[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9iv2: Identification, structure and agonist design of an androgen membr... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9iv2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Identification, structure and agonist design of an androgen membrane receptor. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Complex / agonist / GPCR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of skeletal muscle contraction / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels ...regulation of skeletal muscle contraction / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / GPER1 signaling / G-protein beta-subunit binding / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / extracellular vesicle / sensory perception of taste / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / retina development in camera-type eye / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / Ras protein signal transduction / cell surface receptor signaling pathway / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / nuclear speck / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / lysosomal membrane / GTPase activity / synapse / protein-containing complex binding / signal transduction / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.53 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ping, Y.Q. / Yang, Z. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell / Year: 2025Title: Identification, structure, and agonist design of an androgen membrane receptor. Authors: Zhao Yang / Yu-Qi Ping / Ming-Wei Wang / Chao Zhang / Shu-Hua Zhou / Yue-Tong Xi / Kong-Kai Zhu / Wei Ding / Qi-Yue Zhang / Zhi-Chen Song / Ru-Jia Zhao / Zi-Lu He / Meng-Xin Wang / Lei Qi / ...Authors: Zhao Yang / Yu-Qi Ping / Ming-Wei Wang / Chao Zhang / Shu-Hua Zhou / Yue-Tong Xi / Kong-Kai Zhu / Wei Ding / Qi-Yue Zhang / Zhi-Chen Song / Ru-Jia Zhao / Zi-Lu He / Meng-Xin Wang / Lei Qi / Christian Ullmann / Albert Ricken / Torsten Schöneberg / Zhen-Ji Gan / Xiao Yu / Peng Xiao / Fan Yi / Ines Liebscher / Jin-Peng Sun /   Abstract: Androgens, such as 5α-dihydrotestosterone (5α-DHT), regulate numerous functions by binding to nuclear androgen receptors (ARs) and potential unknown membrane receptors. Here, we report that the ...Androgens, such as 5α-dihydrotestosterone (5α-DHT), regulate numerous functions by binding to nuclear androgen receptors (ARs) and potential unknown membrane receptors. Here, we report that the androgen 5α-DHT activates membrane receptor GPR133 in muscle cells, thereby increasing intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels and enhancing muscle strength. Further cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structural analysis of GPR133-Gs in complex with 5α-DHT or its derivative methenolone (MET) reveals the structural basis for androgen recognition. Notably, the presence of the "Φ(F/L)-F-W" and the "F××N/D" motifs, which recognize the hydrophobic steroid core and polar groups, respectively, are common in adhesion GPCRs (aGPCRs), suggesting that many aGPCRs may recognize different steroid hormones. Finally, we exploited in silico screening methods to identify a small molecule, AP503, which activates GPR133 and separates the beneficial muscle-strengthening effects from side effects mediated by AR. Thus, GPR133 represents an androgen membrane receptor that contributes to normal androgen physiology and has important therapeutic potentials. #1:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for the tethered peptide activation of adhesion GPCRs. Authors: Yu-Qi Ping / Peng Xiao / Fan Yang / Ru-Jia Zhao / Sheng-Chao Guo / Xu Yan / Xiang Wu / Chao Zhang / Yan Lu / Fenghui Zhao / Fulai Zhou / Yue-Tong Xi / Wanchao Yin / Feng-Zhen Liu / Dong-Fang ...Authors: Yu-Qi Ping / Peng Xiao / Fan Yang / Ru-Jia Zhao / Sheng-Chao Guo / Xu Yan / Xiang Wu / Chao Zhang / Yan Lu / Fenghui Zhao / Fulai Zhou / Yue-Tong Xi / Wanchao Yin / Feng-Zhen Liu / Dong-Fang He / Dao-Lai Zhang / Zhong-Liang Zhu / Yi Jiang / Lutao Du / Shi-Qing Feng / Torsten Schöneberg / Ines Liebscher / H Eric Xu / Jin-Peng Sun /   Abstract: Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptors (aGPCRs) are important for organogenesis, neurodevelopment, reproduction and other processes. Many aGPCRs are activated by a conserved internal (tethered) agonist ...Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptors (aGPCRs) are important for organogenesis, neurodevelopment, reproduction and other processes. Many aGPCRs are activated by a conserved internal (tethered) agonist sequence known as the Stachel sequence. Here, we report the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of two aGPCRs in complex with G: GPR133 and GPR114. The structures indicate that the Stachel sequences of both receptors assume an α-helical-bulge-β-sheet structure and insert into a binding site formed by the transmembrane domain (TMD). A hydrophobic interaction motif (HIM) within the Stachel sequence mediates most of the intramolecular interactions with the TMD. Combined with the cryo-EM structures, biochemical characterization of the HIM motif provides insight into the cross-reactivity and selectivity of the Stachel sequences. Two interconnected mechanisms, the sensing of Stachel sequences by the conserved 'toggle switch' W and the constitution of a hydrogen-bond network formed by Q/Y and the P/VφφG motif (φ indicates a hydrophobic residue), are important in Stachel sequence-mediated receptor activation and G coupling. Notably, this network stabilizes kink formation in TM helices 6 and 7 (TM6 and TM7, respectively). A common G-binding interface is observed between the two aGPCRs, and GPR114 has an extended TM7 that forms unique interactions with G. Our structures reveal the detailed mechanisms of aGPCR activation by Stachel sequences and their G coupling. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9iv2.cif.gz 9iv2.cif.gz | 177.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9iv2.ent.gz pdb9iv2.ent.gz | 128.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9iv2.json.gz 9iv2.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/9iv2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/9iv2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/9iv2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/9iv2 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  60918MC  8x9sC  8x9tC  8x9uC  9iv1C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 37784.301 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 7861.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 41879.465 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 65688.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ADGRD1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ADGRD1 / Production host:  |
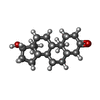
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-DHT / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of GPR133 with agonist and G protein trime / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.53 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 267022 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj