[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-41401: Structural architecture of the acidic region of the B domain of c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structural architecture of the acidic region of the B domain of coagulation factor V | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Plasma Factor V - A1 domain local refinement map | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Coagulation / Pro-cofactor / Factor V / B Domain / Acidic Region / BLOOD CLOTTING | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to vitamin K / platelet alpha granule / Cargo concentration in the ER / blood circulation / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / Post-translational protein phosphorylation ...response to vitamin K / platelet alpha granule / Cargo concentration in the ER / blood circulation / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / blood coagulation / extracellular vesicle / Platelet degranulation / copper ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / extracellular space / extracellular region / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mohammed BM / Basore K / Summers B / Pelc LA / Di Cera E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Thromb Haemost / Year: 2024 Journal: J Thromb Haemost / Year: 2024Title: Structural architecture of the acidic region of the B domain of coagulation factor V. Authors: Bassem M Mohammed / Katherine Basore / Brock Summers / Leslie A Pelc / Enrico Di Cera /  Abstract: BACKGROUND: Coagulation factor (F)V features an A1-A2-B-A3-C1-C2 domain organization and functions as the inactive precursor of FVa, a component of the prothrombinase complex required for rapid ...BACKGROUND: Coagulation factor (F)V features an A1-A2-B-A3-C1-C2 domain organization and functions as the inactive precursor of FVa, a component of the prothrombinase complex required for rapid thrombin generation in the penultimate step of the coagulation cascade. An intramolecular interaction within the large B domain (residues 710-1545) involves the basic region (BR, residues 963-1008) and acidic region (AR, residues 1493-1537) and locks FV in its inactive state. However, structural information on this important regulatory interaction or on the separate architecture of the AR and BR remains elusive due to conformational disorder of the B domain. OBJECTIVES: To reveal the structure of the BR-AR interaction or of its separate components. METHODS: The structure of FV is solved by cryogenic electron microscopy. RESULTS: A new 3.05 Å resolution cryogenic electron microscopy structure of FV confirms the overall organization of the A and C domains but resolves the segment 1507 to 1545 within a largely ...RESULTS: A new 3.05 Å resolution cryogenic electron microscopy structure of FV confirms the overall organization of the A and C domains but resolves the segment 1507 to 1545 within a largely disordered B domain. The segment contains most of the AR and is organized as recently reported in FV short, a spliced variant of FV with a significantly shorter and less disordered B domain. CONCLUSION: The similar architecture of the AR in FV and FV short provides structural context for physiologically important interactions of this region with the BR in FV and with the basic C-terminal ...CONCLUSION: The similar architecture of the AR in FV and FV short provides structural context for physiologically important interactions of this region with the BR in FV and with the basic C-terminal end of tissue factor pathway inhibitor α in FV short. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41401.map.gz emd_41401.map.gz | 32.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41401-v30.xml emd-41401-v30.xml emd-41401.xml emd-41401.xml | 18 KB 18 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_41401_fsc.xml emd_41401_fsc.xml emd_41401_fsc_2.xml emd_41401_fsc_2.xml | 8.4 KB 11.7 KB | Display Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_41401.png emd_41401.png | 116.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_41401_msk_1.map emd_41401_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41401.cif.gz emd-41401.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41401_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41401_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41401_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41401_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.5 MB 59.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41401 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41401 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41401 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41401 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_41401_validation.pdf.gz emd_41401_validation.pdf.gz | 813.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_41401_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_41401_full_validation.pdf.gz | 812.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_41401_validation.xml.gz emd_41401_validation.xml.gz | 16.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_41401_validation.cif.gz emd_41401_validation.cif.gz | 21 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-41401 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-41401 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-41401 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-41401 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8tn9C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41401.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41401.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Plasma Factor V - A1 domain local refinement map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_41401_msk_1.map emd_41401_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
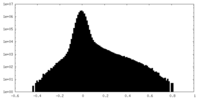
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_41401_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_41401_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Coagulation plasma Factor V
| Entire | Name: Coagulation plasma Factor V |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Coagulation plasma Factor V
| Supramolecule | Name: Coagulation plasma Factor V / type: tissue / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood |
-Macromolecule #1: Coagulation Plasma Factor V
| Macromolecule | Name: Coagulation Plasma Factor V / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood |
| Sequence | String: AQLRQFYVAA QGISWSYRPE PTNSSLNLSV TSFKKIVYRE YEPYFKKEKP QSTISGLLGP TLYAEVGDII KVHFKNKADK PLSIHPQGIR YSKLSEGASY LDHTFPAEKM DDAVAPGREY TYEWSISEDS GPTHDDPPCL THIYYSHENL IEDFNSGLIG PLLICKKGTL ...String: AQLRQFYVAA QGISWSYRPE PTNSSLNLSV TSFKKIVYRE YEPYFKKEKP QSTISGLLGP TLYAEVGDII KVHFKNKADK PLSIHPQGIR YSKLSEGASY LDHTFPAEKM DDAVAPGREY TYEWSISEDS GPTHDDPPCL THIYYSHENL IEDFNSGLIG PLLICKKGTL TEGGTQKTFD KQIVLLFAVF DESKSWSQSS SLMYTVNGYV NGTMPDITVC AHDHISWHLL GMSSGPELFS IHFNGQVLEQ NHHKVSAITL VSATSTTANM TVGPEGKWII SSLTPKHLQA GMQAYIDIKN CPKKTRNLKK ITREQRRHMK RWEYFIAAEE VIWDYAPVIP ANMDKKYRSQ HLDNFSNQIG KHYKKVMYTQ YEDESFTKHT VNPNMKEDGI LGPIIRAQVR DTLKIVFKNM ASRPYSIYPH GVTFSPYEDE VNSSFTSGRN NTMIRAVQPG ETYTYKWNIL EFDEPTENDA QCLTRPYYSD VDIMRDIASG LIGLLLICKS RSLDRRGIQR AADIEQQAVF AVFDENKSWY LEDNINKFCE NPDEVKRDDP KFYESNIMST INGYVPESIT TLGFCFDDTV QWHFCSVGTQ NEILTIHFTG HSFIYGKRHE DTLTLFPMRG ESVTVTMDNV GTWMLTSMNS SPRSKKLRLK FRDVKCIPDD DEDSYEIFEP PESTVMATRK MHDRLEPEDE ESDADYDYQN RLAAALGIRS FRNSSLNQEE EEFNLTALAL ENGTEFVSSN TDIIVGSNYS SPSNISKFTV NNLAEPQKAP SHQQATTAGS PLRHLIGKNS VLNSSTAEHS SPYSEDPIED PLQPDVTGIR LLSLGAGEFR SQEHAKRKGP KVERDQAAKH RFSWMKLLAH KVGRHLSQDT GSPSGMRPWE DLPSQDTGSP SRMRPWEDPP SDLLLLKQSN SSKILVGRWH LASEKGSYEI IQDTDEDTAV NNWLISPQNA SRAWGESTPL ANKPGKQSGH PKFPRVRHKS LQVRQDGGKS RLKKSQFLIK TRKKKKEKHT HHAPLSPRTF HPLRSEAYNT FSERRLKHSL VLHKSNETSL PTDLNQTLPS MDFGWIASLP DHNQNSSNDT GQASCPPGLY QTVPPEEHYQ TFPIQDPDQM HSTSDPSHRS SSPELSEMLE YDRSHKSFPT DISQMSPSSE HEVWQTVISP DLSQVTLSPE LSQTNLSPDL SHTTLSPELI QRNLSPALGQ MPISPDLSHT TLSPDLSHTT LSLDLSQTNL SPELSQTNLS PALGQMPLSP DLSHTTLSLD FSQTNLSPEL SHMTLSPELS QTNLSPALGQ MPISPDLSHT TLSLDFSQTN LSPELSQTNL SPALGQMPLS PDPSHTTLSL DLSQTNLSPE LSQTNLSPDL SEMPLFADLS QIPLTPDLDQ MTLSPDLGET DLSPNFGQMS LSPDLSQVTL SPDISDTTLL PDLSQISPPP DLDQIFYPSE SSQSLLLQEF NESFPYPDLG QMPSPSSPTL NDTFLSKEFN PLVIVGLSKD GTDYIEIIPK EEVQSSEDDY AEIDYVPYDD PYKTDVRTNI NSSRDPDNIA AWYLRSNNGN RRNYYIAAEE ISWDYSEFVQ RETDIEDSDD IPEDTTYKKV VFRKYLDSTF TKRDPRGEYE EHLGILGPII RAEVDDVIQV RFKNLASRPY SLHAHGLSYE KSSEGKTYED DSPEWFKEDN AVQPNSSYTY VWHATERSGP ESPGSACRAW AYYSAVNPEK DIHSGLIGPL LICQKGILHK DSNMPVDMRE FVLLFMTFDE KKSWYYEKKS RSSWRLTSSE MKKSHEFHAI NGMIYSLPGL KMYEQEWVRL HLLNIGGSQD IHVVHFHGQT LLENGNKQHQ LGVWPLLPGS FKTLEMKASK PGWWLLNTEV GENQRAGMQT PFLIMDRDCR MPMGLSTGII SDSQIKASEF LGYWEPRLAR LNNGGSYNAW SVEKLAAEFA SKPWIQVDMQ KEVIITGIQT QGAKHYLKSC YTTEFYVAYS SNQINWQIFK GNSTRNVMYF NGNSDASTIK ENQFDPPIVA RYIRISPTRA YNRPTLRLEL QGCEVNGCST PLGMENGKIE NKQITASSFK KSWWGDYWEP FRARLNAQGR VNAWQAKANN NKQWLEIDLL KIKKITAIIT QGCKSLSSEM YVKSYTIHYS EQGVEWKPYR LKSSMVDKIF EGNTNTKGHV KNFFNPPIIS RFIRVIPKTW NQSITLRLEL FGCDIY UniProtKB: Coagulation factor V |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 20 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4000 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4000 pixel / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 8429 / Average exposure time: 1.65 sec. / Average electron dose: 66.0 e/Å2 Details: 2 Grids imaged one at 0.1 mg/mL and the second at 0.2 mg/mL using the same acquisition parameters. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 0.01 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)