[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9h9e: Cryo-EM structure of the human GABAA receptor alpha1 subunit in c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9h9e | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
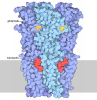
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human GABAA receptor alpha1 subunit in complex with the assembly factor NACHO/TMEM35A | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Assembly intermediate / ion channel / chaperone / Neurotransmitter receptor / Membrane protein biogenesis | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationacetylcholine receptor regulator activity / GABA receptor complex / positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface / GABA receptor activation / inhibitory synapse assembly / GABA-gated chloride ion channel activity / GABA-A receptor complex / GABA-A receptor activity / peroxisomal membrane / postsynaptic specialization membrane ...acetylcholine receptor regulator activity / GABA receptor complex / positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface / GABA receptor activation / inhibitory synapse assembly / GABA-gated chloride ion channel activity / GABA-A receptor complex / GABA-A receptor activity / peroxisomal membrane / postsynaptic specialization membrane / gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway / synaptic transmission, GABAergic / Signaling by ERBB4 / chloride channel complex / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / dendrite membrane / chloride transmembrane transport / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / GABA-ergic synapse / cytoplasmic vesicle / dendritic spine / postsynapse / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / endoplasmic reticulum / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hooda, Y. / Sente, A. / Judy, R.M. / Smalinskaite, L. / Peak-Chew, S. / Naydenova, K. / Malinauskas, T. / Hardwick, S.W. / Chirgadze, D.Y. / Aricescu, A.R. / Hegde, R.S. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024Title: Mechanism of NACHO-mediated assembly of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels. Authors: Yogesh Hooda / Andrija Sente / Ryan M Judy / Luka Smalinskaitė / Sew-Yeu Peak-Chew / Katerina Naydenova / Tomas Malinauskas / Steven W Hardwick / Dimitri Y Chirgadze / A Radu Aricescu / Ramanujan S Hegde /  Abstract: Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs) are cell surface receptors of crucial importance for animal physiology. This diverse protein family mediates the ionotropic signals triggered by major ...Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs) are cell surface receptors of crucial importance for animal physiology. This diverse protein family mediates the ionotropic signals triggered by major neurotransmitters and includes γ-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABARs) and acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). Receptor function is fine-tuned by a myriad of endogenous and pharmacological modulators. A functional pLGIC is built from five homologous, sometimes identical, subunits, each containing a β-scaffold extracellular domain (ECD), a four-helix transmembrane domain (TMD) and intracellular loops of variable length. Although considerable progress has been made in understanding pLGICs in structural and functional terms, the molecular mechanisms that enable their assembly at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in a vast range of potential subunit configurations remain unknown. Here, we identified candidate pLGICs assembly factors selectively associated with an unassembled GABAR subunit. Focusing on one of the candidates, we determined the cryo-EM structure of an assembly intermediate containing two α1 subunits of GABAR each bound to an ER-resident membrane protein NACHO. The structure showed how NACHO shields the principal (+) transmembrane interface of α1 subunits containing an immature extracellular conformation. Crosslinking and structure-prediction revealed an adjacent surface on NACHO for β2 subunit interactions to guide stepwise oligimerisation. Mutations of either subunit-interacting surface on NACHO also impaired the formation of homopentameric α7 nAChRs, pointing to a generic framework for pLGIC assembly. Our work provides the foundation for understanding the regulatory principles underlying pLGIC structural diversity. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9h9e.cif.gz 9h9e.cif.gz | 496.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9h9e.ent.gz pdb9h9e.ent.gz | 331.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9h9e.json.gz 9h9e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h9/9h9e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h9/9h9e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h9/9h9e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h9/9h9e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  51963MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj