+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ABCG25 Wild Type in Apo-state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ABA / ABCG / plant hormone / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Protein of unknown function DUF1425 / YcfL-like superfamily / Protein of unknown function (DUF1425) / Prokaryotic membrane lipoprotein lipid attachment site profile. / DUF1425 domain-containing protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sun L / Liu X / Ying W / Liao L / Wei H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for abscisic acid efflux mediated by ABCG25 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Authors: Wei Ying / Lianghuan Liao / Hong Wei / Yongxiang Gao / Xin Liu / Linfeng Sun /  Abstract: Abscisic acid (ABA) is a phytohormone essential to the regulation of numerous aspects of plant growth and development. The cellular level of ABA is critical to its signalling and is determined by its ...Abscisic acid (ABA) is a phytohormone essential to the regulation of numerous aspects of plant growth and development. The cellular level of ABA is critical to its signalling and is determined by its rate of biosynthesis, catabolism and the rates of ABA transport. ABCG25 in Arabidopsis thaliana has been identified to be an ABA exporter and play roles in regulating stomatal closure and seed germination. However, its ABA transport mechanism remains unknown. Here we report the structures of ABCG25 under different states using cryo-electron microscopy single particle analysis: the apo state and ABA-bound state of the wild-type ABCG25 and the ATP-bound state of the ATPase catalytic mutant. ABCG25 forms a homodimer. ABA binds to a cone-shaped, cytosolic-facing cavity formed in the middle of the transmembrane domains. Key residues in ABA binding are identified and verified by a cell-based ABA transport assay. ATP binding leads to closing of the nucleotide-binding domains of opposing monomers and conformational transitions of the transmembrane domains. Together, these results provide insights into the substrate recognition and transport mechanisms of ABCG25 in Arabidopsis, and facilitate our understanding of the ABA transport and signalling pathway in plants. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35768.map.gz emd_35768.map.gz | 49.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35768-v30.xml emd-35768-v30.xml emd-35768.xml emd-35768.xml | 13.5 KB 13.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_35768.png emd_35768.png | 155 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35768.cif.gz emd-35768.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35768_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35768_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35768_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35768_half_map_2.map.gz | 48.1 MB 48.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35768 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35768 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_35768_validation.pdf.gz emd_35768_validation.pdf.gz | 747.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_35768_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_35768_full_validation.pdf.gz | 747.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_35768_validation.xml.gz emd_35768_validation.xml.gz | 11.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_35768_validation.cif.gz emd_35768_validation.cif.gz | 13.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35768 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35768 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8iwjMC  8iwkC  8iwnC  8k0xC  8k0zC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35768.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35768.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
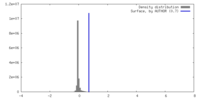
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half map 1
| File | emd_35768_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map 2
| File | emd_35768_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ABCG25 from Arabidopsis thaliana
| Entire | Name: ABCG25 from Arabidopsis thaliana |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ABCG25 from Arabidopsis thaliana
| Supramolecule | Name: ABCG25 from Arabidopsis thaliana / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: ABC transporter G family member 25
| Macromolecule | Name: ABC transporter G family member 25 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 72.983867 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSAFDGVENQ MNGPDSSPRL SQDPREPRSL LSSSCFPITL KFVDVCYRVK IHGMSNDSCN IKKLLGLKQK PSDETRSTEE RTILSGVTG MISPGEFMAV LGPSGSGKST LLNAVAGRLH GSNLTGKILI NDGKITKQTL KRTGFVAQDD LLYPHLTVRE T LVFVALLR ...String: MSAFDGVENQ MNGPDSSPRL SQDPREPRSL LSSSCFPITL KFVDVCYRVK IHGMSNDSCN IKKLLGLKQK PSDETRSTEE RTILSGVTG MISPGEFMAV LGPSGSGKST LLNAVAGRLH GSNLTGKILI NDGKITKQTL KRTGFVAQDD LLYPHLTVRE T LVFVALLR LPRSLTRDVK LRAAESVISE LGLTKCENTV VGNTFIRGIS GGERKRVSIA HELLINPSLL VLDEPTSGLD AT AALRLVQ TLAGLAHGKG KTVVTSIHQP SSRVFQMFDT VLLLSEGKCL FVGKGRDAMA YFESVGFSPA FPMNPADFLL DLA NGVCQT DGVTEREKPN VRQTLVTAYD TLLAPQVKTC IEVSHFPQDN ARFVKTRVNG GGITTCIATW FSQLCILLHR LLKE RRHES FDLLRIFQVV AASILCGLMW WHSDYRDVHD RLGLLFFISI FWGVLPSFNA VFTFPQERAI FTRERASGMY TLSSY FMAH VLGSLSMELV LPASFLTFTY WMVYLRPGIV PFLLTLSVLL LYVLASQGLG LALGAAIMDA KKASTIVTVT MLAFVL TGG YYVNKVPSGM VWMKYVSTTF YCYRLLVAIQ YGSGEEILRM LGCDSKGKQG ASAATSAGCR FVEEEVIGDV GMWTSVG VL FLMFFGYRVL AYLALRRIKH UniProtKB: DUF1425 domain-containing protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 2.3000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 174479 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)