+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9vdm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
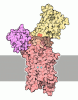
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human ATP9A (AMPPCP) E2P state open form | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase IIA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / P-type ATPase / flippase / human | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of endocytic recycling / negative regulation of exosomal secretion / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / regulation of retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / neuron projection morphogenesis / trans-Golgi network membrane ...regulation of endocytic recycling / negative regulation of exosomal secretion / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / regulation of retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / neuron projection morphogenesis / trans-Golgi network membrane / trans-Golgi network / recycling endosome / recycling endosome membrane / endocytosis / late endosome / late endosome membrane / protease binding / early endosome membrane / early endosome / endosome / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.01 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Abe, K. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 1items Japan, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025Title: A unique gating mechanism revealed by the cryo-EM structure of monomeric ATP9A flippase. Authors: Kazuhiro Abe / Parthiban Marimuthu / Yuheng Qian / Chai C Gopalasingam / Christoph Gerle / Hideki Shigematsu / Kotaro Tanaka / Himanshu Khandelia /    Abstract: Among mammalian P4-ATPase flippases, only ATP9A and ATP9B do not require the auxiliary subunit CDC50 protein. Whilst its yeast homolog, Neo1, is essential for cell survival, little is known about ...Among mammalian P4-ATPase flippases, only ATP9A and ATP9B do not require the auxiliary subunit CDC50 protein. Whilst its yeast homolog, Neo1, is essential for cell survival, little is known about mammalian ATP9A. We present cryo-EM structures of human monomeric ATP9A at a resolution reaching 2.2 Å, in the outward-facing E2P state. Two distinguishable conformations were obtained from a single sample, one with its outward gate open and the other in its closed form. Unlike canonical gating observed for most P-type ATPases, which is driven by the movement of transmembrane (TM) helices 1 and 2 linked to the A domain, outward gating in ATP9A is achieved by the movement of TM6-10 helices, likely initiated by the unwinding of TM6. As a result, the volume of the phospholipid binding cavity in the open state surpasses that of other flippases, which could allow binding of phospholipids with larger hydrophilic headgroups than that of phosphatidylserine. ATP9A shows an ATPase activity that is significantly increased by the addition of phospholipids that retain the overall negative charge, including phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylinositol, and its phosphorylated species, compared with other electroneutral phospholipids. The observation of spontaneous binding of phosphorylated species of phosphatidylinositol in molecular simulation reinforces this fact. Our data provide mechanistic rationales for ATP9A gating, achieved by the rearrangement of the second half of the TM helices. Since TM4-TM10 is anchored by the CDC50 protein subunit in other flippases, the here-observed outward gating mechanism is unique to P4B-type flippases, which function as a monomer. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9vdm.cif.gz 9vdm.cif.gz | 261.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9vdm.ent.gz pdb9vdm.ent.gz | 163.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9vdm.json.gz 9vdm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vd/9vdm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vd/9vdm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vd/9vdm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vd/9vdm | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  64988MC  9vdkC  9vdlC  9vdnC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 114971.773 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATP9A, ATPIIA, KIAA0611 / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATP9A, ATPIIA, KIAA0611 / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: O75110, P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-P5S / |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-CLR / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: human ATP9A / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.1 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL CRYO ARM 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 10000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.01 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 59377 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 87.99 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj