+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21138 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
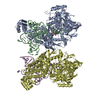
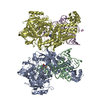
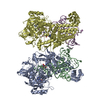
| Title | Mono-ubiquitinated Fanconi Anemia ID complex bound to ICL DNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | consensus reconstruction | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of CD40 signaling pathway / regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation / homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis / gamete generation / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / neuronal stem cell population maintenance / brain morphogenesis / DNA repair complex / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / interstrand cross-link repair ...regulation of CD40 signaling pathway / regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation / homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis / gamete generation / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / neuronal stem cell population maintenance / brain morphogenesis / DNA repair complex / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / interstrand cross-link repair / DNA polymerase binding / condensed chromosome / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Pexophagy / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLI / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Josephin domain DUBs / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / response to gamma radiation / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / Regulation of signaling by CBL / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Degradation of DVL / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / Iron uptake and transport / Negative regulation of FGFR2 signaling / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / Degradation of AXIN / Peroxisomal protein import Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pavletich NP | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: DNA clamp function of the monoubiquitinated Fanconi anaemia ID complex. Authors: Renjing Wang / Shengliu Wang / Ankita Dhar / Christopher Peralta / Nikola P Pavletich /  Abstract: The ID complex, involving the proteins FANCI and FANCD2, is required for the repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICL) and related lesions. These proteins are mutated in Fanconi anaemia, a disease ...The ID complex, involving the proteins FANCI and FANCD2, is required for the repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICL) and related lesions. These proteins are mutated in Fanconi anaemia, a disease in which patients are predisposed to cancer. The Fanconi anaemia pathway of ICL repair is activated when a replication fork stalls at an ICL; this triggers monoubiquitination of the ID complex, in which one ubiquitin molecule is conjugated to each of FANCI and FANCD2. Monoubiquitination of ID is essential for ICL repair by excision, translesion synthesis and homologous recombination; however, its function remains unknown. Here we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of the monoubiquitinated human ID complex bound to DNA, and reveal that it forms a closed ring that encircles the DNA. By comparison with the structure of the non-ubiquitinated ID complex bound to ICL DNA-which we also report here-we show that monoubiquitination triggers a complete rearrangement of the open, trough-like ID structure through the ubiquitin of one protomer binding to the other protomer in a reciprocal fashion. These structures-together with biochemical data-indicate that the monoubiquitinated ID complex loses its preference for ICL and related branched DNA structures, and becomes a sliding DNA clamp that can coordinate the subsequent repair reactions. Our findings also reveal how monoubiquitination in general can induce an alternative protein structure with a new function. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21138.map.gz emd_21138.map.gz | 59.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21138-v30.xml emd-21138-v30.xml emd-21138.xml emd-21138.xml | 25 KB 25 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21138.png emd_21138.png | 147.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_21138_additional_1.map.gz emd_21138_additional_1.map.gz emd_21138_additional_2.map.gz emd_21138_additional_2.map.gz emd_21138_additional_3.map.gz emd_21138_additional_3.map.gz emd_21138_additional_4.map.gz emd_21138_additional_4.map.gz | 1.9 MB 59.8 MB 59.9 MB 59.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21138 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21138 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21138 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21138 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_21138_validation.pdf.gz emd_21138_validation.pdf.gz | 443 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_21138_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_21138_full_validation.pdf.gz | 442.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_21138_validation.xml.gz emd_21138_validation.xml.gz | 5.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_21138_validation.cif.gz emd_21138_validation.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21138 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21138 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21138 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21138 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 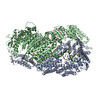 6vaeMC  6vaaC  6vadC  6vafC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21138.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21138.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
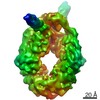
| Annotation | consensus reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08847 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
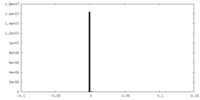
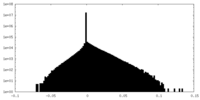
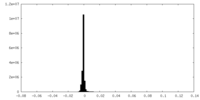
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: refmac composite map
| File | emd_21138_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | refmac composite map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
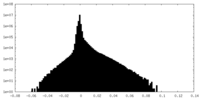
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: focus3 map
| File | emd_21138_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | focus3 map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: focus2 map
| File | emd_21138_additional_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | focus2 map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: focus1 map
| File | emd_21138_additional_4.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | focus1 map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Mono-ubiquitinated Fanconi Anemia ID complex bound to DNA
| Entire | Name: Mono-ubiquitinated Fanconi Anemia ID complex bound to DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Mono-ubiquitinated Fanconi Anemia ID complex bound to DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: Mono-ubiquitinated Fanconi Anemia ID complex bound to DNA type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Fanconi anemia, complementation group I
| Macromolecule | Name: Fanconi anemia, complementation group I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: isopeptide bond between Lys523 Nz and the C-terminus of ubiquitin (chain C) Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 149.566047 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDQKILSLAA EKTADKLQEF LQTLREGDLT NLLQNQAVKG KVAGALLRAI FKGSPCSEEA GTLRRRKIYT CCIQLVESGD LQKEIVSEI IGLLMLEAHH FPGPLLVELA NEFISAVREG SLVNGKSLEL LPIILTVLAT KKENLAYGKG VLSGEECKKQ L INTLCSGR ...String: MDQKILSLAA EKTADKLQEF LQTLREGDLT NLLQNQAVKG KVAGALLRAI FKGSPCSEEA GTLRRRKIYT CCIQLVESGD LQKEIVSEI IGLLMLEAHH FPGPLLVELA NEFISAVREG SLVNGKSLEL LPIILTVLAT KKENLAYGKG VLSGEECKKQ L INTLCSGR WDQQYVIQLT SMFKDVPLTA EEVEFVVEKA LSMFSKMNLQ EIPPLVYQLL VLSSKGSRKS VLEGIIAFFS AL DKQHNEE QSGDELLDVV TVPSGELRHV EGTIILHIVF AIKLDYELGR ELVKHLKVGQ QGDSNNNLSP FSIALLLSVT RIQ RFQDQV LDLLKTSVVK SFKDLQLLQG SKFLQNLVPH RSYVSTMILE VVKNSVHSWD HVTQGLVELG FILMDSYGPK KVLD GKTIE TSPSLSRMPN QHACKLGANI LLETFKIHEM IRQEILEQVL NRVVTRASSP ISHFLDLLSN IVMYAPLVLQ NCSSK VTEA FDYLSFLPLQ TVQRLLKAVQ PLLKVSMSMR DCLILVLRKA MFANQLDARK SAVAGFLLLL KNFKVLGSLS SSQCSQ SLS VSQVHVDVHS HYNSVANETF CLEIMDSLRR CLSQQADVRL MLYEGFYDVL RRNSQLANSV MQTLLSQLKQ FYEPEPD LL PPLKLEACIL TQGDQISLQE PLDYLLCCIQ HCLAWYKNTV IPLQQGEEEE EEEEAFYEDL DDILESITNR MIKSELED F ELDKSADFSQ STSIGIKNNI SAFLVMGVCE VLIEYNFSIS SFSKNRFEDI LSLFMCYKKL SDILNEKAGK AKTKMANKT SDSLLSMKFV SSLLTALFRD SIQSHQESLS VLRSSNEFMR YAVNVALQKV QQLKETGHVS GPDGQNPEKI FQNLCDLTRV LLWRYTSIP TSVEESGKKE KGKSISLLCL EGLQKIFSAV QQFYQPKIQQ FLRALDVTDK EGEEREDADV SVTQRTAFQI R QFQRSLLN LLSSQEEDFN SKEALLLVTV LTSLSKLLEP SSPQFVQMLS WTSKICKENS REDALFCKSL MNLLFSLHVS YK SPVILLR DLSQDIHGHL GDIDQDVEVE KTNHFAIVNL RTAAPTVCLL VLSQAEKVLE EVDWLITKLK GQVSQETLSE EAS SQATLP NQPVEKAIIM QLGTLLTFFH ELVQTALPSG SCVDTLLKDL CKMYTTLTAL VRYYLQVCQS SGGIPKNMEK LVKL SGSHL TPLCYSFISY VQNKSKSLNY TGEKKEKPAV VATAMARVLR ETKPIPNLIF AIEQYEKFLI HLSKKSKVSL MQHMK LSTS RDFKIKGNIL DMVLREDGED ENEEGTASEH GGQNKEPAKK KRKK |
-Macromolecule #2: Fanconi anemia group D2 protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Fanconi anemia group D2 protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: isopeptide bond between Lys561 Nz and the C-terminus of ubiquitin (chain D) Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 164.314516 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVSKRRLSKS EDKESLTEDA SKTRKQPLSK KTKKSHIANE VEENDSIFVK LLKISGIILK TGESQNQLAV DQIAFQKKLF QTLRRHPSY PKIIEEFVSG LESYIEDEDS FRNCLLSCER LQDEEASMGA SYSKSLIKLL LGIDILQPAI IKTLFEKLPE Y FFENKNSD ...String: MVSKRRLSKS EDKESLTEDA SKTRKQPLSK KTKKSHIANE VEENDSIFVK LLKISGIILK TGESQNQLAV DQIAFQKKLF QTLRRHPSY PKIIEEFVSG LESYIEDEDS FRNCLLSCER LQDEEASMGA SYSKSLIKLL LGIDILQPAI IKTLFEKLPE Y FFENKNSD EINIPRLIVS QLKWLDRVVD GKDLTTKIMQ LISIAPENLQ HDIITSLPEI LGDSQHADVG KELSDLLIEN TS LTVPILD VLSSLRLDPN FLLKVRQLVM DKLSSIRLED LPVIIKFILH SVTAMDTLEV ISELREKLDL QHCVLPSRLQ ASQ VKLKSK GRASSSGNQE SSGQSCIILL FDVIKSAIRY EKTISEAWIK AIENTASVSE HKVFDLVMLF IIYSTNTQTK KYID RVLRN KIRSGCIQEQ LLQSTFSVHY LVLKDMCSSI LSLAQSLLHS LDQSIISFGS LLYKYAFKFF DTYCQQEVVG ALVTH ICSG NEAEVDTALD VLLELVVLNP SAMMMNAVFV KGILDYLDNI SPQQIRKLFY VLSTLAFSKQ NEASSHIQDD MHLVIR KQL SSTVFKYKLI GIIGAVTMAG IMAADRSESP SLTQERANLS DEQCTQVTSL LQLVHSCSEQ SPQASALYYD EFANLIQ HE KLDPKALEWV GQTICNDFQD AFVVDSCVVP EGDFPFPVKA LYGLEEYDTQ NGIAINLLPL LFSQDFAKDG GPVTSQES G QKLVSPLCLA PYFRLLRLCV ERQHNGNLEE IDGLLDCPIF LTDLEPGEKL ESMSAKERSF MCSLIFLTLN WFREIVNAF CQETSPEMKG KVLTRLKHIV ELQIILEKYL AVTPDYVPPL GNFDVETLDI TPHTVTAISA KIRKKGKIER KQKTDGSKTS SSDTLSEEK NSECDPTPSH RGQLNKEFTG KEEKTSLLLH NSHAFFRELD IEVFSILHCG LVTKFILDTE MHTEATEVVQ L GPPELLFL LEDLSQKLES MLTPPIARRV PFLKNKGSRN IGFSHLQQRS AQEIVHCVFQ LLTPMCNHLE NIHNYFQCLA AE NHGVVDG PGVKVQEYHI MSSCYQRLLQ IFHGLFAWSG FSQPENQNLL YSALHVLSSR LKQGEHSQPL EELLSQSVHY LQN FHQSIP SFQCALYLIR LLMVILEKST ASAQNKEKIA SLARQFLCRV WPSGDKEKSN ISNDQLHALL CIYLEHTESI LKAI EEIAG VGVPELINSP KDASSSTFPT LTRHTFVVFF RVMMAELEKT VKKIEPGTAA DSQQIHEEKL LYWNMAVRDF SILIN LIKV FDSHPVLHVC LKYGRLFVEA FLKQCMPLLD FSFRKHREDV LSLLETFQLD TRLLHHLCGH SKIHQDTRLT QHVPLL KKT LELLVCRVKA MLTLNNCREA FWLGNLKNRD LQGEEIKSQN SQESTADESE DDMSSQASKS KATEDGEEDE VSAGEKE QD SDESYDDSD |
-Macromolecule #3: Ubiquitin
| Macromolecule | Name: Ubiquitin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: isopeptide bond between C-terminus of ubiquitin (chain C) and Lys523 Nz of FANCI (chain A); isopeptide bond between C-terminus of ubiquitin (chain D) and Lys561 Nz of FANCD2 (chain B) Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.576831 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQIFVKTLTG KTITLEVEPS DTIENVKAKI QDKEGIPPDQ QRLIFAGKQL EDGRTLSDYN IQKESTLHLV LRLRGG |
-Macromolecule #4: DNA (29-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (29-MER) / type: dna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.951746 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC) |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (29-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (29-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.880711 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 51.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Software - Name: CTFFIND (ver. 4) |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 301158 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










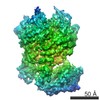





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)