[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDEN6: Glucosamine kinase from Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis in presenc... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDEN6 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | Glucosamine kinase from Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis in presence of 1 mM ATP
|
| Function / homology | glucosamine kinase / Glucosamine kinase / glucosamine kinase activity / carbohydrate metabolic process / Protein kinase-like domain superfamily / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / Glucosamine kinase Function and homology information Function and homology information |
| Biological species |  Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis (bacteria) Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis (bacteria) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2019 Journal: mBio / Year: 2019Title: Molecular Fingerprints for a Novel Enzyme Family in with Glucosamine Kinase Activity. Authors: José A Manso / Daniela Nunes-Costa / Sandra Macedo-Ribeiro / Nuno Empadinhas / Pedro José Barbosa Pereira /  Abstract: have long been the main source of antibiotics, secondary metabolites with tightly controlled biosynthesis by environmental and physiological factors. Phosphorylation of exogenous glucosamine has ... have long been the main source of antibiotics, secondary metabolites with tightly controlled biosynthesis by environmental and physiological factors. Phosphorylation of exogenous glucosamine has been suggested as a mechanism for incorporation of this extracellular material into secondary metabolite biosynthesis, but experimental evidence of specific glucosamine kinases in is lacking. Here, we present the molecular fingerprints for the identification of a unique family of actinobacterial glucosamine kinases. Structural and biochemical studies on a distinctive kinase from the soil bacterium unveiled its preference for glucosamine and provided structural evidence of a phosphoryl transfer to this substrate. Conservation of glucosamine-contacting residues across a large number of uncharacterized actinobacterial proteins unveiled a specific glucosamine binding sequence motif. This family of kinases and their genetic context may represent the missing link for the incorporation of environmental glucosamine into the antibiotic biosynthesis pathways in and can be explored to enhance antibiotic production. The discovery of novel enzymes involved in antibiotic biosynthesis pathways is currently a topic of utmost importance. The high levels of antibiotic resistance detected worldwide threaten our ability to combat infections and other 20th-century medical achievements, namely, organ transplantation or cancer chemotherapy. We have identified and characterized a unique family of enzymes capable of phosphorylating glucosamine to glucosamine-6-phosphate, a crucial molecule directly involved in the activation of antibiotic production pathways in , nature's main source of antimicrobials. The consensus sequence identified for these glucosamine kinases will help establish a molecular fingerprint to reveal yet-uncharacterized sequences in antibiotic producers, which should have an important impact in biotechnological and biomedical applications, including the enhancement and optimization of antibiotic production. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Models
| Model #2521 | 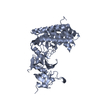 Type: atomic Comment: Volume fraction for this structure was of 0.75 as determined OLIGOMER Chi-square value: 23.31  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #2522 |  Type: atomic Comment: Volume fraction for this structure was of 0.25 as determined OLIGOMER Chi-square value: 23.31  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Glucosamine kinase from Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis in presence of 1 mM ATP Specimen concentration: 1.25-10.00 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM DTT, 1 mM ATP pH: 8 |
| Entity #1337 | Type: protein / Description: Glucosamine kinase / Formula weight: 48.377 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis / References: UniProt: A0A1H7TQR5 Sequence: MTPNWSELVA AADPALVLPS GERRAEVAVP GPLRLDALLD LGEGHAVGVV RSADAARWTV PLVRDGAGGV RRSRPGDGTA EHLVAALARR GATPDAAFVL EAFTGAAPVT GERGIIVDQT NESVIVGECA VVKWAVRLPA EGEPGSPAAQ RIAALARGGF TEMPRPWGLL ...Sequence: MTPNWSELVA AADPALVLPS GERRAEVAVP GPLRLDALLD LGEGHAVGVV RSADAARWTV PLVRDGAGGV RRSRPGDGTA EHLVAALARR GATPDAAFVL EAFTGAAPVT GERGIIVDQT NESVIVGECA VVKWAVRLPA EGEPGSPAAQ RIAALARGGF TEMPRPWGLL TLAEGAQPVL LASVVAYLPG ALDGWDWAVD DVRRLARGEL TMDQALLPAA QLGTLTARMH AALAARGRTP ATAADVAAWG VRMREELDEA VASVPGAEGE RLKAWAPRIA DVYAELDALA GTPLIDVHGD FHVGQILRAD GRYAVVDFDG NPVLPADQRA ARQPAALDVV GMTASLDHVG RVVVFRTPDV DPAPVRAWIA AAQRSFLDAY RTTLARLDAD DLFDDRLLTP LRYAQEVREY LYAVRHLPHW VYVPDLSLTD LLPERLKDKK LAAALEHHHH HH |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: ESRF BM29 / City: Grenoble / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.09919 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.867 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.09919 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.867 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 1M / Type: Dectris / Pixsize x: 172 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan | Measurement date: Nov 24, 2016 / Storage temperature: 10 °C / Cell temperature: 10 °C / Exposure time: 1 sec. / Number of frames: 10 / Unit: 1/nm /
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

 SASDEN6
SASDEN6