+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8k0z | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ABCG25 Wild Type purified with DDM in the apo-state | ||||||
 Components Components | ABC transporter G family member 25 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / ABA / ABCG / plant hormone | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintercellular transport / negative regulation of post-embryonic development / abscisic acid transport / export from cell / response to abscisic acid / abscisic acid-activated signaling pathway / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type transporter activity / response to cold ...intercellular transport / negative regulation of post-embryonic development / abscisic acid transport / export from cell / response to abscisic acid / abscisic acid-activated signaling pathway / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type transporter activity / response to cold / transmembrane transport / response to heat / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Sun, L. / Liu, X. / Ying, W. / Liao, L. / Wei, H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for abscisic acid efflux mediated by ABCG25 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Authors: Wei Ying / Lianghuan Liao / Hong Wei / Yongxiang Gao / Xin Liu / Linfeng Sun /  Abstract: Abscisic acid (ABA) is a phytohormone essential to the regulation of numerous aspects of plant growth and development. The cellular level of ABA is critical to its signalling and is determined by its ...Abscisic acid (ABA) is a phytohormone essential to the regulation of numerous aspects of plant growth and development. The cellular level of ABA is critical to its signalling and is determined by its rate of biosynthesis, catabolism and the rates of ABA transport. ABCG25 in Arabidopsis thaliana has been identified to be an ABA exporter and play roles in regulating stomatal closure and seed germination. However, its ABA transport mechanism remains unknown. Here we report the structures of ABCG25 under different states using cryo-electron microscopy single particle analysis: the apo state and ABA-bound state of the wild-type ABCG25 and the ATP-bound state of the ATPase catalytic mutant. ABCG25 forms a homodimer. ABA binds to a cone-shaped, cytosolic-facing cavity formed in the middle of the transmembrane domains. Key residues in ABA binding are identified and verified by a cell-based ABA transport assay. ATP binding leads to closing of the nucleotide-binding domains of opposing monomers and conformational transitions of the transmembrane domains. Together, these results provide insights into the substrate recognition and transport mechanisms of ABCG25 in Arabidopsis, and facilitate our understanding of the ABA transport and signalling pathway in plants. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8k0z.cif.gz 8k0z.cif.gz | 193.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8k0z.ent.gz pdb8k0z.ent.gz | 154.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8k0z.json.gz 8k0z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k0/8k0z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k0/8k0z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k0/8k0z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k0/8k0z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  36781MC  8iwjC  8iwkC  8iwnC  8k0xC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 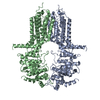
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 72983.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ABCG25 wild-type from Arabidopsis thaliana purified with DDM Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 2300 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Category: model refinement |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 172609 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj

