+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-31399 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
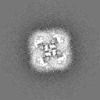
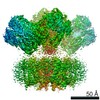
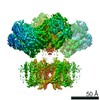
| タイトル | CryoEM structure of human Kv4.2 | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | membrane protein | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex / A-type (transient outward) potassium channel activity / Phase 1 - inactivation of fast Na+ channels / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / anchoring junction / postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuronal cell body membrane / locomotor rhythm ...Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex / A-type (transient outward) potassium channel activity / Phase 1 - inactivation of fast Na+ channels / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / anchoring junction / postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuronal cell body membrane / locomotor rhythm / regulation of heart contraction / action potential / plasma membrane raft / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / neuronal action potential / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sensory perception of pain / muscle contraction / protein homooligomerization / GABA-ergic synapse / cellular response to hypoxia / perikaryon / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / postsynaptic membrane / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse / metal ion binding / plasma membrane 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Kise Y / Nureki O | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  日本, 1件 日本, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2021 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2021タイトル: Structural basis of gating modulation of Kv4 channel complexes. 著者: Yoshiaki Kise / Go Kasuya / Hiroyuki H Okamoto / Daichi Yamanouchi / Kan Kobayashi / Tsukasa Kusakizako / Tomohiro Nishizawa / Koichi Nakajo / Osamu Nureki /  要旨: Modulation of voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels by auxiliary subunits is central to the physiological function of channels in the brain and heart. Native Kv4 tetrameric channels form ...Modulation of voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels by auxiliary subunits is central to the physiological function of channels in the brain and heart. Native Kv4 tetrameric channels form macromolecular ternary complexes with two auxiliary β-subunits-intracellular Kv channel-interacting proteins (KChIPs) and transmembrane dipeptidyl peptidase-related proteins (DPPs)-to evoke rapidly activating and inactivating A-type currents, which prevent the backpropagation of action potentials. However, the modulatory mechanisms of Kv4 channel complexes remain largely unknown. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the Kv4.2-DPP6S-KChIP1 dodecamer complex, the Kv4.2-KChIP1 and Kv4.2-DPP6S octamer complexes, and Kv4.2 alone. The structure of the Kv4.2-KChIP1 complex reveals that the intracellular N terminus of Kv4.2 interacts with its C terminus that extends from the S6 gating helix of the neighbouring Kv4.2 subunit. KChIP1 captures both the N and the C terminus of Kv4.2. In consequence, KChIP1 would prevent N-type inactivation and stabilize the S6 conformation to modulate gating of the S6 helices within the tetramer. By contrast, unlike the reported auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated channel complexes, DPP6S interacts with the S1 and S2 helices of the Kv4.2 voltage-sensing domain, which suggests that DPP6S stabilizes the conformation of the S1-S2 helices. DPP6S may therefore accelerate the voltage-dependent movement of the S4 helices. KChIP1 and DPP6S do not directly interact with each other in the Kv4.2-KChIP1-DPP6S ternary complex. Thus, our data suggest that two distinct modes of modulation contribute in an additive manner to evoke A-type currents from the native Kv4 macromolecular complex. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_31399.map.gz emd_31399.map.gz | 3.8 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-31399-v30.xml emd-31399-v30.xml emd-31399.xml emd-31399.xml | 14 KB 14 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_31399.png emd_31399.png | 61.5 KB | ||
| マスクデータ |  emd_31399_msk_1.map emd_31399_msk_1.map | 30.5 MB |  マスクマップ マスクマップ | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-31399.cif.gz emd-31399.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_31399_half_map_1.map.gz emd_31399_half_map_1.map.gz emd_31399_half_map_2.map.gz emd_31399_half_map_2.map.gz | 20.4 MB 20.4 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31399 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31399 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_31399_validation.pdf.gz emd_31399_validation.pdf.gz | 668.5 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_31399_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_31399_full_validation.pdf.gz | 668.1 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_31399_validation.xml.gz emd_31399_validation.xml.gz | 10.4 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_31399_validation.cif.gz emd_31399_validation.cif.gz | 12.3 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31399 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31399 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  7f0jMC  7e7zC  7e83C  7e84C  7e87C  7e89C  7e8bC  7e8eC  7e8gC  7e8hC  7f3fC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_31399.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 30.5 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_31399.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 30.5 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
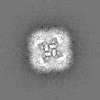
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.411 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
-マスク #1
| ファイル |  emd_31399_msk_1.map emd_31399_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
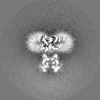
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_31399_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_31399_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : human Kv4.2
| 全体 | 名称: human Kv4.2 |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: human Kv4.2
| 超分子 | 名称: human Kv4.2 / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: #1 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
-分子 #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2
| 分子 | 名称: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2 タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 4 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 70.61843 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 配列 | 文字列: MAAGVAAWLP FARAAAIGWM PVASGPMPAP PRQERKRTQD ALIVLNVSGT RFQTWQDTLE RYPDTLLGSS ERDFFYHPET QQYFFDRDP DIFRHILNFY RTGKLHYPRH ECISAYDEEL AFFGLIPEII GDCCYEEYKD RRRENAERLQ DDADTDTAGE S ALPTMTAR ...文字列: MAAGVAAWLP FARAAAIGWM PVASGPMPAP PRQERKRTQD ALIVLNVSGT RFQTWQDTLE RYPDTLLGSS ERDFFYHPET QQYFFDRDP DIFRHILNFY RTGKLHYPRH ECISAYDEEL AFFGLIPEII GDCCYEEYKD RRRENAERLQ DDADTDTAGE S ALPTMTAR QRVWRAFENP HTSTMALVFY YVTGFFIAVS VIANVVETVP CGSSPGHIKE LPCGERYAVA FFCLDTACVM IF TVEYLLR LAAAPSRYRF VRSVMSIIDV VAILPYYIGL VMTDNEDVSG AFVTLRVFRV FRIFKFSRHS QGLRILGYTL KSC ASELGF LLFSLTMAII IFATVMFYAE KGSSASKFTS IPAAFWYTIV TMTTLGYGDM VPKTIAGKIF GSICSLSGVL VIAL PVPVI VSNFSRIYHQ NQRADKRRAQ KKARLARIRA AKSGSANAYM QSKRNGLLSN QLQSSEDEQA FVSKSGSSFE TQHHH LLHC LEKTTNHEFV DEQVFEESCM EVATVNRPSS HSPSLSSQQG VTSTCCSRRH KKTFRIPNAN VSGSHQGSIQ ELSTIQ IRC VERTPLSNSR SSLNAKMEEC VKLNCEQPYV TTAIISIPTP PVTTPEGDDR PESPEYSGGN IVRVSAL UniProtKB: A-type voltage-gated potassium channel KCND2 |
-分子 #2: ZINC ION
| 分子 | 名称: ZINC ION / タイプ: ligand / ID: 2 / コピー数: 4 / 式: ZN |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 65.409 Da |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 初期モデル | モデルのタイプ: OTHER |
|---|---|
| 最終 再構成 | 想定した対称性 - 点群: C4 (4回回転対称) / 解像度のタイプ: BY AUTHOR / 解像度: 2.9 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 使用した粒子像数: 70625 |
| 初期 角度割当 | タイプ: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| 最終 角度割当 | タイプ: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
-原子モデル構築 1
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL |
|---|---|
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-7f0j: |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)