+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDC53 |
|---|---|
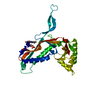
 Sample Sample | Colicin N Translocation domain
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of ion transmembrane transporter activity / pore-forming activity / killing of cells of another organism / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / transmembrane transporter binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biophys J / Year: 2017 Journal: Biophys J / Year: 2017Title: The Two-State Prehensile Tail of the Antibacterial Toxin Colicin N. Authors: Christopher L Johnson / Alexandra S Solovyova / Olli Hecht / Colin Macdonald / Helen Waller / J Günter Grossmann / Geoffrey R Moore / Jeremy H Lakey /  Abstract: Intrinsically disordered regions within proteins are critical elements in many biomolecular interactions and signaling pathways. Antibacterial toxins of the colicin family, which could provide new ...Intrinsically disordered regions within proteins are critical elements in many biomolecular interactions and signaling pathways. Antibacterial toxins of the colicin family, which could provide new antibiotic functions against resistant bacteria, contain disordered N-terminal translocation domains (T-domains) that are essential for receptor binding and the penetration of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Here we investigate the conformational behavior of the T-domain of colicin N (ColN-T) to understand why such domains are widespread in toxins that target Gram-negative bacteria. Like some other intrinsically disordered proteins in the solution state of the protein, ColN-T shows dual recognition, initially interacting with other domains of the same colicin N molecule and later, during cell killing, binding to two different receptors, OmpF and TolA, in the target bacterium. ColN-T is invisible in the high-resolution x-ray model and yet accounts for 90 of the toxin's 387 amino acid residues. To reveal its solution structure that underlies such a dynamic and complex system, we carried out mutagenic, biochemical, hydrodynamic and structural studies using analytical ultracentrifugation, NMR, and small-angle x-ray scattering on full-length ColN and its fragments. The structure was accurately modeled from small-angle x-ray scattering data by treating ColN as a flexible system, namely by the ensemble optimization method, which enables a distribution of conformations to be included in the final model. The results reveal, to our knowledge, for the first time the dynamic structure of a colicin T-domain. ColN-T is in dynamic equilibrium between a compact form, showing specific self-recognition and resistance to proteolysis, and an extended form, which most likely allows for effective receptor binding. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Models
| Model #1211 |  Type: atomic / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Chi-square value: 1.507984 / P-value: 0.000494  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #1212 |  Type: atomic / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Chi-square value: 1.507984 / P-value: 0.000494  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Colicin N Translocation domain / Specimen concentration: 0.40-6.30 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 50 mM Na-Phosphate 300 mM NaCl / pH: 7.6 |
| Entity #627 | Name: ColN-T / Type: protein / Description: Colicin N Translocation domain / Formula weight: 9.965 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Escherichia coli / References: UniProt: P08083 Sequence: MGSNGADNAH NNAFGGGKNP GIGNTSGAGS NGSASSNRGN SNGWSWSNKP HKNDGFHSDG SYHITFHGDN NSKPKPGGNS GNRGNNGDGA SSHHHHHH |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: ESRF BM29 / City: Grenoble / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.15 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.85 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.15 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.85 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 1M / Type: Dectris / Pixsize x: 172 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result | Comments: The results obtained from the bayesapp estimation of distribution functions from small-angle scattering data (http://www.bayesapp.org/) are included in the full entry zip archive.
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 SASDC53
SASDC53