[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6s0z: Erythromycin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus 50S ribosome (delta ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6s0z | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Erythromycin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus 50S ribosome (delta R88 A89 uL22) in complex with erythromycin. | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  RIBOSOME / RIBOSOME /  antibiotics / resistance / antibiotics / resistance /  Staphylococcus aureus / exit tunnel / Staphylococcus aureus / exit tunnel /  RNA / rProteins / RNA / rProteins /  erythromycin erythromycin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlarge ribosomal subunit /  5S rRNA binding / 5S rRNA binding /  transferase activity / transferase activity /  tRNA binding / tRNA binding /  rRNA binding / rRNA binding /  ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome /  ribonucleoprotein complex / ribonucleoprotein complex /  translation / translation /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Halfon, Y. / Matozv, D. / Eyal, Z. / Bashan, A. / Zimmerman, E. / Kjeldgaard, J. / Ingmer, H. / Yonath, A. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Denmark, 2items Denmark, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019Title: Exit tunnel modulation as resistance mechanism of S. aureus erythromycin resistant mutant. Authors: Yehuda Halfon / Donna Matzov / Zohar Eyal / Anat Bashan / Ella Zimmerman / Jette Kjeldgaard / Hanne Ingmer / Ada Yonath /   Abstract: The clinical use of the antibiotic erythromycin (ery) is hampered owing to the spread of resistance genes that are mostly mutating rRNA around the ery binding site at the entrance to the protein exit ...The clinical use of the antibiotic erythromycin (ery) is hampered owing to the spread of resistance genes that are mostly mutating rRNA around the ery binding site at the entrance to the protein exit tunnel. Additional effective resistance mechanisms include deletion or insertion mutations in ribosomal protein uL22, which lead to alterations of the exit tunnel shape, located 16 Å away from the drug's binding site. We determined the cryo-EM structures of the Staphylococcus aureus 70S ribosome, and its ery bound complex with a two amino acid deletion mutation in its ß hairpin loop, which grants the bacteria resistance to ery. The structures reveal that, although the binding of ery is stable, the movement of the flexible shorter uL22 loop towards the tunnel wall creates a wider path for nascent proteins, thus enabling bypass of the barrier formed by the drug. Moreover, upon drug binding, the tunnel widens further. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6s0z.cif.gz 6s0z.cif.gz | 3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6s0z.ent.gz pdb6s0z.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6s0z.json.gz 6s0z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/6s0z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/6s0z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/6s0z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s0/6s0z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 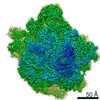 10077MC  6s0xC  6s12C  6s13C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: RNA chain |  Mass: 940976.000 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain |  Mass: 36669.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 28 types, 28 molecules CDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 1 molecules 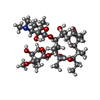
| #31: Chemical | ChemComp-ERY /  Erythromycin Erythromycin |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Erythromycin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus 70S ribosome (delta R88 A89 uL22) in complex with erythromycin. Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#30 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.076 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: RELION / Version: 3 / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) |
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 378309 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj































