[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9pc6: Antibody (1B2) Bound Crosslinked Rifamycin Synthetase Module 1 wi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9pc6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
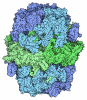
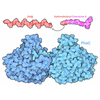
| Title | Antibody (1B2) Bound Crosslinked Rifamycin Synthetase Module 1 with a C-terminal Type II Thioesterase | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Transferase/Immune System / Polyketide Synthase Module / Antibody (Fab) / Transferase-Immune System complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information6-deoxyerythronolide-B synthase / erythronolide synthase activity / fatty acid synthase activity / lipid biosynthetic process / phosphopantetheine binding / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / fatty acid biosynthetic process / hydrolase activity Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Amycolatopsis mediterranei (bacteria) Amycolatopsis mediterranei (bacteria) Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.96 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Cogan, D.P. / Liu, C. / West, R.C. / Chen, M. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: Molecular Basis for Asynchronous Chain Elongation During Rifamycin Antibiotic Biosynthesis. Authors: Chengli Liu / Ryan C West / Muyuan Chen / Whitaker Cohn / George Wang / Aryan M Mandot / Selena Kim / Dillon P Cogan /  Abstract: The rifamycin synthetase (RIFS) from the bacterium is a large (3.5 MDa) multienzyme system that catalyzes over 40 chemical reactions to generate a complex precursor to the antibiotic rifamycin B. It ...The rifamycin synthetase (RIFS) from the bacterium is a large (3.5 MDa) multienzyme system that catalyzes over 40 chemical reactions to generate a complex precursor to the antibiotic rifamycin B. It is considered a hybrid enzymatic assembly line and consists of an N-terminal nonribosomal peptide synthetase loading module followed by a decamodular polyketide synthase (PKS). While the biosynthetic functions are known for each enzymatic domain of RIFS, structural and biochemical analyses of this system from purified components are relatively scarce. Here, we examine the biosynthetic mechanism of RIFS through complementary crosslinking, kinetic, and structural analyses of its first PKS module (M1). Thiol-selective crosslinking of M1 provided a plausible molecular basis for previously observed conformational asymmetry with respect to ketosynthase (KS)-substrate carrier protein (CP) interactions during polyketide chain elongation. Our data suggest that C-terminal dimeric interfaces-which are ubiquitous in bacterial PKSs-force their adjacent CP domains to co-migrate between two equivalent KS active site chambers. Cryogenic electron microscopy analysis of M1 further supported this observation while uncovering its unique architecture. Single-turnover kinetic analysis of M1 indicated that although removal of C-terminal dimeric interfaces supported 2-fold greater KS-CP interactions, it did not increase the partial product occupancy of the homodimeric protein. Our findings cast light on molecular details of natural antibiotic biosynthesis that will aid in the design of artificial megasynth(et)ases with untold product structures and bioactivities. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9pc6.cif.gz 9pc6.cif.gz | 659.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9pc6.ent.gz pdb9pc6.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9pc6.json.gz 9pc6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pc/9pc6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pc/9pc6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pc/9pc6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pc/9pc6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  71497MC  9patC  9pavC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 196008.141 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Amycolatopsis mediterranei (bacteria) / Strain: NRRL B-3240 / Gene: rifA, rifR / Plasmid: pDC85 / Production host: Amycolatopsis mediterranei (bacteria) / Strain: NRRL B-3240 / Gene: rifA, rifR / Plasmid: pDC85 / Production host:  References: UniProt: O54666, UniProt: Q7BUF9, 6-deoxyerythronolide-B synthase #2: Antibody | Mass: 26447.611 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  #3: Antibody | Mass: 25715.832 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Two antibody fragments (Fabs) in complex with homodimeric, crosslinked polyketide synthase module 1 of the rifamycin synthetase fused with a C-terminal type II thioesterase Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.49504131 MDa / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Amycolatopsis mediterranei (bacteria) / Strain: NRRL B-3240 Amycolatopsis mediterranei (bacteria) / Strain: NRRL B-3240 | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.2 / Details: 100 mM citric acid, 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.2 (NaOH) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3677 nm / Nominal defocus min: 100 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 7631 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1229709 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.96 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 91575 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.96 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj