v5/5v5c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v5/5v5c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v5/5v5c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8635MC 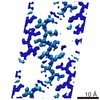 8634C  5v5bC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 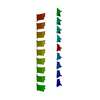
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide |  Tau protein / Neurofibrillary tangle protein / Paired helical filament-tau / PHF-tau Tau protein / Neurofibrillary tangle protein / Paired helical filament-tau / PHF-tauMass: 714.873 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: Repeat 2 peptide (UNP residues 592-597) / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P10636*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P10636*PLUS |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: 3D ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method:  electron crystallography electron crystallography |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: VQIINK Tau peptide / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| EM crystal formation | Temperature: 291 K |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES / Details: 3D micro-crystal : YES / Details: 3D micro-crystal |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 1.48 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 17.08 % |
Crystal grow | Temperature: 291 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7 / Details: 0.29 M lithium nitrate, 24% PEG3350 |
-Data collection
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image recording | Electron dose: 0.1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F416 (4k x 4k) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM diffraction | Camera length: 730 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM diffraction shell | Resolution: 1.25→1.31 Å / Fourier space coverage: 71.6 % / Multiplicity: 2.5 / Num. of structure factors: 106 / Phase residual: 0.1 ° | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM diffraction stats | Details: This is a crystallography experiment. Phases were not measured. Fourier space coverage: 86.8 % / High resolution: 1.25 Å / Num. of intensities measured: 5454 / Num. of structure factors: 1226 / Phase error: 0.1 ° / Phase residual: 0.1 ° / Phase error rejection criteria: 0.1 / Rmerge: 23.9 / Rsym: 23.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diffraction source | Source: ELECTRON MICROSCOPE / Type: TECNAI F20 TEM / Wavelength: 0.0251 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: TVIPS TEMCAM-F416 / Detector: CMOS / Date: Aug 25, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 0.0251 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 0.0251 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.25→10.18 Å / Num. obs: 1226 / % possible obs: 86.8 % / Observed criterion σ(I): -3 / Redundancy: 4.449 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 5.87 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.986 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.239 / Rrim(I) all: 0.265 / Χ2: 0.821 / Net I/σ(I): 3.58 / Num. measured all: 5454 / Scaling rejects: 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement |
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM 3D crystal entity | ∠α: 90 ° / ∠β: 90 ° / ∠γ: 90 ° / A: 20.36 Å / B: 43.22 Å / C: 4.82 Å / Space group name: P21212 / Space group num: 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution method: DIFFRACTION PATTERN/LAYERLINES / Symmetry type: 3D CRYSTAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.25→10.18 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.9086 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.9428 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 0.072 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / SU R Blow DPI: 0.067 / SU Rfree Blow DPI: 0.074 / SU Rfree Cruickshank DPI: 0.07 MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.25→10.18 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.9086 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.9428 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 0.072 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / SU R Blow DPI: 0.067 / SU Rfree Blow DPI: 0.074 / SU Rfree Cruickshank DPI: 0.07
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 49.96 Å2 / Biso mean: 15.3 Å2 / Biso min: 3 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 1.25→1.4 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 5
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj





