[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-50947: Xenopus tropicalis undecorated microtubule - 15 protofilament, 3-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Xenopus tropicalis undecorated microtubule - 15 protofilament, 3-start helix | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Microtubule Tubulin Cytoskeleton Filament / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule-based process / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / GTP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species | ||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Troman LA / Moores CA | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4 items United Kingdom, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Curr Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Curr Biol / Year: 2025Title: Mechanistic basis of temperature adaptation in microtubule dynamics across frog species. Authors: Luca Troman / Ella de Gaulejac / Abin Biswas / Jennifer Stiens / Benno Kuropka / Carolyn A Moores / Simone Reber /   Abstract: Cellular processes are remarkably effective across diverse temperature ranges, even with highly conserved proteins. In the context of the microtubule cytoskeleton, which is critically involved in a ...Cellular processes are remarkably effective across diverse temperature ranges, even with highly conserved proteins. In the context of the microtubule cytoskeleton, which is critically involved in a wide range of cellular activities, this is particularly striking, as tubulin is one of the most conserved proteins while microtubule dynamic instability is highly temperature sensitive. Here, we leverage the diversity of natural tubulin variants from three closely related frog species that live at different temperatures. We determine the microtubule structure across all three species at between 3.0 and 3.6 Å resolution by cryo-electron microscopy and find small differences at the β-tubulin lateral interactions. Using in vitro reconstitution assays and quantitative biochemistry, we show that tubulin's free energy scales inversely with temperature. The observed weakening of lateral contacts and the low apparent activation energy for tubulin incorporation provide an explanation for the overall stability and higher growth rates of microtubules in cold-adapted frog species. This study thus broadens our conceptual framework for understanding microtubule dynamics and provides insights into how conserved cellular processes are tailored to different ecological niches. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_50947.map.gz emd_50947.map.gz | 217.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-50947-v30.xml emd-50947-v30.xml emd-50947.xml emd-50947.xml | 22.6 KB 22.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_50947_fsc.xml emd_50947_fsc.xml | 14.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_50947.png emd_50947.png | 203 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_50947_msk_1.map emd_50947_msk_1.map | 274.6 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-50947.cif.gz emd-50947.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_50947_additional_1.map.gz emd_50947_additional_1.map.gz emd_50947_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50947_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50947_half_map_2.map.gz emd_50947_half_map_2.map.gz | 241.9 MB 218.2 MB 218.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50947 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50947 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50947 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50947 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_50947_validation.pdf.gz emd_50947_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_50947_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_50947_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_50947_validation.xml.gz emd_50947_validation.xml.gz | 22.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_50947_validation.cif.gz emd_50947_validation.cif.gz | 29.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-50947 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-50947 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-50947 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-50947 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9g0tMC  9fvjC  9g0oC  9g0pC  9g0qC  9g0rC  9g0sC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_50947.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 274.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_50947.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 274.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
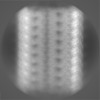
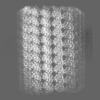
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.067 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_50947_msk_1.map emd_50947_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_50947_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_50947_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_50947_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Undecorated tubulin lattice following polymerisation with GTP (no...
| Entire | Name: Undecorated tubulin lattice following polymerisation with GTP (no stabilising ligands). |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Undecorated tubulin lattice following polymerisation with GTP (no...
| Supramolecule | Name: Undecorated tubulin lattice following polymerisation with GTP (no stabilising ligands). type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: The native tubulin was isolated from the Xenopus eggs using TOG-affinity chromatography. Microtubules were polymerised on the cryo-EM grid. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 49.87877 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHLQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEATGGKYV PRAVLVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHLQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEATGGKYV PRAVLVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQMFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNVQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMSAT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY QDATAEEEGE FEEGEEEENA UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin alpha chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.114223 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHIG QAGVQMGNAC WELYCLEHGI QQDGIIPDEK TAATDSSFGT FFSETGSGKH VPRAVFVDLE QTVIGEIRTG HYRSLFHPE QLITGKEDAA NNYARGHYTI GKEIVDSVLD RVRKMADQCS GLQGFLIFHS FGGGTGSGFT SLLMERLSVD Y GKKSKLEF ...String: MRECISIHIG QAGVQMGNAC WELYCLEHGI QQDGIIPDEK TAATDSSFGT FFSETGSGKH VPRAVFVDLE QTVIGEIRTG HYRSLFHPE QLITGKEDAA NNYARGHYTI GKEIVDSVLD RVRKMADQCS GLQGFLIFHS FGGGTGSGFT SLLMERLSVD Y GKKSKLEF SVYPAPQIST AVVEPYNSIL TTHTTLEHSD CAFMVDNEAI YDICNRNLDI ERPTYTNLNR LIGQIVSSIT AS LRFDGAL NVDLTEFQTN LVPYPRIHFP LVTYSPIISA EKAYHEQLSV PEITNACFEY SNQMVKCDPR RGKYMACCLL YRG DVVPKD VNAAIAAIKT RRSIQFVDWC PTGFKVGINY QPPTVVPGGD LAKVQRAVCM LSNTTAIAEA WARLDHKFDL MYSK RAFVH WYVGEGMEEG EFSEAREDMA ALEKDYEEVG TESGDGGDEE EDEY UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha chain |
-Macromolecule #3: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: GDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 443.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GDP: |
-Macromolecule #4: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.6 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 Component:
Details: BRB80 + 1 mM GTP | |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 40 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.00025 kPa | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 303 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP Details: The sample was incubated on the grid for 10 minutes within the Leica chamber to allow for tubulin polymerisation.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6200 / Average exposure time: 3.4 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | Chain - Source name: Other / Chain - Initial model type: other Details: 14-3 X. tropicalis tubulin dimer from this publication. |
|---|---|
| Details | Initially a tubulin dimer was docked into the density within ChimeraX, then molecular dynamics force field-based model fitting was carried out by ISOLDE using unsharpened and deepEMhancer processed density. The model was refined through iterations of ISOLDE and Phenix real_space_refinement softwares. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-9g0t: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)