+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6hd5 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
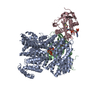
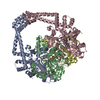
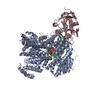
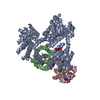
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the ribosome-NatA complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSLATION / N-terminal acetylation / protein modification / ribosome / expansion segments | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein-N-terminal-glutamate acetyltransferase activity / N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatE / N-terminal amino-acid Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatA / NatA complex / protein N-terminal-serine acetyltransferase activity / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal-alanine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / acetyltransferase activator activity / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion ...protein-N-terminal-glutamate acetyltransferase activity / N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatE / N-terminal amino-acid Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatA / NatA complex / protein N-terminal-serine acetyltransferase activity / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal-alanine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / acetyltransferase activator activity / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / ribosome binding / mitochondrion / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Knorr, A.G. / Becker, T. / Beckmann, R. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019Title: Ribosome-NatA architecture reveals that rRNA expansion segments coordinate N-terminal acetylation. Authors: Alexandra G Knorr / Christian Schmidt / Petr Tesina / Otto Berninghausen / Thomas Becker / Birgitta Beatrix / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: The majority of eukaryotic proteins are N-terminally α-acetylated by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). Acetylation usually occurs co-translationally and defects have severe consequences. ...The majority of eukaryotic proteins are N-terminally α-acetylated by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). Acetylation usually occurs co-translationally and defects have severe consequences. Nevertheless, it is unclear how these enzymes act in concert with the translating ribosome. Here, we report the structure of a native ribosome-NatA complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. NatA (comprising Naa10, Naa15 and Naa50) displays a unique mode of ribosome interaction by contacting eukaryotic-specific ribosomal RNA expansion segments in three out of four binding patches. Thereby, NatA is dynamically positioned directly underneath the ribosomal exit tunnel to facilitate modification of the emerging nascent peptide chain. Methionine amino peptidases, but not chaperones or signal recognition particle, would be able to bind concomitantly. This work assigns a function to the hitherto enigmatic ribosomal RNA expansion segments and provides mechanistic insights into co-translational protein maturation by N-terminal acetylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6hd5.cif.gz 6hd5.cif.gz | 248.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6hd5.ent.gz pdb6hd5.ent.gz | 196.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6hd5.json.gz 6hd5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hd/6hd5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hd/6hd5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hd/6hd5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hd/6hd5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0201MC  0202C  0203C  6hd7C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 99050.133 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: ribosome binding subunit Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P12945 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 27635.168 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: catalytic subunit Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P07347, N-terminal amino-acid Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatA |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 19753.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: ribosome binding subunit Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: Q08689, N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatE |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ribosome-NatA complex / Type: COMPLEX Details: Map was refined on NatA. Coordinates are deposited for NatA only. Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 2.5 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 262507 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj





