[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-16888: Cryo-EM structure of ADP-bound, filamentous beta-actin harboring ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
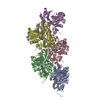
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of ADP-bound, filamentous beta-actin harboring the R183W mutation | ||||||||||||
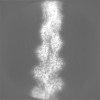
 Map data Map data | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of filamentous beta-actin harboring the R183W mutation. | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Actin filament / cytoskeletal protein / ATPase / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / cellular response to cytochalasin B / bBAF complex / npBAF complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / nBAF complex / brahma complex / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / protein localization to adherens junction / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton ...positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / cellular response to cytochalasin B / bBAF complex / npBAF complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / nBAF complex / brahma complex / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / protein localization to adherens junction / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Formation of annular gap junctions / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Tat protein binding / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / dense body / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / regulation of double-strand break repair / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / apical junction complex / nitric-oxide synthase binding / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / brush border / kinesin binding / negative regulation of cell differentiation / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / substantia nigra development / calyx of Held / axonogenesis / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / adherens junction / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / actin filament / positive regulation of cell differentiation / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / cell motility / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / tau protein binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / kinetochore / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / platelet aggregation / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / nuclear matrix / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / UCH proteinases / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / nucleosome / cell-cell junction / lamellipodium / actin cytoskeleton / presynapse / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / HATs acetylate histones / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / regulation of apoptotic process / blood microparticle Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
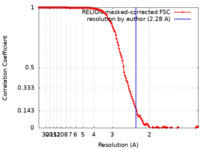
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.28 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert W / Blanc FEC / Roy A / Belyy A / Hofnagel O / Hummer G / Bieling P / Raunser S | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3 items Germany, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Molecular mechanisms of inorganic-phosphate release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Florian E C Blanc / Ankit Roy / Alexander Belyy / Micaela Boiero Sanders / Oliver Hofnagel / Gerhard Hummer / Peter Bieling / Stefan Raunser /  Abstract: The release of inorganic phosphate (P) from actin filaments constitutes a key step in their regulated turnover, which is fundamental to many cellular functions. The mechanisms underlying P release ...The release of inorganic phosphate (P) from actin filaments constitutes a key step in their regulated turnover, which is fundamental to many cellular functions. The mechanisms underlying P release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments remain unclear. Here, using human and bovine actin isoforms, we combine cryo-EM with molecular-dynamics simulations and in vitro reconstitution to demonstrate how actin releases P through a 'molecular backdoor'. While constantly open at the barbed end, the backdoor is predominantly closed in filament-core subunits and opens only transiently through concerted amino acid rearrangements. This explains why P escapes rapidly from the filament end but slowly from internal subunits. In a nemaline-myopathy-associated actin variant, the backdoor is predominantly open in filament-core subunits, resulting in accelerated P release and filaments with drastically shortened ADP-P caps. Our results provide the molecular basis for P release from actin and exemplify how a disease-linked mutation distorts the nucleotide-state distribution and atomic structure of the filament. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16888.map.gz emd_16888.map.gz | 129.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16888-v30.xml emd-16888-v30.xml emd-16888.xml emd-16888.xml | 24.2 KB 24.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16888_fsc.xml emd_16888_fsc.xml | 13.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16888.png emd_16888.png | 89.9 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_16888_msk_1.map emd_16888_msk_1.map | 216 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16888.cif.gz emd-16888.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16888_additional_1.map.gz emd_16888_additional_1.map.gz emd_16888_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16888_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16888_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16888_half_map_2.map.gz | 169.1 MB 170.8 MB 170.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16888 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16888 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16888 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16888 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_16888_validation.pdf.gz emd_16888_validation.pdf.gz | 810.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_16888_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_16888_full_validation.pdf.gz | 809.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_16888_validation.xml.gz emd_16888_validation.xml.gz | 20.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_16888_validation.cif.gz emd_16888_validation.cif.gz | 26.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16888 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16888 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16888 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16888 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 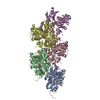 8oi8MC  8oi6C  8oidC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
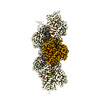
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16888.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16888.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
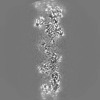
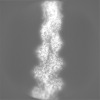
| Annotation | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of filamentous beta-actin harboring the R183W mutation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.695 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
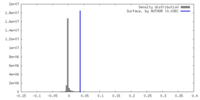
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_16888_msk_1.map emd_16888_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
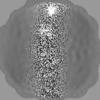
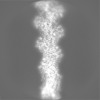
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
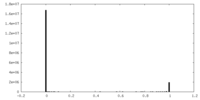
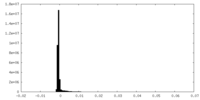
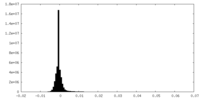
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: 3D refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of filamentous...
| File | emd_16888_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of filamentous beta-actin harboring the R183W mutation. | ||||||||||||
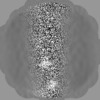
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
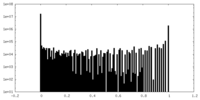
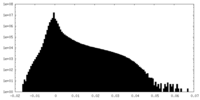
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 1 of the refinement of filamentous...
| File | emd_16888_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1 of the refinement of filamentous beta-actin harboring the R183W mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2 of the refinement of filamentous...
| File | emd_16888_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2 of the refinement of filamentous beta-actin harboring the R183W mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Actin filament harboring the R183W mutation.
| Entire | Name: Actin filament harboring the R183W mutation. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Actin filament harboring the R183W mutation.
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament harboring the R183W mutation. / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: Actin was purified as monomer from insect cells. It was then polymerized into a filament in vitro. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, cytoplasmic 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.792633 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GIV TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSG DG VTHTVPIYEG ...String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GIV TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSG DG VTHTVPIYEG YALPHAILRL DLAGWDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFTTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFEQEMA TAASSSSL E KSYELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PEALFQPSFL GMESAGIHET TFNSIMKCDV DIRKDLYANT VLSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKE ITALAPSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ISKQEYDESG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 585 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.3 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.1 Component:
Details: 1x KMEH (10 mM HEPES pH 7.1, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA) supplemented with 0.02% Tween20 (v/v) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 90 sec. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | Actin filaments were reconstituted by adding salt to monomeric actin. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 15 eV |
| Details | Titan Krios G3 microscope was aligned using Sherpa (FEI). Data collected in superresolution mode. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 7916 / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model |
|---|---|
| Details | The structure was refined using phenix-real-space refine. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-8oi8: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)